A.Clam and Fish
(题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5668/A)
题意:1.游戏有n阶段,从1到n编号
2.4种类型的阶段(0~3)
0:0鱼 0蛤
1:0鱼 1蛤
2:1鱼 0蛤
3:1鱼 1蛤
每个阶段,都可以执行如下4个动作中的一个:
1.有一蛤,可以制作成一包鱼饵,接下来阶段用来抓鱼
2.有一鱼,抓这鱼不需要鱼饵,鱼饵数不变
3.至少有一鱼饵,用鱼饵抓鱼,即使这个阶段没鱼,鱼饵数减1
4.什么都不干
分析:2和3阶段有鱼就抓鱼,直接累加到答案里面,然后每次遇到一个1,就制作一包鱼饵,然后在接下来遇到0的时候,判断有没有鱼饵,有就抓一条,然后最后多出来的鱼饵的1类型,可以制作一半鱼饵用来给另一半抓鱼。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
string s;
int res = 0, n;
cin >> n >> s;
//鱼饵数量
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (s[i] == '2' || s[i] == '3') ++res;
else if (s[i] == '0')
{
if (cnt) ++res, --cnt;
}
else if (s[i] == '1') ++cnt;
}
//多出来的鱼饵
if (cnt != 0)
{
//一半的鱼饵给另一半抓鱼
res += cnt / 2;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B.Classical String Problem(字符串循环)
(题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5668/B)
题意:给一个只包含小写字母的字符串S,你会执行如下的Q个操作。
每个操作是如下的两个类型:
1.修改:给予一个整数x,你需要修改字符串S,如果x>0,你需要移动最左边的x个字符到s的最右边,否则如果x<0,移动字符串的最右边x个字符到s的最左边。
2.询问:给予一个整数型x,询问第x个字符是什么。
分析:一道原题。过的人很多,说明不是非常复杂的数据结构。因此可以找下规律,用一个变量p一开始指向字符串的开头,如果是修改操作,则移动指针的位置,p + num,如果是询问操作,则直接询问p + num即可。注意需要复制字符串两倍,看成一个环,如果指针指向了n,那么就要取模回到起点。
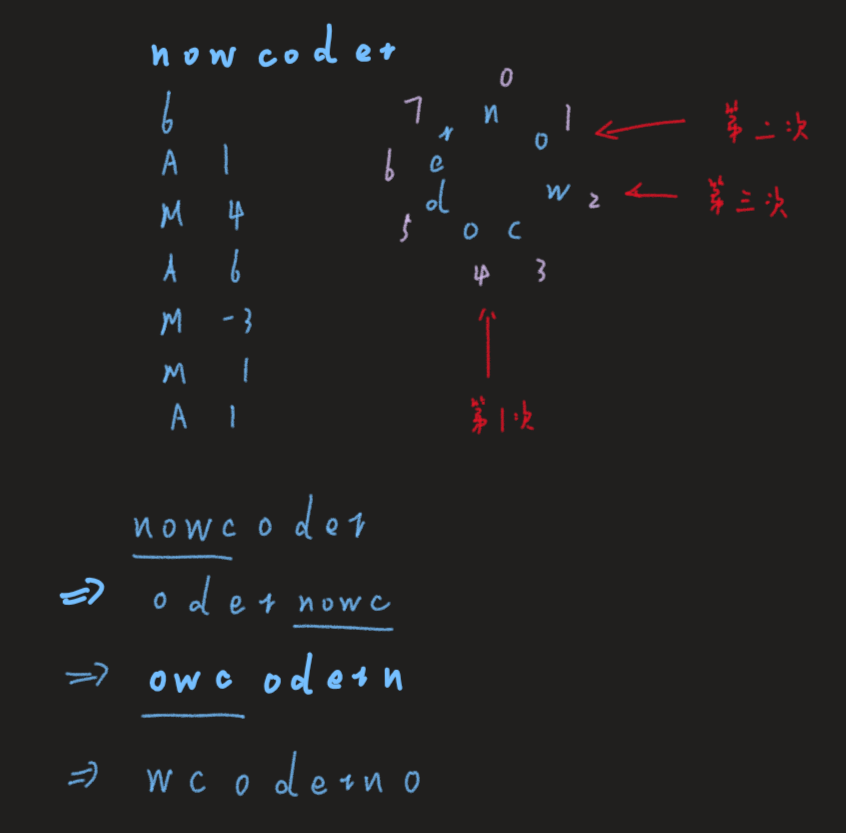
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
int n = s.size();
//成环
s += s;
int q;
cin >> q;
char op[2];
int num, p = 0;
while (q--)
{
scanf("%s%d", &op, &num);
if (op[0] == 'M')
{
p = ((p + num) % n + n) % n;
}
else
{
printf("%c
", s[p + num - 1]);
}
}
return 0;
}
C.Operation Love
(题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5668/C)
分析:如果我们把一个多边形的所有相邻点对到原点的向量求叉积全部加起来,我们可以得到多边形的有向面积,如果这个面积为正,说明是逆时针,否则是顺时针。一个比较重要的知识点。然后我们可以发现左右手的特征区别是,如果点都从顺时针开始,那么对于右手来说,有8-9两条相邻的边,对于左手来说,有9-8两条相邻的边。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-2;
int dcmp(double x)
{
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
struct Point
{
