1.简介
带有相机位姿和空间点的图优化称为BA,能够有效的求解大范围的定位与建图问题,但是随着时间,规模越来越大,计算效率会大幅下降。我们发现,特征点在优化问题中占了很大部分,经过若干次迭代之后,特征点就会收敛,此时再进行优化的意义并不大,因此,在优化几次后,可以把特征点固定住,把他们看做位姿估计的约束,不再优化他们的位姿。
位姿图即只考虑位姿,构建一个只有轨迹的图优化,而位姿节点之间的边,由两个关键帧之间通过特征匹配后得到的运动估计来给定初始值,一旦初始值完成,就不再优化路标点的位置,只关心相机位姿之间的联系。
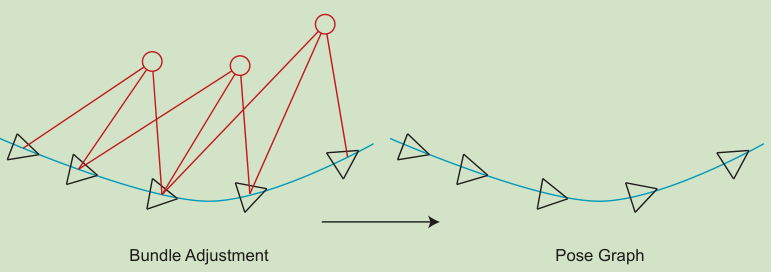
2.位姿优化:
图优化中的节点表示相机位姿,以(xi_{1}, ..., xi_{n})来表示。边,则是两个位姿节点之间的相对运动估计。
(xi_{i})和(xi_{j})之间的一个运动(Delta xi_{ij})。
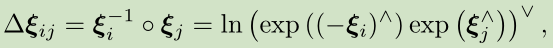
按李群写法:
构建误差(e_{ij}):

注意优化变量有两个:(xi_{i})和(xi_{j}),因此求(e_{ij})关于这两个变量的导数,按照李代数的求导方式,给两个优化变量各一个左扰动,于是误差变为:
把扰动项移至式子的左侧或右侧,有: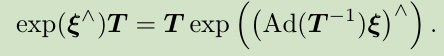

因此,按照李代数上的求导法则,我们求出来误差关于两个位姿的雅可比矩阵。
关于Ti的: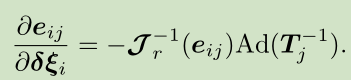
关于Tj的: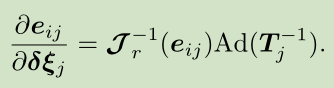
由于雅可比矩阵Jr形式过于复杂,我们通常取它的近似。如果误差接近于零,我们设它近似于I或: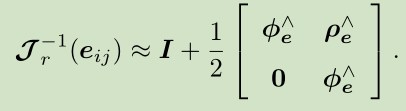
得到雅可比矩阵后,剩下的部分就和普通的图优化一样了,所有的位姿顶点和位姿边构成了一个图优化,本质上是一个最小二乘问题,优化变量为各个顶点的位姿,边来自于位姿观测约束。则总体的目标函数为:
3.实践
++ g2o自带的数据类型,默认使用四元数和平移向量表达位姿。
顶点:(ID, t_{x}, t_{y}, t_{z}, q_{x}, q_{y}, q_{z}, q_{w})。前面为平移向量,后面为旋转的单位四元数。
边:(两个节点的ID, t_{x}, t_{y}, t_{z}, q_{x}, q_{y}, q_{z}, q_{w}),信息矩阵的右上角
(信息矩阵为对称矩阵,只保留一半即可)。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <g2o/types/slam3d/types_slam3d.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/eigen/linear_solver_eigen.h>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "Usage: pose_graph_g2o_SE3 sphere.g2o" << endl;
return 1;
}
ifstream fin(argv[1]);
if (!fin) {
cout << "file " << argv[1] << " does not exist." << endl;
return 1;
}
// 设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 6>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverEigen<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
int vertexCnt = 0, edgeCnt = 0; // 顶点和边的数量
while (!fin.eof()) {
string name;
fin >> name;
if (name == "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT") {
// SE3 顶点
g2o::VertexSE3 *v = new g2o::VertexSE3();
int index = 0;
fin >> index;
v->setId(index);
v->read(fin);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertexCnt++;
if (index == 0)
v->setFixed(true);
} else if (name == "EDGE_SE3:QUAT") {
// SE3-SE3 边
g2o::EdgeSE3 *e = new g2o::EdgeSE3();
int idx1, idx2; // 关联的两个顶点
fin >> idx1 >> idx2;
e->setId(edgeCnt++);
e->setVertex(0, optimizer.vertices()[idx1]);
e->setVertex(1, optimizer.vertices()[idx2]);
e->read(fin);
optimizer.addEdge(e);
}
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
cout << "read total " << vertexCnt << " vertices, " << edgeCnt << " edges." << endl;
cout << "optimizing ..." << endl;
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(30);
cout << "saving optimization results ..." << endl;
optimizer.save("result.g2o");
return 0;
}
++ 自定义李代数数据类型
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/eigen/linear_solver_eigen.h>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
using Sophus::SE3d;
using Sophus::SO3d;
typedef Matrix<double, 6, 6> Matrix6d;
// 给定误差求J_R^{-1}的近似
Matrix6d JRInv(const SE3d &e) {
Matrix6d J;
J.block(0, 0, 3, 3) = SO3d::hat(e.so3().log());
J.block(0, 3, 3, 3) = SO3d::hat(e.translation());
J.block(3, 0, 3, 3) = Matrix3d::Zero(3, 3);
J.block(3, 3, 3, 3) = SO3d::hat(e.so3().log());
// J = J * 0.5 + Matrix6d::Identity();
J = Matrix6d::Identity(); // try Identity if you want
return J;
}
// 李代数顶点
typedef Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
class VertexSE3LieAlgebra : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, SE3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual bool read(istream &is) override {
double data[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
is >> data[i];
setEstimate(SE3d(
Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])
));
}
virtual bool write(ostream &os) const override {
os << id() << " ";
Quaterniond q = _estimate.unit_quaternion();
os << _estimate.translation().transpose() << " ";
os << q.coeffs()[0] << " " << q.coeffs()[1] << " " << q.coeffs()[2] << " " << q.coeffs()[3] << endl;
return true;
}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = SE3d();
}
// 左乘更新
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
Vector6d upd;
upd << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate = SE3d::exp(upd) * _estimate;
}
};
// 两个李代数节点之边
class EdgeSE3LieAlgebra : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<6, SE3d, VertexSE3LieAlgebra, VertexSE3LieAlgebra> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual bool read(istream &is) override {
