SpringMVC
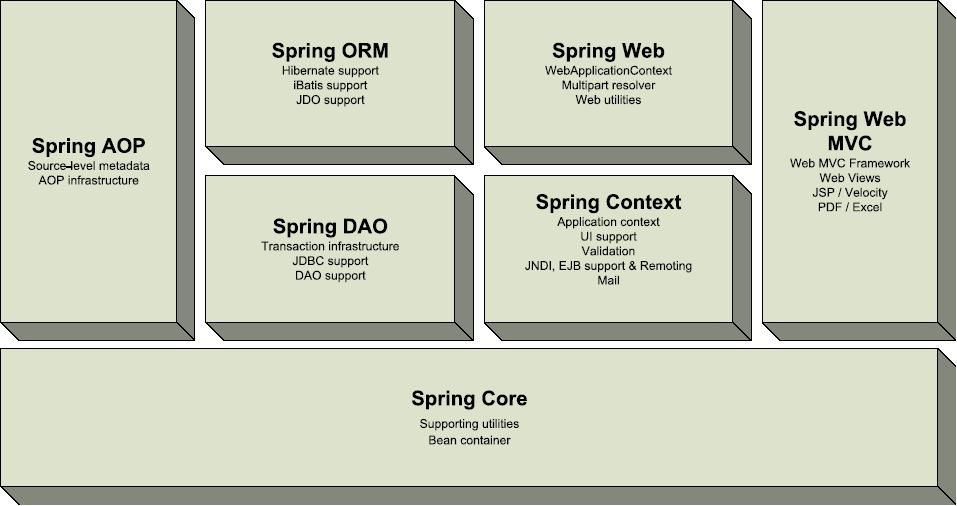
Spring Web MVC 和 Struct2都属于表现层的框架,它是Spring框架的一部分,我们可以从Spring的整体结构中看出:
创建相应的数据库来为后续工作提供基础:
drop table if exists `items`;
create table `items` (
`id` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`name` varchar(32) not null comment '商品名称',
`price` float(10,1) not null comment '商品定价',
`detail` text comment '商品描述',
`pic` varchar(64) default null comment '商品图片',
`createtime` datetime not null comment '生产日期',
primary key (`id`)
) engine=innodb auto_increment=4 default charset=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- records of items
-- ----------------------------
insert into `items` values ('1', '台式机', '3000.0', '该电脑质量非常好!!!!', null, '2016-02-03 13:22:53');
insert into `items` values ('2', '笔记本', '6000.0', '笔记本性能好,质量好!!!!!', null, '2015-02-09 13:22:57');
insert into `items` values ('3', '背包', '200.0', '名牌背包,容量大质量好!!!!', null, '2015-02-06 13:23:02');
-- ----------------------------
-- table structure for user
-- ----------------------------
drop table if exists `user`;
create table `user` (
`id` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`username` varchar(32) not null comment '用户名称',
`birthday` date default null comment '生日',
`sex` char(1) default null comment '性别',
`address` varchar(256) default null comment '地址',
primary key (`id`)
) engine=innodb auto_increment=27 default charset=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- records of user
-- ----------------------------
insert into `user` values ('1', '王五', null, '2', null);
insert into `user` values ('10', '张三', '2014-07-10', '1', '北京市');
insert into `user` values ('16', '张小明', null, '1', '河南郑州');
insert into `user` values ('22', '陈小明', null, '1', '河南郑州');
insert into `user` values ('24', '张三丰', null, '1', '河南郑州');
insert into `user` values ('25', '陈小明', null, '1', '河南郑州');
insert into `user` values ('26', '王五', null, null, null);
SpringMVC入门
SpringMVC独立运行需要导入相关的依赖文件:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.legend</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMVCDemo</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>SpringMVCDemo Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.3.13.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- pring IOC的基础实现,包含访问配置文件、创建和管理bean等 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringMVCDemo</finalName>
</build>
</project>
前端控制器
SpringMVC在使用前需要配置核心的前端控制器DispatcherServlet,在web.xml中配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<!--配置SpringMVC前端控制器-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SpringMvcServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SpringMvcServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet的拦截规则,也就是<url-pattern>有三种方式:
1、/* 拦截任意请求,包括jsp。
2、*.action,*.do 拦截以do action结尾的请求,开发可以使用。
3、/ 拦截所有,不包括jsp,开发推荐使用。
处理器配置
1、创建普通类ItemController,在类上添加@Contoller注解来将其交给Spring管理。在方法上添加@RequestMapping注解,指定请求的url。
@Controller
public class ItemController {
// itemlist.action中后面的.action可以加也可以不加
@RequestMapping(value = "/itemlist.action")
public ModelAndView itemList() {
// 创建页面需要显示的商品数据
List<Items> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Items(1, "1华为 荣耀8", 2399, new Date(), "质量好!1"));
list.add(new Items(2, "2华为 荣耀8", 2399, new Date(), "质量好!2"));
list.add(new Items(3, "3华为 荣耀8", 2399, new Date(), "质量好!3"));
list.add(new Items(4, "4华为 荣耀8", 2399, new Date(), "质量好!4"));
list.add(new Items(5, "5华为 荣耀8", 2399, new Date(), "质量好!5"));
list.add(new Items(6, "6华为 荣耀8", 2399, new Date(), "质量好!6"));