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y){}
};
typedef Point Vector;
//向量 + 向量 = 向量, 点 + 向量 = 点
Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B) { return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); }
//点 - 点 = 向量
Vector operator - (Point A, Point B) { return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); }
//向量 * 标量 = 向量
Vector operator * (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x * p, A.y * p); }
//向量 / 数 = 向量
Vector operator / (Vector A, double p) { return Vector(A.x / p, A.y / p); }
bool operator<(const Point& a, const Point& b)
{
return dcmp(a.x - b.x) < 0 || dcmp(a.x - b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y - b.y) < 0;
}
bool operator == (const Point& a, const Point& b)
{
return dcmp(a.x - b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y - b.y) == 0;
}
//求点积
double Dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; }
//求模
double Length(Vector A) { return sqrt(Dot(A, A)); }
//求角度
double Angle(Vector A, Vector B) { return acos(Dot(A, B) / Length(A) / Length(B)); }
//求叉积
double Cross(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x; }
Point p[25];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
scanf("%lf%lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
}
double res = 0;
p[20] = p[0];
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; ++i)
{
res += Cross(p[i], p[i + 1]);
}
//顺时针
if (dcmp(res) < 0)
{
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; ++i)
{
double len1 = Length(p[i % 20] - p[(i + 1) % 20]);
double len2 = Length(p[(i + 1) % 20] - p[(i + 2) % 20]);
if (dcmp(len1 - 8.0) == 0 && dcmp(len2 - 9.0) == 0)
{
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (flag) puts("right");
else puts("left");
}
else
{
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; ++i)
{
double len1 = Length(p[i % 20] - p[(i + 1) % 20]);