double data[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
is >> data[i];
Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
q.normalize();
setMeasurement(SE3d(q, Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])));
for (int i = 0; i < information().rows() && is.good(); i++)
for (int j = i; j < information().cols() && is.good(); j++) {
is >> information()(i, j);
if (i != j)
information()(j, i) = information()(i, j);
}
return true;
}
virtual bool write(ostream &os) const override {
VertexSE3LieAlgebra *v1 = static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> (_vertices[0]);
VertexSE3LieAlgebra *v2 = static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> (_vertices[1]);
os << v1->id() << " " << v2->id() << " ";
SE3d m = _measurement;
Eigen::Quaterniond q = m.unit_quaternion();
os << m.translation().transpose() << " ";
os << q.coeffs()[0] << " " << q.coeffs()[1] << " " << q.coeffs()[2] << " " << q.coeffs()[3] << " ";
// information matrix
for (int i = 0; i < information().rows(); i++)
for (int j = i; j < information().cols(); j++) {
os << information()(i, j) << " ";
}
os << endl;
return true;
}
// 误差计算与书中推导一致
virtual void computeError() override {
SE3d v1 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> (_vertices[0]))->estimate();
SE3d v2 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> (_vertices[1]))->estimate();
_error = (_measurement.inverse() * v1.inverse() * v2).log();
}
// 雅可比计算
virtual void linearizeOplus() override {
SE3d v1 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> (_vertices[0]))->estimate();
SE3d v2 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> (_vertices[1]))->estimate();
Matrix6d J = JRInv(SE3d::exp(_error));
// 尝试把J近似为I?
_jacobianOplusXi = -J * v2.inverse().Adj();
_jacobianOplusXj = J * v2.inverse().Adj();
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "Usage: pose_graph_g2o_SE3_lie sphere.g2o" << endl;
return 1;
}
ifstream fin(argv[1]);
if (!fin) {
cout << "file " << argv[1] << " does not exist." << endl;
return 1;
}
// 设定g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 6>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverEigen<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
int vertexCnt = 0, edgeCnt = 0; // 顶点和边的数量
vector<VertexSE3LieAlgebra *> vectices;
vector<EdgeSE3LieAlgebra *> edges;
while (!fin.eof()) {
string name;
fin >> name;
if (name == "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT") {
// 顶点
VertexSE3LieAlgebra *v = new VertexSE3LieAlgebra();
int index = 0;
fin >> index;
v->setId(index);
v->read(fin);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertexCnt++;
vectices.push_back(v);
if (index == 0)
v->setFixed(true);
} else if (name == "EDGE_SE3:QUAT") {
// SE3-SE3 边
EdgeSE3LieAlgebra *e = new EdgeSE3LieAlgebra();
int idx1, idx2; // 关联的两个顶点
fin >> idx1 >> idx2;
e->setId(edgeCnt++);
e->setVertex(0, optimizer.vertices()[idx1]);
e->setVertex(1, optimizer.vertices()[idx2]);
e->read(fin);
optimizer.addEdge(e);
edges.push_back(e);
}
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
cout << "read total " << vertexCnt << " vertices, " << edgeCnt << " edges." << endl;
cout << "optimizing ..." << endl;
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(30);
cout << "saving optimization results ..." << endl;
// 因为用了自定义顶点且没有向g2o注册,这里保存自己来实现
// 伪装成 SE3 顶点和边,让 g2o_viewer 可以认出
ofstream fout("result_lie.g2o");
for (VertexSE3LieAlgebra *v:vectices) {
fout << "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT ";
v->write(fout);
}
for (EdgeSE3LieAlgebra *e:edges) {
fout << "EDGE_SE3:QUAT ";
e->write(fout);
}
fout.close();
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(pose_graph)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O2")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules)
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
# sophus
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# g2o
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
include_directories(${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(pose_graph_g2o_SE3 pose_graph_g2o_SE3.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_graph_g2o_SE3
g2o_core g2o_stuff g2o_types_slam3d ${CHOLMOD_LIBRARIES}
)
add_executable(pose_graph_g2o_lie pose_graph_g2o_lie_algebra.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_graph_g2o_lie
g2o_core g2o_stuff
${CHOLMOD_LIBRARIES}
${Sophus_LIBRARIES}
)