// 创建ModelAndView,用来存放数据和视图
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 设置数据到模型中
modelAndView.addObject("itemList", list);
// 设置视图jsp,需要设置视图的物理地址
modelAndView.setViewName("/WEB-INF/jsp/itemList.jsp");
return modelAndView;
}
}
2、创建pojo类,映射数据库的表名
public class Items {
// 商品id
private int id;
// 商品名称
private String name;
// 商品价格
private double price;
// 商品创建时间
private Date createtime;
// 商品描述
private String detail;
public Items(int id, String name, double price, Date createtime, String detail) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.createtime = createtime;
this.detail = detail;
}
...Get 和 Set方法....
}
3、使用组件扫描器省去在spring容器配置每个Controller类的繁琐,它会自动扫描标记@Controller的控制器类。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 配置controller扫描包下的注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.legend.springmvc"/>
</beans>
然后可以通过url进行访问:
三大组件
SpringMVC的框架结构图如下所示:
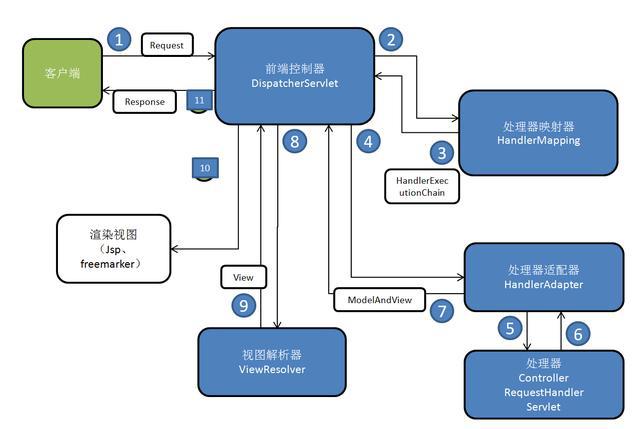
在springmvc的各个组件中,处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器称为springmvc的三大组件。需要用户开发的组件有handler、view
处理器映射器
注解式处理器映射器,对类中标记了@ResquestMapping的方法进行映射。根据@ResquestMapping定义的url匹配@ResquestMapping标记的方法,匹配成功返回
HandlerMethod对象给前端控制器。HandlerMethod对象中封装url对应的方法Method。
从spring3.1版本开始,废除了DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping的使用,推荐使用RequestMappingHandlerMapping完成注解式处理器映射。
在springmvc.xml配置文件中配置如下:
<!--配置处理器映射器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/>
注解描述:
@RequestMapping:定义请求url到处理器功能方法的映射
处理器适配器
注解式处理器适配器,对标记@ResquestMapping的方法进行适配。从spring3.1版本开始,废除了AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter的使用,推荐使用Request
MappingHandlerAdapter完成注解式处理器适配。
在springmvc.xml配置文件中配置如下:
<!--配置处理器适配器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/>
注解驱动
直接配置处理器映射器和处理器适配器比较麻烦,可以使用注解驱动来加载。可以在springmvc.xml配置文件中使用<mvc:annotation-driven>替代注解处理器和适配器的配置。
<!--配置注解驱动代替处理器映射器和处理器适配器的配置-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
视图解析器
// 设置视图jsp,需要设置视图的物理地址
modelAndView.setViewName("itemList");
最终jsp物理地址:前缀 + 逻辑视图名 + 后缀。
常用注解
参数绑定注解
-
默认参数
当前端jsp页面传递过来的参数的获取方式和servlet几乎一致,获取参数的代码如下:
@RequestMapping(value = "/itemEdit.action")
public ModelAndView toEdit(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HttpSession session, Model model) {
String id = request.getParameter("id");
// 通过id查询商品
Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(Integer.parseInt(id));
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("item", items);
modelAndView.setViewName("editItem");
return modelAndView;
}
-
简单参数
简单参数的获取直接可以在方法的参数中定义一个和传递的参数名相同的参数即可,SpringMVC会自动帮我们对该参数进行管理
// 简单参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/itemEdit.action")
public ModelAndView toEdit(Integer id, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session, Model model) {
Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(id);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("item", items);
modelAndView.setViewName("editItem");
return modelAndView;
}
如果方法的参数名和传递过来的参数名不一致,则需要通过@RequestParam来进行指定
// 简单参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/itemEdit.action")
public ModelAndView toEdit(@RequestParam(value = "id", required = false, defaultValue = "1") Integer idee,
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session, Model model) {
Items items = itemService.selectItemsById(idee);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("item", items);
modelAndView.setViewName("editItem");
return modelAndView;
}
其中@RequestParam注解中value表示传递的参数名,required表示参数是否必须存在,defaultValue则表示默认值。
-
pojo参数
在实际开发过程中一般都会有大量的参数传递,使用简单参数的方式则不再好用,所以我们可以使用pojo的方式来存储参数
