-
Recursion
layer by layer
private xxxx recursion(level, param1, param2, ...) { // recursion terminator if (level > MAX_LEVEL) { process_result; return xxx; } // process logic in current level process(level, data...); // drill down recursion(level + 1, p1, p2, ...); // reverse the current level status if needed } -
70. Climbing Stairs
You are climbing a staircase. It takes
nsteps to reach the top.Each time you can either climb
1or2steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?Example 1:
Input: n = 2 Output: 2 Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top. 1. 1 step + 1 step 2. 2 stepsExample 2:
Input: n = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top. 1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step 2. 1 step + 2 steps 3. 2 steps + 1 stepConstraints:
1 <= n <= 45
class Solution { public int climbStairs(int n) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(1, 1); map.put(2, 2); return helper(map, n); } private int helper(Map<Integer, Integer> map, int n) { if (map.containsKey(n)) { return map.get(n); } int nStair = helper(map, n-2) + helper(map, n-1); map.put(n, nStair); return nStair; } } -
22. Generate Parentheses
Given
npairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.Example 1:
Input: n = 3 Output: ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: ["()"]Constraints:
1 <= n <= 8
class Solution { public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) { List<String> res = new ArrayList<>(); helper(res, 0, 0, n*2, ""); return res; } private void helper(List<String> list, int l, int r, int max, String s) { if (l + r == max) { list.add(s); return ; } if (l < max / 2) helper(list, l + 1, r, max, s + "("); if (l > r) helper(list, l, r + 1, max, s + ")"); } } -
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
Given the
rootof a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).A valid BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:

Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: trueExample 2:

Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] Output: false Explanation: The root node's value is 5 but its right child's value is 4.Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
// inorder class Solution { private long cur = Long.MIN_VALUE; boolean flag = true; public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return true; if (flag && root.left != null) isValidBST(root.left); if (root.val <= cur) flag = false; cur = root.val; if (flag && root.right != null) isValidBST(root.right); return flag; } }// min bound max bound class Solution { public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return true; return recur(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE); } private boolean recur(TreeNode root, long min, long max) { if (root.val <= min || root.val >= max) { return false; } boolean left = true, right = true; if (root.left != null) left = recur(root.left, min, root.val); if (root.right != null) right = recur(root.right, root.val, max); return left && right; } } -
226. Invert Binary Tree
Given the
rootof a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.Example 1:

Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]Example 2:
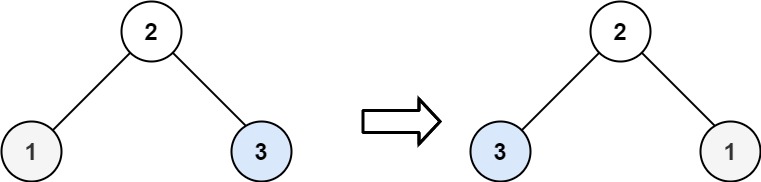
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: [2,3,1]Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: []Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return null; TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left); TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right); root.left = right; root.right = left; return root; } } - The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Given the
rootof a binary tree, return its maximum depth.A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: 2Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: 0Example 4:
Input: root = [0] Output: 1Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; return 1 + Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)); } } - The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 2Example 2:
Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] Output: 5Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 105]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { return 1; } int left = root.left == null ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : minDepth(root.left); int right = root.right == null ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : minDepth(root.right); return 1 + Math.min(left, right); } } - The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes
pandqas the lowest node inTthat has bothpandqas descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”Example 1:

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.Example 2:

Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2 Output: 1Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 105]. -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.valare unique. p != qpandqwill exist in the tree.
class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root; TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); if(left == null) return right; if(right == null) return left; return root; } } - The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
-
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
Given two integer arrays
preorderandinorderwherepreorderis the preorder traversal of a binary tree andinorderis the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.Example 1:

Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]Example 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] Output: [-1]Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorderandinorderconsist of unique values.- Each value of
inorderalso appears inpreorder. preorderis guaranteed to be the preorder traversal of the tree.inorderis guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.
class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { int len = preorder.length; if (len == 0) return null; return recur(preorder, 0, len - 1, inorder, 0, len - 1); } private TreeNode recur(int[] preorder, int pl, int pr, int[] inorder, int il, int ir) { if (pl > pr) return null; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pl]); int i = il; for ( ; i <= ir; i++) { if (preorder[pl] == inorder[i]) { break; } } int leftNums = i - il; TreeNode left = recur(preorder, pl + 1, pl + 1 + leftNums - 1, inorder, il, i - 1); TreeNode right = recur(preorder, pl + 1 + leftNums, pr, inorder, i + 1, ir); root.left = left; root.right = right; return root; } } -
77. Combinations
Given two integers n and k, return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 ... n.
You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, k = 2 Output: [ [2,4], [3,4], [2,3], [1,2], [1,3], [1,4], ]Example 2:
Input: n = 1, k = 1 Output: [[1]]Constraints:
1 <= n <= 201 <= k <= n
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); recur(res, n, k, list, 1); return res; } private void recur(List<List<Integer>> lists, int n, int k, List<Integer> list, int num) { if (list.size() == k) { lists.add(new ArrayList(list)); return ; } for (int i = num; i <= n; i++) { list.add(i); recur(lists, n, k, list, i + 1); list.remove(list.size() - 1); } } }