参考内核文档: Documentation/printk-formats.txt
在内核中使用dump_stack的时候可以看到如下用法:
static inline void print_ip_sym(unsigned long ip) { printk("[<%px>] %pS ", (void *) ip, (void *) ip); }
然后我们就可以看到类似如下的内核log:
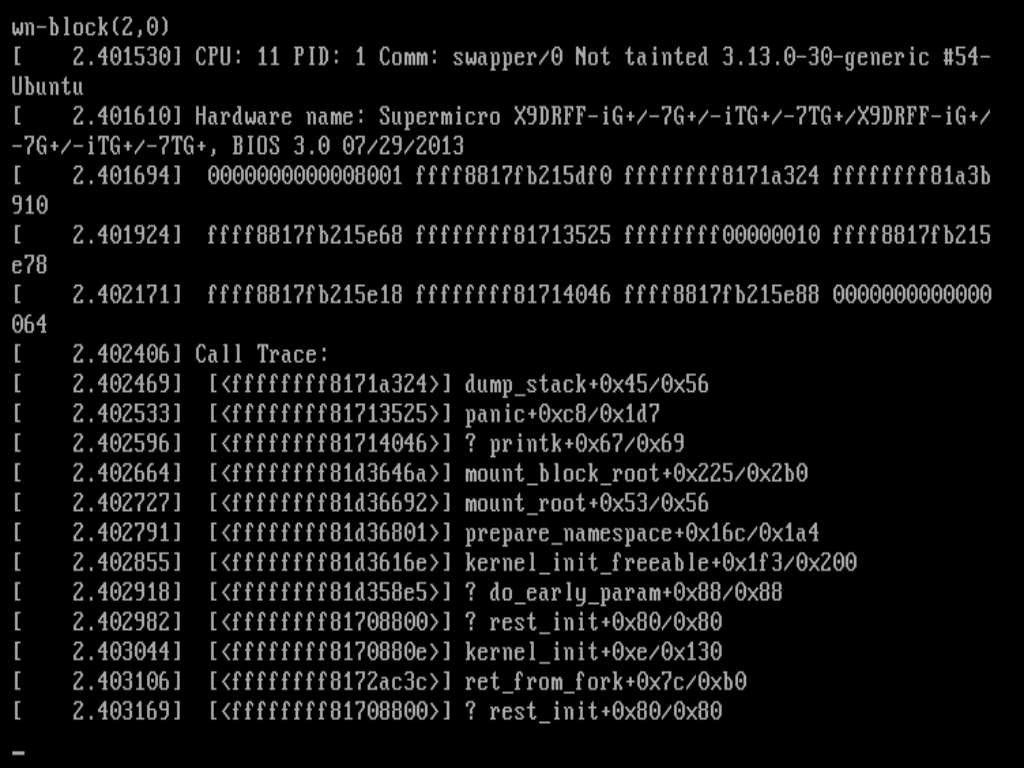
可以看到,上面不光输出了运行地址,还把对应的函数名以及偏移地址都列了出来,内核是如何做到的呢?