// pojo参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateitem.action")
public ModelAndView updateItem(Items items) {
// 修改商品
items.setCreatetime(new Date());
itemService.updateItemsById(items);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
当然pojo类必须和传递的参数名保持一致。
- 包装pojo
1、我们新创建一个包装类,里面包含Items对象,然后生成Get和Set方法:
public class QueryVo {
private Items items;
public Items getItems() {
return items;
}
public void setItems(Items items) {
this.items = items;
}
}
2、然后我们在获取参数的时候,方法名的参数直接放包装对象
// pojo参数
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateitem.action")
public ModelAndView updateItem(QueryVo queryVo) {
// 修改商品
Items items = queryVo.getItems();
items.setCreatetime(new Date());
itemService.updateItemsById(items);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
3、在JSP页面中name属性传递的参数名则需要使用items.name、items.price的形式传递
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>修改商品信息</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="itemForm" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/updateitem.action" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="items.id" value="${item.id }" /> 修改商品信息:
<table width="100%" border=1>
<tr>
<td>商品名称</td>
<td><input type="text" name="items.name" value="${item.name }" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>商品价格</td>
<td><input type="text" name="items.price" value="${item.price }" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>商品简介</td>
<td><textarea rows="3" cols="30" name="items.detail">${item.detail }</textarea>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center"><input type="submit" value="提交" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
-
转换器配置
有时候我们会遇到如下场景,某些提交过来的参数值进行一些的操作,比如格式化日期、去除首位空格等。我们就可以使用到转换器来处理着一些需求。
1、创建一个类继承Converter类,并实现接口中的方法
/**
* 转换日期类型的数据
* S:页面传递过来的类型
* T:转换后的类型
*/
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
@Override
public Date convert(String s) {
try {
if (null != s) {
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy:MM-dd HH_mm-ss");
Date parse = dateFormat.parse(s);
return parse;
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
2、在SpringMVC的配置文件springmvc.xml中配置转换器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 注解扫描 @controller、@Service-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.legend.springmvc"/>
<!-- 注解驱动,并注册转换器 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionbean"/>
<!--配置Converter转换器,转换工厂,比如转换日期格式、去掉前后空格等操作-->
<bean id="conversionbean" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<list>
<!--配置转换器-->
<bean class="com.legend.springmvc.conversion.DateConverter"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置视图解释器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 数组参数
1、如果我们想在上方的例子中添加选择,然后删除的操作可以使用如下jsp页面
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>查询商品列表</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/item/queryitem.action" method="post">
查询条件:
<table width="100%" border=1>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="查询"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/deletes.action" method="post">
商品列表:
<table width="100%" border=1>
<tr>
<td><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="item"></td>
<td>商品名称</td>
<td>商品价格</td>
<td>生产日期</td>
<td>商品描述</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${itemList }" var="item">
<tr>
<td><input type="checkbox" name="ids" value="${item.id}"></td>
<td>${item.name }</td>
<td>${item.price }</td>
