原文链接:http://www.one2know.cn/nlp3/
- 分词
from nltk.tokenize import LineTokenizer,SpaceTokenizer,TweetTokenizer
from nltk import word_tokenize
# 根据行分词,将每行作为一个元素放到list中
lTokenizer = LineTokenizer()
print('Line tokenizer output :',lTokenizer.tokenize('hello hello
python
world'))
# 根据空格分词
rawText = 'hello python,world'
sTokenizer = SpaceTokenizer()
print('Space tokenizer output :',sTokenizer.tokenize(rawText))
# word_tokenize分词
print('Word tokenizer output :',word_tokenize(rawText))
# 能使特殊符号不被分开
tTokenizer = TweetTokenizer()
print('Tweet tokenizer output :',tTokenizer.tokenize('This is a cooool #dummysmiley: :-) :-p <3'))
输出:
Line tokenizer output : ['hello hello', 'python', 'world']
Space tokenizer output : ['hello', 'python,world']
Word tokenizer output : ['hello', 'python', ',', 'world']
Tweet tokenizer output : ['This', 'is', 'a', 'cooool', '#dummysmiley', ':', ':-)', ':-p', '<3']
- 词干提取
去除词的后缀,输出词干,如wanted=>want
from nltk import PorterStemmer,LancasterStemmer,word_tokenize
# 创建raw并将raw分词
raw = 'he wants to be loved by others'
tokens = word_tokenize(raw)
print(tokens)
# 输出词干
porter = PorterStemmer()
pStems = [porter.stem(t) for t in tokens]
print(pStems)
# 这种方法去除的多,易出错
lancaster = LancasterStemmer()
lTems = [lancaster.stem(t) for t in tokens]
print(lTems)
输出:
['he', 'wants', 'to', 'be', 'loved', 'by', 'others']
['he', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'love', 'by', 'other']
['he', 'want', 'to', 'be', 'lov', 'by', 'oth']
- 词形还原
词干提取只是去除后缀,词形还原是对应字典匹配还原
from nltk import word_tokenize,PorterStemmer,WordNetLemmatizer
raw = 'Tom flied kites last week in Beijing'
tokens = word_tokenize(raw)
# 去除后缀
porter = PorterStemmer()
stems = [porter.stem(t) for t in tokens]
print(stems)
# 还原器:字典找到才还原,特殊大写词不还原
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
lemmas = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(t) for t in tokens]
print(lemmas)
输出:
['tom', 'fli', 'kite', 'last', 'week', 'in', 'beij']
['Tom', 'flied', 'kite', 'last', 'week', 'in', 'Beijing']
- 停用词
古登堡语料库:18个未分类的纯文本
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import gutenberg
# nltk.download('gutenberg')
# nltk.download('stopwords')
print(gutenberg.fileids())
# print(stopwords)
# 获得bible-kjv.txt的所有单词,并过滤掉长度<3的单词
gb_words = gutenberg.words('bible-kjv.txt')
words_filtered = [e for e in gb_words if len(e) >= 3]
# 加载英文的停用词,并用它过滤
stopwords = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english')
words = [w for w in words_filtered if w.lower() not in stopwords]
# 处理的词表和未做处理的词表 词频的比较
fdistPlain = nltk.FreqDist(words)
fdist = nltk.FreqDist(gb_words)
# 观察他们的频率分布特征
print('Following are the most common 10 words in the bag')
print(fdistPlain.most_common(10))
print('Following are the most common 10 words in the bag minus the stopwords')
