1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 3 public class BubbleSort { 4 5 private static int[] intArray = { 100, -2, 56, 65, 46, 488, 145, 666, 555, 71, 0, 1, 65, 68 }; 6 7 public static void bubbleSort(int[] intArray) { 8 for (int i = 0; i < intArray.length - 1; i++) { 9 for (int j = 0; j < intArray.length - 1 - i; j++) {
//j值的范围随着i值增加而减小。外层每一趟循环,较大的元素浮到顶端之前。 10 if (intArray[j] > intArray[j + 1]) { 11 int temp = intArray[j]; 12 intArray[j] = intArray[j + 1]; 13 intArray[j + 1] = temp; 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(intArray)); 18 } 19 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 bubbleSort(intArray); 23 } 24 }
//排序后结果:[-2, 0, 1, 46, 56, 65, 65, 68, 71, 100, 145, 488, 555, 666]
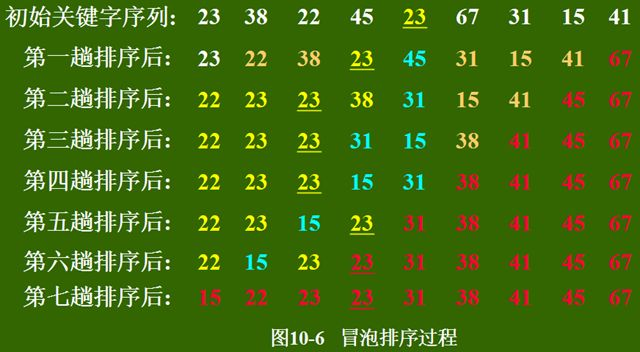
冒泡排序的基本思想是,对相邻的元素进行两两比较,顺序相反则进行交换,这样,每一趟会将最小或最大的元素“浮”到顶端,最终达到完全有序。如下图