<td><fmt:formatDate value="${item.createtime}" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"/></td>
<td>${item.detail }</td>
<td><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/itemEdit.action?id=${item.id}">修改</a></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<input type="submit" value="删除">
</form>
</body>
</html>
2、此时传递过来的ids参数是数组形式,我们在接收的时候可以这样写
@RequestMapping(value = "/deletes.action")
public ModelAndView deleteItem(Integer[] ids) {
// 删除操作
for (int i = 0; i < ids.length; i++) {
itemService.deleteById(ids[i]);
}
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
如果是List类型的数据可以通过包装类中添加List集合的方式来接收,如果直接在形参上放List的话会导致无法接收。
@RequestMapping
RequestMapping是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径
RequestMapping注解有六个属性,如下表所示:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| value | 指定请求的实际地址,指定的地址可以是URI Template 模式。 |
| method | 指定请求的method类型, GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等。 |
| consumes | 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html。 |
| produces | 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回。 |
| params | 指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理。 |
| headers | 指定request中必须包含某些指定的header值,才能让该方法处理请求。 |
-
URL路径映射
@RequestMapping在进行路径映射时,有两种写法:
@RequestMapping(value="item")
@RequestMapping("/item")
value的值是数组,可以将多个url映射到同一个方法
@RequestMapping(value = { "itemList1", "itemList2" })
-
添加在类上
在class上添加@RequestMapping(url)指定通用请求前缀, 限制此类下的所有方法请求url必须以请求前缀开头。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("item")
public class ItemController {
@Autowired
private ItemService itemService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/itemlist.action")
public ModelAndView itemList() {
......
return modelAndView;
}
}
此时需要进入itemList()方法请的url为:
-
请求方法限定
除了可以对url进行设置,还可以限定请求进来的方法。
1、限定GET方法
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
如果通过POST访问则报错:
HTTP Status 405 - Request method 'POST' not supported
2、限定POST方法
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
如果通过GET访问则报错:
HTTP Status 405 - Request method 'GET' not supported
3、GET和POST都可以
@RequestMapping(method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
@Controller
@Controller 用于标记在一个类上,使用它标记的类就是一个SpringMVC Controller 对象。
我们还需要把这个控制器类交给Spring 来管理。有两种方式:
// 在SpringMVC 的配置文件中定义MyController 的bean 对象。
<bean class="com.legend.controller.controller.MyController"/>
// 在SpringMVC 的配置文件中告诉Spring 该到哪里去找标记为@Controller 的Controller 控制器。
< context:component-scan base-package = "com.legend.controller"/>
@Resource和@Autowired
@Resource和@Autowired都是做bean的注入时使用,其实@Resource并不是Spring的注解,它的包是javax.annotation.Resource,需要导入,但是Spring支持该注解的注入。
两者都可以写在字段和setter方法上。两者如果都写在字段上,那么就不需要再写setter方法。
- @Autowired
@Autowired为Spring提供的注解,需要导入包org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired
public class TestServiceImpl {
// 下面两种@Autowired只要使用一种即可
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao; // 用于字段上
@Autowired
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { // 用于属性的方法上
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
@Autowired注解是按照类型(byType)装配依赖对象,默认情况下它要求依赖对象必须存在,如果允许null值,可以设置它的required属性为false。如果我们想使用按照名称(byName)来装配,可以结合@Qualifier注解一起使用。如下:
public class TestServiceImpl {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
}
- @Resource
@Resource有两个重要的属性:name和type,而Spring将@Resource注解的name属性解析为bean的名字,而type属性则解析为bean的类型。所以,如果使用name属性,则使用byName的自动注入策略,而使用type属性时则使用byType自动注入策略。如果既不制定name也不制定type属性,这时将通过反射机制使用byName自动注入策略。
public class TestServiceImpl {
// 下面两种@Resource只要使用一种即可
@Resource(name="userDao")
private UserDao userDao; // 用于字段上