print(fdist.most_common(10))
输出:
['austen-emma.txt', 'austen-persuasion.txt', 'austen-sense.txt', 'bible-kjv.txt', 'blake-poems.txt', 'bryant-stories.txt', 'burgess-busterbrown.txt', 'carroll-alice.txt', 'chesterton-ball.txt', 'chesterton-brown.txt', 'chesterton-thursday.txt', 'edgeworth-parents.txt', 'melville-moby_dick.txt', 'milton-paradise.txt', 'shakespeare-caesar.txt', 'shakespeare-hamlet.txt', 'shakespeare-macbeth.txt', 'whitman-leaves.txt']
Following are the most common 10 words in the bag
[('shall', 9760), ('unto', 8940), ('LORD', 6651), ('thou', 4890), ('thy', 4450), ('God', 4115), ('said', 3995), ('thee', 3827), ('upon', 2730), ('man', 2721)]
Following are the most common 10 words in the bag minus the stopwords
[(',', 70509), ('the', 62103), (':', 43766), ('and', 38847), ('of', 34480), ('.', 26160), ('to', 13396), ('And', 12846), ('that', 12576), ('in', 12331)]
- 编辑距离 Levenshtein_distance
从一个字符串变到另外一个字符串所需要最小的步骤,衡量两个字符串的相似度
动态规划算法:创建一个二维表,若相等,则=左上;否则=min(左,上,左上)+1
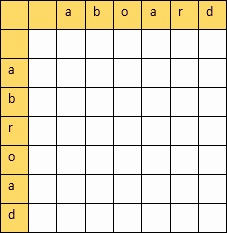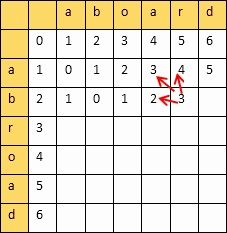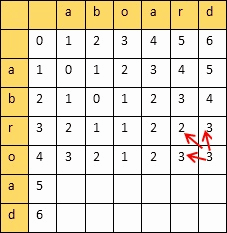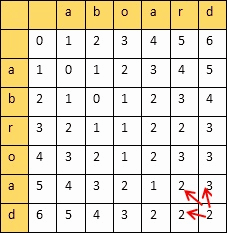
填完表计算编辑距离和相似度:
设两个字符串的长度分别是m,n,填的二维表为A
则
编辑距离 = A[m][n]
相似度 = 1 - 编辑距离/max(m,n)
代码实现:
from nltk.metrics.distance import edit_distance
def my_edit_distance(str1,str2):
m = len(str1) + 1
n = len(str2) + 1
# 创建二维表,初始化第一行和第一列
table = {}
for i in range(m): table[i,0] = i
for j in range(n): table[0,j] = j
# 填表
for i in range(1,m):
for j in range(1,n):
cost = 0 if str1[i-1] == str2[j-1] else 1
table[i,j] = min(table[i,j-1]+1,table[i-1,j]+1,table[i-1,j-1]+cost)
return table[i,j],1-table[i,j]/max(i,j)
print('My Algorithm :',my_edit_distance('aboard','abroad'))
print('NLTK Algorithm :',edit_distance('aboard','abroad'))
输出:
My Algorithm : (2, 0.6666666666666667)
NLTK Algorithm : 2
- 提取两个文本共有词汇
story1 = open('story1.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read()
story2 = open('story2.txt','r',encoding='utf-8').read()
# 删除特殊字符,所有字符串小写
story1 = story1.replace(',',' ').replace('
',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('"',' ')
.replace("'",' ').replace('!',' ').replace('?',' ').casefold()
story2 = story2.replace(',',' ').replace('
',' ').replace('.',' ').replace('"',' ')
.replace("'",' ').replace('!',' ').replace('?',' ').casefold()
# 分词
story1_words = story1.split(' ')
story2_words = story2.split(' ')
# 去掉重复词
story1_vocab = set(story1_words)
story2_vocab = set(story2_words)
# 找共同词
common_vocab = story1_vocab & story2_vocab
print('Common Vocabulary :',common_vocab)
输出:
Common Vocabulary : {'', 'got', 'for', 'but', 'out', 'you', 'caught', 'so', 'very', 'away', 'could', 'to', 'not', 'it', 'a', 'they', 'was', 'of', 'and', 'said', 'ran', 'the', 'saw', 'have'}