在调用printk的时候:
printk --> vprintk_default --> vprintk_emit --> vprintk_store --> vscnprintf --> vsnprintf --> pointer
上面的转换就是在pointer中完成的:
1 /* 2 * Show a '%p' thing. A kernel extension is that the '%p' is followed 3 * by an extra set of alphanumeric characters that are extended format 4 * specifiers. 5 * 6 * Please update scripts/checkpatch.pl when adding/removing conversion 7 * characters. (Search for "check for vsprintf extension"). 8 * 9 * Right now we handle: 10 * 11 * - 'F' For symbolic function descriptor pointers with offset 12 * - 'f' For simple symbolic function names without offset 13 * - 'S' For symbolic direct pointers with offset 14 * - 's' For symbolic direct pointers without offset 15 * - '[FfSs]R' as above with __builtin_extract_return_addr() translation 16 * - 'B' For backtraced symbolic direct pointers with offset 17 * - 'R' For decoded struct resource, e.g., [mem 0x0-0x1f 64bit pref] 18 * - 'r' For raw struct resource, e.g., [mem 0x0-0x1f flags 0x201] 19 * - 'b[l]' For a bitmap, the number of bits is determined by the field 20 * width which must be explicitly specified either as part of the 21 * format string '%32b[l]' or through '%*b[l]', [l] selects 22 * range-list format instead of hex format 23 * - 'M' For a 6-byte MAC address, it prints the address in the 24 * usual colon-separated hex notation 25 * - 'm' For a 6-byte MAC address, it prints the hex address without colons 26 * - 'MF' For a 6-byte MAC FDDI address, it prints the address 27 * with a dash-separated hex notation 28 * - '[mM]R' For a 6-byte MAC address, Reverse order (Bluetooth) 29 * - 'I' [46] for IPv4/IPv6 addresses printed in the usual way 30 * IPv4 uses dot-separated decimal without leading 0's (1.2.3.4) 31 * IPv6 uses colon separated network-order 16 bit hex with leading 0's 32 * [S][pfs] 33 * Generic IPv4/IPv6 address (struct sockaddr *) that falls back to 34 * [4] or [6] and is able to print port [p], flowinfo [f], scope [s] 35 * - 'i' [46] for 'raw' IPv4/IPv6 addresses 36 * IPv6 omits the colons (01020304...0f) 37 * IPv4 uses dot-separated decimal with leading 0's (010.123.045.006) 38 * [S][pfs] 39 * Generic IPv4/IPv6 address (struct sockaddr *) that falls back to 40 * [4] or [6] and is able to print port [p], flowinfo [f], scope [s] 41 * - '[Ii][4S][hnbl]' IPv4 addresses in host, network, big or little endian order 42 * - 'I[6S]c' for IPv6 addresses printed as specified by 43 * http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5952 44 * - 'E[achnops]' For an escaped buffer, where rules are defined by combination 45 * of the following flags (see string_escape_mem() for the 46 * details): 47 * a - ESCAPE_ANY 48 * c - ESCAPE_SPECIAL 49 * h - ESCAPE_HEX 50 * n - ESCAPE_NULL 51 * o - ESCAPE_OCTAL 52 * p - ESCAPE_NP 53 * s - ESCAPE_SPACE 54 * By default ESCAPE_ANY_NP is used. 55 * - 'U' For a 16 byte UUID/GUID, it prints the UUID/GUID in the form 56 * "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" 57 * Options for %pU are: 58 * b big endian lower case hex (default) 59 * B big endian UPPER case hex 60 * l little endian lower case hex 61 * L little endian UPPER case hex 62 * big endian output byte order is: 63 * [0][1][2][3]-[4][5]-[6][7]-[8][9]-[10][11][12][13][14][15] 64 * little endian output byte order is: 65 * [3][2][1][0]-[5][4]-[7][6]-[8][9]-[10][11][12][13][14][15] 66 * - 'V' For a struct va_format which contains a format string * and va_list *, 67 * call vsnprintf(->format, *->va_list). 68 * Implements a "recursive vsnprintf". 69 * Do not use this feature without some mechanism to verify the 70 * correctness of the format string and va_list arguments. 71 * - 'K' For a kernel pointer that should be hidden from unprivileged users 72 * - 'NF' For a netdev_features_t 73 * - 'h[CDN]' For a variable-length buffer, it prints it as a hex string with 74 * a certain separator (' ' by default): 75 * C colon 76 * D dash 77 * N no separator 78 * The maximum supported length is 64 bytes of the input. Consider 79 * to use print_hex_dump() for the larger input. 