@Resource(name="userDao")
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { // 用于属性的setter方法上
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
注:最好是将@Resource放在setter方法上,因为这样更符合面向对象的思想,通过set、get去操作属性,而不是直接去操作属性。
@PathVariable
用于将请求URL中的模板变量映射到功能处理方法的参数上,即取出uri模板中的变量作为参数。如:
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value="/user/{userId}/roles/{roleId}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getLogin(@PathVariable("userId") String userId,
@PathVariable("roleId") String roleId){
System.out.println("User Id : " + userId);
System.out.println("Role Id : " + roleId);
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/product/{productId}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getProduct(@PathVariable("productId") String productId){
System.out.println("Product Id : " + productId);
return "hello";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/javabeat/{regexp1:[a-z-]+}",
method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getRegExp(@PathVariable("regexp1") String regexp1){
System.out.println("URI Part 1 : " + regexp1);
return "hello";
}
}
还有一些常用的注解如下所示:
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @ModelAttribute | Controller的所有方法在调用前,先执行此@ModelAttribute方法,可用于注解和方法参数中。 |
| @SessionAttributes | 将值放到session作用域中,写在class上面。 |
| @requestParam | 该注解用于将Controller的方法返回的对象,通过适当的HttpMessageConverter转换为指定格式后,写入到Response对象的body数据区。 |
| @Component | 相当于通用的注解,当不知道一些类归到哪个层时使用,但是不建议。 |
| @Repository | 用于注解dao层,在daoImpl类上面注解。 |
Controller返回值
-
返回ModelAndView
controller方法中定义ModelAndView对象并返回,对象中可添加model数据、指定view(不推荐,因为不解耦)。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("item")
public class ItemController {
@Autowired
private ItemService itemService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/itemlist.action")
public ModelAndView itemList() {
......
return modelAndView;
}
}
-
返回void
在Controller方法形参上可以定义request和response,使用request或response指定响应结果:
1、使用request转发页面,如下:
request.getRequestDispatcher("页面路径").forward(request, response);
2、可以通过response页面重定向:
response.sendRedirect("url")
3、可以通过response指定响应结果,例如响应json数据如下:
response.getWriter().print("{"abc":123}");
- 返回字符串
1、controller方法返回字符串可以指定逻辑视图名,通过视图解析器解析为物理视图地址。
//指定逻辑视图名,经过视图解析器解析为jsp物理路径:/WEB-INF/jsp/itemList.jsp
return "itemList"
2、重定向:Contrller方法返回字符串可以重定向到一个url地址
// 如果要指定请求参数,需要在重定向的url后面添加 ?itemId=1 这样的请求参数
return "redirect:/itemEdit.action?itemId=2";
3、转发: Controller方法执行后继续执行另一个Controller方法
//结果转发到editItem.action,request可以带过去
return "forward: /itemEdit.action";
SpringMVC进阶
异常处理
SpringMVC在处理请求过程中出现异常信息交由异常处理器进行处理,自定义异常处理器可以实现系统放异常处理逻辑。
-
异常处理思路
系统的异常包含两大类:
预期异常
运行时异常
预期异常通过捕获异常从而获取异常信息,运行时异常主要通过规范代码开发、测试等手段减少异常发生。
系统的Dao、Service、Controller出现都通过throws Exception向上抛出,最后由SpringMVC前端控制器交由异常处理器处理:

-
自定义异常类
为了区别不同的异常,通常根据异常类型进行区分,这里我们创建一个自定义系统异常。如果controller、service、dao抛出此类异常
说明是系统预期处理的异常信息。
public class MyException extends Exception{
// 异常信息
private String message;
public MyException() {
super();
}
public MyException(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
我们可以创建一个异常捕捉类来抓取出现的异常,然后在出现异常后跳转到指定页面
public class CustomExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) {
// 其中object是包名+类名+方法名,是异常发生的地方
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 判断异常的类型
if (e instanceof MyException) {
// 表示是预期异常
MyException me = (MyException) e;
modelAndView.addObject("error", me.getMessage());
}else {
modelAndView.addObject("error", "未知异常");
}
modelAndView.setViewName("error");
return modelAndView;
}
}
然后在SpringMVC的配置文件中springmvc.xml配置异常处理器
