tomcat Container容器处理请求是使用Pipeline-Valve管道来处理的,后续写的tomcat内存马,和他紧密结合
Pipeline-Valve是责任链模式,责任链模式是指在一个请求处理的过程有多个处理者依次对请求进行处理,每个处理者负责做自己相应的处理,处理完成后将处理后的请求返回,再让下一个处理者继续处理. 简单点来说就是Pipeline就是请求,发起各种请求, Valve用于处理过来的所有请求,你的请求都会走Valve,进行处理检查.
(1)每个Pipeline都有特定的Valve,而且是在管道的最后一个执行,Valve的接口实现类是ValveBase
(2)在上层容器的管道的ValveBase会调用下层容器的管道
ValveBase的子类,有很多,分别有这些:
我着重讲下这四个子类
其中要讲的是这四个类,他们和Context,Engine,Host和Wrapper的请求处理息息相关.
Pipeline-Valve的实现方法:
Pipeline的接口实现类是org.apache.catalina.core.StandardPipeline:
StandardPipeline继承自LifecycleBase,所以StandardPipeline是生命周期类
查看startInternal方法:
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { Valve current = this.first; if (current == null) { current = this.basic; } for(; current != null; current = current.getNext()) { if (current instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle)current).start(); } } this.setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); }
学过数据结构的话,会感到很熟悉,我博客文章之前写过类似的代码,他是个链式结构,遍历所有的Valve并调用start方法,最后设置状态.
stopInternal和destroyInternal方法如下:
protected synchronized void stopInternal() throws LifecycleException { this.setState(LifecycleState.STOPPING); Valve current = this.first; if (current == null) { current = this.basic; } for(; current != null; current = current.getNext()) { if (current instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle)current).stop(); } } } protected void destroyInternal() { Valve[] valves = this.getValves(); Valve[] arr$ = valves; int len$ = valves.length; for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) { Valve valve = arr$[i$]; this.removeValve(valve); } }
代码和startInternal相似,都是使用current临时变量遍历Valve的所有Valve,destoryInternal是删除所有的valve
Pipeline管道处理请求的实现方法:
Engine,先从ValveBase的子类StandEngineValve类开始org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve
Pipeline管道调用所包含Valve的invoke来处理请求,invoke方法来处理请求
invoke方法:
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { Host host = request.getHost(); if (host == null) { response.sendError(400, sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost", new Object[]{request.getServerName()})); } else { if (request.isAsyncSupported()) { request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); } host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); } }

首先通过reuquest获取Host站点,然后调用管道的第一个Valve的invoke方法进行处理
Host,org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve#invoke方法: 
代码太长,截取部分,Host的ValveBase调用的是Context的Pipeline
Context,org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve#invoke方法:

代码太长,截取部分,Context的ValveBase调用的是Wrapper的Pipeline
Wrapper,org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve#invoke方法:
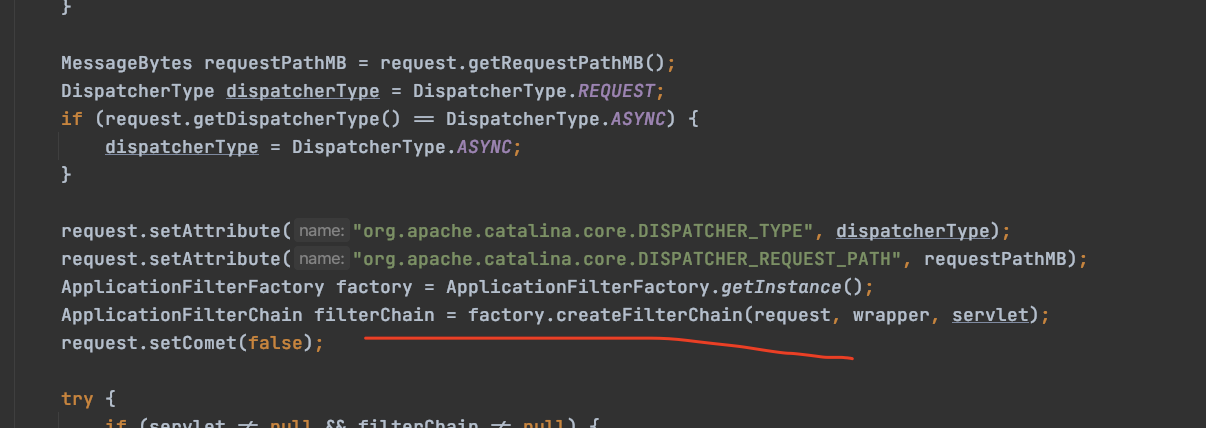

代码太长,截取部分,Wrapper是封装Servlet的,ValveBase内部调用的是filterChain来处理请求的
Filter和Servlet的实际处理请求的方法在Wrapper的管道Pipeline->Valve-ValveBase-StandardWrapperValve#invoke方法中调用,Wrapper生命周期是在org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper中调用,因为StandardWrapper继承自ContainerBase,ContainerBase又继承自LifecycleMBeanBase