80 * - 'a[pd]' For address types [p] phys_addr_t, [d] dma_addr_t and derivatives 81 * (default assumed to be phys_addr_t, passed by reference) 82 * - 'd[234]' For a dentry name (optionally 2-4 last components) 83 * - 'D[234]' Same as 'd' but for a struct file 84 * - 'g' For block_device name (gendisk + partition number) 85 * - 'C' For a clock, it prints the name (Common Clock Framework) or address 86 * (legacy clock framework) of the clock 87 * - 'Cn' For a clock, it prints the name (Common Clock Framework) or address 88 * (legacy clock framework) of the clock 89 * - 'Cr' For a clock, it prints the current rate of the clock 90 * - 'G' For flags to be printed as a collection of symbolic strings that would 91 * construct the specific value. Supported flags given by option: 92 * p page flags (see struct page) given as pointer to unsigned long 93 * g gfp flags (GFP_* and __GFP_*) given as pointer to gfp_t 94 * v vma flags (VM_*) given as pointer to unsigned long 95 * - 'O' For a kobject based struct. Must be one of the following: 96 * - 'OF[fnpPcCF]' For a device tree object 97 * Without any optional arguments prints the full_name 98 * f device node full_name 99 * n device node name 100 * p device node phandle 101 * P device node path spec (name + @unit) 102 * F device node flags 103 * c major compatible string 104 * C full compatible string 105 * 106 * ** Please update also Documentation/printk-formats.txt when making changes ** 107 * 108 * Note: The difference between 'S' and 'F' is that on ia64 and ppc64 109 * function pointers are really function descriptors, which contain a 110 * pointer to the real address. 111 */ 112 static noinline_for_stack 113 char *pointer(const char *fmt, char *buf, char *end, void *ptr, 114 struct printf_spec spec) 115 { 116 const int default_width = 2 * sizeof(void *); 117 118 if (!ptr && *fmt != 'K') { 119 /* 120 * Print (null) with the same width as a pointer so it makes 121 * tabular output look nice. 122 */ 123 if (spec.field_width == -1) 124 spec.field_width = default_width; 125 return string(buf, end, "(null)", spec); 126 } 127 128 switch (*fmt) { 129 case 'F': 130 case 'f': 131 ptr = dereference_function_descriptor(ptr); 132 /* Fallthrough */ 133 case 'S': 134 case 's': 135 case 'B': 136 return symbol_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 137 case 'R': 138 case 'r': 139 return resource_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 140 case 'h': 141 return hex_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 142 case 'b': 143 switch (fmt[1]) { 144 case 'l': 145 return bitmap_list_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 146 default: 147 return bitmap_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 148 } 149 case 'M': /* Colon separated: 00:01:02:03:04:05 */ 150 case 'm': /* Contiguous: 000102030405 */ 151 /* [mM]F (FDDI) */ 152 /* [mM]R (Reverse order; Bluetooth) */ 153 return mac_address_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 154 case 'I': /* Formatted IP supported 155 * 4: 1.2.3.4 156 * 6: 0001:0203:...:0708 157 * 6c: 1::708 or 1::1.2.3.4 158 */ 159 case 'i': /* Contiguous: 160 * 4: 001.002.003.004 161 * 6: 000102...0f 162 */ 163 switch (fmt[1]) { 164 case '6': 165 return ip6_addr_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 166 case '4': 167 return ip4_addr_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 168 case 'S': { 169 const union { 170 struct sockaddr raw; 171 struct sockaddr_in v4; 172 struct sockaddr_in6 v6; 173 } *sa = ptr; 174 175 switch (sa->raw.sa_family) { 176 case AF_INET: 177 return ip4_addr_string_sa(buf, end, &sa->v4, spec, fmt); 178 case AF_INET6: 179 return ip6_addr_string_sa(buf, end, &sa->v6, spec, fmt); 