<!--SpringMVC的异常处理器-->
<bean class="com.legend.springmvc.exception.CustomExceptionResolver"/>
图片上传
1、在图片上传时,前端需要指定enctype="multipart/form-data"类型,我们编写方法来接收文件:
// 上传文件
@RequestMapping(value = "/updateitem.action")
public String uploadFile(QueryVo queryVo, MultipartFile pictureFile) throws IOException {
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "");
// 获取后缀名
String exit = FilenameUtils.getExtension(pictureFile.getOriginalFilename());
// 保存图片
pictureFile.transferTo(new File("D:/upload/" + name + "." + exit));
// 存储到数据库
queryVo.getItems().setPic(name + "." + exit);
return "redirect:success";
}
注意:其中MultipartFile pictureFile是固定写法,不允许修改,否则会无法上传。
2、然后在SpringMVC的配置文件中注册上传图片实现类
<!-- 上传图片配置实现类 -->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!-- 上传图片的大小5M-->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="5000000"/>
</bean>
其中这里的id也是固定写法,不允许修改,否则无法上传。
Json传输
- @RequestBody
@RequestBody注解用于读取Http请求的内容(字符串),通过SpringMVC提供的HttpMessageConverter接口将读取的Json字符串转换
成对象,并绑定到Controller方法的参数上
-
@ResponseBody
@ResponseBody注解用于将Contoller的方法返回的对象,通过HttpMessageConverter接口转换为指定格式的数据(json或xml),通过
Response响应给客户端。
下面是请求的Json字符串和响应Json字符串的操作
@RequestMapping("/json.action")
// @ResponseBody
public @ResponseBody Item testJson(@RequestBody Item item) {
return item;
}
如果没有配置注解驱动<mvc:annotation-driven/>,则需要给处理适配器配置json转换器,在springmvc.xml中配置:
<!--处理器适配器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter"></bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
RestFull风格
Restful是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格。不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格。基于该风格设计的软件更加简洁、有层次感,更易于实现缓存机制。
资源:互联网所有的事务都可以被抽象为资源。
资源操作:使用POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,使用不同方法对资源进行操作,分别对应于添加、删除、修改、查询。
- 传统方式操作资源
http://127.0.0.1/item/queryItem.action?id=1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item/saveItem.action 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/updateItem.action 更新,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteItem.action?id=1 删除,GET或POST
- Restful操作资源
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item 更新,PUT
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 删除,DELETE
Restful中在URL中的{xxx}叫做占位符,所以我们的URL可以是"item/1"或"ite,/2"等方式,同时使用(@PathVariable() Integer id)获取URL中占位符的数据。
@RequestMapping("/item.action/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public Item queryItemById(@PathVariable() Integer id) {
Item item = this.itemService.queryItemById(id);
return item;
}
如果@RequestMapping中表示为"item/{id}",id和形参名称一致,@PathVariable不用指定名称。如果id和形参名称不一致,例如"item/{ItemId}"则需要指定
名称@PathVariable("itemId")。
注意:@PathVariable是获取url上数据的。@RequestParam获取请求参数的(包括post表单提交)
拦截器
Spring Web MVC 的处理器拦截器类似于Servlet 开发中的过滤器Filter,用于对处理器进行预处理和后处理。
-
拦截器定义
编写一个类实现HandlerInterceptor接口,如下:
public class MyHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* Controller执行前调用此方法返回true表示继续执行,返回false中止执行,可以加入登录校验、权限拦截等
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyHandlerInterceptor....preHandle");
return true;
}
/**
* controller执行后但未返回视图前调用此方法,可在返回用户前对模型数据进行加工处理,比如这里加入公用信息以便页面显示
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o, ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyHandlerInterceptor....postHandle");
}
/**
* controller执行后且视图返回后调用此方法,可得到执行controller时的异常信息,也可记录操作日志。
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o, Exception e)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyHandlerInterceptor....afterHandle");
}
}
-
拦截器配置
在springmvc.xml配置文件中配置自定义的拦截器