double len2 = Length(p[(i + 1) % 20] - p[(i + 2) % 20]);
if (dcmp(len1 - 9.0) == 0 && dcmp(len2 - 8.0) == 0)
{
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (flag) puts("right");
else puts("left");
}
}
return 0;
}
D.Points Construction Problem
题意:想象你有一个无穷的2D平面。初始的,平面上的所有点都是白色,你被给予了两个整数n,m。在这个平面上涂抹n个点变黑,使得存在m对点,满足如下的情况:1.两个顶点被涂成不同的颜色2.这两个顶点是相邻的,即(|x1-x2|+|y1-y2| = 1)。构造一个方案并输出,如果不存在这个方案,则输出-1。
分析:考虑上界情况,n个点,每个点都和4个白点相邻,那么则会有4 * n对。如果m > 4 * n,则是不合法的,再考虑下界情况,如果所有的点挨在一起,会有2 * (a + b)的点对满足情况,可以看下图
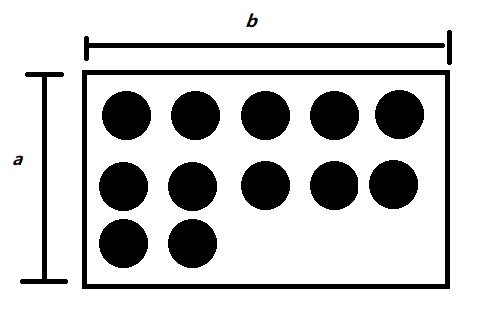 ,这些黑点只能与周边的白点相邻,有2 * (a + b)个点对满足情况,如何让2 * (a + b)最小呢?可以考虑等周定律,当面积相等时,我们的正方形比长方形的周长小,具体的做法是枚举a和b。然后我们把这些紧挨着的点放进容器里。然后我们再考虑贡献,我们现在的最小贡献是2 * (a + b)。我们每次拿出一个点,增加的贡献如下两张图,可以分为两种情况。
,这些黑点只能与周边的白点相邻,有2 * (a + b)个点对满足情况,如何让2 * (a + b)最小呢?可以考虑等周定律,当面积相等时,我们的正方形比长方形的周长小,具体的做法是枚举a和b。然后我们把这些紧挨着的点放进容器里。然后我们再考虑贡献,我们现在的最小贡献是2 * (a + b)。我们每次拿出一个点,增加的贡献如下两张图,可以分为两种情况。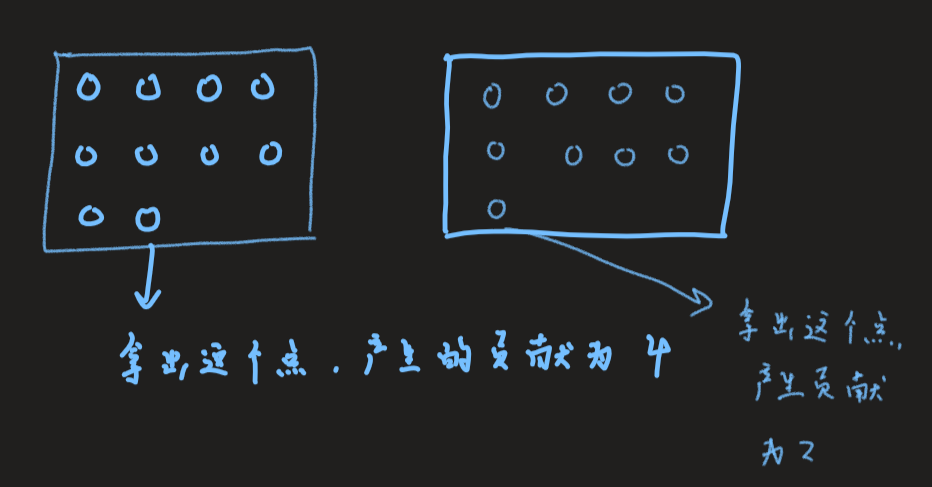 。可以看出,当我们靠近第一行和第一列的时候,如果把这个白点拿出来涂黑,放在任何一个地方,我们的贡献值就加2,否则加4。直到当且的贡献值变为小于等于m - 4,然后最后一个我们再仔细考虑一下,拼凑成m。
。可以看出,当我们靠近第一行和第一列的时候,如果把这个白点拿出来涂黑,放在任何一个地方,我们的贡献值就加2,否则加4。直到当且的贡献值变为小于等于m - 4,然后最后一个我们再仔细考虑一下,拼凑成m。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
using PII = pair<int, int>;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
vector<PII> res1, res2;
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
res1.clear(), res2.clear();
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
int a, b;
int mn = inf;
//枚举矩形的行与列
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
{
if (i * j >= n && (i - 1) * j < n && i * (j - 1) < n)
{
if (2 * (i + j) < mn)
{
//等周定理
mn = 2 * (i + j);
a = i, b = j;
}
}
}
if (m % 2 == 1 || m > 4 * n || m < mn)
{
puts("No");
continue;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= a; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= b; ++j)
{
if (n == 0) break;