180 default: 181 return string(buf, end, "(invalid address)", spec); 182 }} 183 } 184 break; 185 case 'E': 186 return escaped_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 187 case 'U': 188 return uuid_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 189 case 'V': 190 { 191 va_list va; 192 193 va_copy(va, *((struct va_format *)ptr)->va); 194 buf += vsnprintf(buf, end > buf ? end - buf : 0, 195 ((struct va_format *)ptr)->fmt, va); 196 va_end(va); 197 return buf; 198 } 199 case 'K': 200 switch (kptr_restrict) { 201 case 0: 202 /* Always print %pK values */ 203 break; 204 case 1: { 205 const struct cred *cred; 206 207 /* 208 * kptr_restrict==1 cannot be used in IRQ context 209 * because its test for CAP_SYSLOG would be meaningless. 210 */ 211 if (in_irq() || in_serving_softirq() || in_nmi()) { 212 if (spec.field_width == -1) 213 spec.field_width = default_width; 214 return string(buf, end, "pK-error", spec); 215 } 216 217 /* 218 * Only print the real pointer value if the current 219 * process has CAP_SYSLOG and is running with the 220 * same credentials it started with. This is because 221 * access to files is checked at open() time, but %pK 222 * checks permission at read() time. We don't want to 223 * leak pointer values if a binary opens a file using 224 * %pK and then elevates privileges before reading it. 225 */ 226 cred = current_cred(); 227 if (!has_capability_noaudit(current, CAP_SYSLOG) || 228 !uid_eq(cred->euid, cred->uid) || 229 !gid_eq(cred->egid, cred->gid)) 230 ptr = NULL; 231 break; 232 } 233 case 2: 234 default: 235 /* Always print 0's for %pK */ 236 ptr = NULL; 237 break; 238 } 239 break; 240 241 case 'N': 242 return netdev_bits(buf, end, ptr, fmt); 243 case 'a': 244 return address_val(buf, end, ptr, fmt); 245 case 'd': 246 return dentry_name(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 247 case 'C': 248 return clock(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 249 case 'D': 250 return dentry_name(buf, end, 251 ((const struct file *)ptr)->f_path.dentry, 252 spec, fmt); 253 #ifdef CONFIG_BLOCK 254 case 'g': 255 return bdev_name(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt); 256 #endif 257 258 case 'G': 259 return flags_string(buf, end, ptr, fmt); 260 case 'O': 261 switch (fmt[1]) { 262 case 'F': 263 return device_node_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt + 1); 264 } 265 } 266 spec.flags |= SMALL; 267 if (spec.field_width == -1) { 268 spec.field_width = default_width; 269 spec.flags |= ZEROPAD; 270 } 271 spec.base = 16; 272 273 return number(buf, end, (unsigned long) ptr, spec); 274 }
第136行, symbol_string(buf, end, ptr, spec, fmt);
1 static noinline_for_stack 2 char *symbol_string(char *buf, char *end, void *ptr, 3 struct printf_spec spec, const char *fmt) 4 { 5 unsigned long value; 6 #ifdef CONFIG_KALLSYMS 7 char sym[KSYM_SYMBOL_LEN]; 8 #endif 9 10 if (fmt[1] == 'R') 11 ptr = __builtin_extract_return_addr(ptr); 12 value = (unsigned long)ptr; 13 14 #ifdef CONFIG_KALLSYMS 15 if (*fmt == 'B') 16 sprint_backtrace(sym, value); 17 else if (*fmt != 'f' && *fmt != 's') 18 sprint_symbol(sym, value); 19 else 20 sprint_symbol_no_offset(sym, value); 21 22 return string(buf, end, sym, spec); 23 #else 24 return special_hex_number(buf, end, value, sizeof(void *)); 25 #endif 26 }
第20行:sprint_symbol_no_offset
1 /** 2 * sprint_symbol_no_offset - Look up a kernel symbol and return it in a text buffer 3 * @buffer: buffer to be stored 4 * @address: address to lookup 5 * 6 * This function looks up a kernel symbol with @address and stores its name 7 * and module name to @buffer if possible. If no symbol was found, just saves 8 * its @address as is. 9 * 10 * This function returns the number of bytes stored in @buffer. 11 */ 12 int sprint_symbol_no_offset(char *buffer, unsigned long address) 13 { 14 return __sprint_symbol(buffer, address, 0, 0); 15 }
完。