<!-- 配置拦截器 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!-- 所有的请求都进入拦截器 -->
<mvc:mapping path="/**" />
<!-- 配置具体的拦截器 -->
<bean class="com.legend.springmvc.filter.MyHandlerInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
然后运行项目访问Contoller后,控制台输出结果如下:
MyHandlerInterceptor....preHandle
MyHandlerInterceptor....postHandle
MyHandlerInterceptor....afterHandle
-
拦截器流程
我们知道拦截器中包含三个方法:
preHandle 访问Contoller前调用
postHandle Contoller执行后还未返回视图前调用
afterCompletion Conroller执行后且视图已返回后调用
所以该三个方法的执行顺序如下:
preHandle => postHandle => afterCompletion
注意:如果在调用preHandle方法时返回true,则后续两个方法会依次执行;如果返回false,后续两个方法都不会执行。
- 拦截器应用
案例:判断用户是否登录,如果登录则跳转到商品列表页面,如果用户未登录则跳转到登录页面。
1、编写拦截器,在拦截器中通过session判断用户是否登录,没有登录则进入登录页面,并拦截
public class MyHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* Controller执行前调用此方法返回true表示继续执行,返回false中止执行,可以加入登录校验、权限拦截等
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o)
throws Exception {
// 判断用户是否登录
String username = (String) request.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION");
if(null == username){
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/tologin.action");
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* controller执行后但未返回视图前调用此方法,可在返回用户前对模型数据进行加工处理,比如这里加入公用信息以便页面显示
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o, ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
}
/**
* controller执行后且视图返回后调用此方法,可得到执行controller时的异常信息,也可记录操作日志。
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o, Exception e)
throws Exception {
}
}
2、配置拦截器,只拦截带/item/的请求,也就是访问商品列表的请求都需要拦截。
<!-- 配置拦截器 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!-- 所有的请求都进入拦截器 -->
<mvc:mapping path="/item/**" />
<!-- 配置具体的拦截器 -->
<bean class="com.legend.springmvc.filter.MyHandlerInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
如果我们没有在拦截器中配置只拦截带"/item/"的请求的话,也可以在拦截器判断URI是否携带"/item/"
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object o)
throws Exception {
// 判断用户是否登录
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
if (requestURI.contains("/item/")){
String username = (String) request.getSession().getAttribute("USER_SESSION");
if(null == username){
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/tologin.action");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
3、在Contoller中编写查看商品、跳转登录、以及登录的方法
@Controller
public class ItemController {
@Autowired
private ItemService itemService;
// itemlist.action中后面的.action可以加也可以不加
@RequestMapping(value = "/item/itemlist.action")
public ModelAndView itemList() {
// 从Mysql中查询商品数据
List<Items> items = itemService.selectItemsList();
// 创建ModelAndView,用来存放数据和视图
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
// 设置数据到模型中
modelAndView.addObject("itemList", items);
// 设置视图jsp,需要设置视图的物理地址
modelAndView.setViewName("itemList");
return modelAndView;
}
// 去登录的页面
@RequestMapping(value = "/tologin.action")
public ModelAndView toLogin() {
System.out.println("在去登录页面的路上...");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("login");
return modelAndView;
}
// 用户登录
@RequestMapping(value = "/login.action")
public String login(String username, String password, HttpSession session) {
// 校验用户登录
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
// 将用户名放入session域中
session.setAttribute("USER_SESSION", username);
// 重定向到商品列表页
return "redirect:/item/itemlist.action";
}
}
4、使用到的login.jsp页面
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/login.action">
<label>用户名:</label><br>
<input type="text" name="username"><br>
<label>密码:</label><br>
<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>