res1.push_back({ i, j });
--n;
}
//当且点对的贡献值,要凑成m
int now = mn;
int nx = 1000, ny = 1000;
while (res1.size() > 1 && m >= now + 4)
{
PII q = res1.back();
res1.pop_back();
if (q.first == 1 || q.second == 1)
now += 2;
else
now += 4;
//随便抛出去一个
res2.push_back({ nx, ny });
nx += 2;
}
//还剩2没凑够
if (m == now + 2)
{
PII q = res1.back();
res1.pop_back();
if (q.first == 1 || q.second == 1)
res2.push_back({ nx, ny });
else
res2.push_back({ q.first - 1, b + 1 });
}
puts("Yes");
for (int i = 0; i < res1.size(); ++i)
{
printf("%d %d
", res1[i].first, res1[i].second);
}
for (int i = 0; i < res2.size(); ++i)
{
printf("%d %d
", res2[i].first, res2[i].second);
}
}
return 0;
}
E.Two Matchings
(题目链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5668/E)
分析:一个p是可匹配的,当且仅当(p_i
eq i),并且(p_{pi}
eq i),假设(pi为k),那么(p[p[i]] = p[k] = i),那么可以得到(p[i] = k, p[k] = i),也就意味者找到两个数组,这两个数组中的每个数对都是两两匹配的。也就是右边这个图: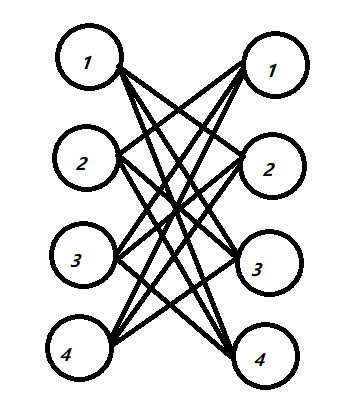
我们可以从这些边里面选出两组,使得和原先的a数组的(cost(sumlimits_{i = 1}^{n})abs(ai - api) / 2)最小。如样例里面的两组:
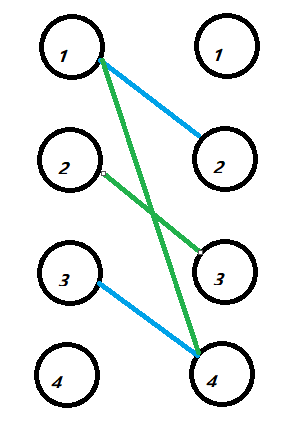
那么比如一组蓝的花费是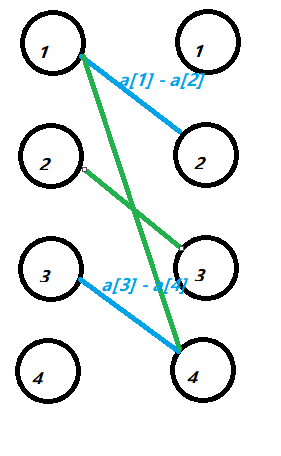
,即(frac{(abs(a[1] - a[2]) + abs(a[2] - a[1]) + abs(a[3] - a[4]) + abs(a[4] - a[3]))}{2}),我们的目的就是为了选取这些匹配边的最小值的和。等价于从上面那张黑色的图里面选取一些边,使得这些边的边权的和最小。这张图可以看成从原先的图里面选取一个环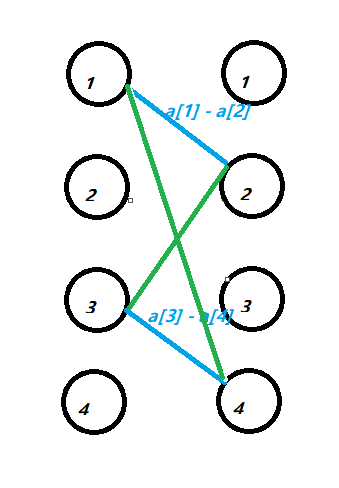 。等价于我们从原图选取一个偶数边的环,然后某个环长度>=8,可以拆成一些长度为4或6的环且总边权更小。我们可以排序a数组,利用动态规划转移。
。等价于我们从原图选取一个偶数边的环,然后某个环长度>=8,可以拆成一些长度为4或6的环且总边权更小。我们可以排序a数组,利用动态规划转移。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200005;
int a[N];
int f[N];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1);
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof f);
f[0] = 0;
for(int i = 4; i <= n; i += 2)
{
if(i >= 6)
f[i] = min(f[i], f[i - 6] + a[i] - a[i - 5]);
f[i] = min(f[i], f[i - 4] + a[i] - a[i - 3]);
}
printf("%d
", 2 * f[n]);
}
return 0;
}