概述
布局(Layout)的概念是针对Activity的,Activity就是布满整个Android设备的窗口或者悬浮于其他窗口上的交互界面。在一个应用程序中通常由多个Activity构成,每个需要显示的Activity都需要在AndroidManifest.xml文件之中声明。
通常情况下,开发人员可以使用两种方式来创建UI组件,一种方式是使用XML方式来配置UI组件的相关属性,然后装载这些UI组件,这也是最常用的方式。但是有些特殊情况下,需要动态生成UI组件,则需要使用第二种方式,完全使用Java代码来创建UI组件。
XML布局文件是Android系统中定义的Layout的常用方式,所有布局文件必须包含在res/layout目录中,且必须符合Java的命名规范。当在res/layout目录下新增了布局文件之后,R.java文件会自动收录该布局资源,Java代码可通过setContentView方法在Activity中显示该Layout。
setContentView(R.layout.<资源名称>);
Android应用的绝大部分UI组件都放在android.widget包及其子包、android.view包及其子包中,Android应用的所有UI组件都继承了View类。View类还有一个重要的子类:ViewGroup,ViewGroup类是所有布局管理器的父类。
ViewGroup容器控制其子组件的分布依赖于ViewGroup.LayoutParams、ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams两个内部类。
ViewGroup.LayoutParams提供两个XML属性设定组件的大小。
- android:layout_height:指定该子组件的基本高度;
- android:layout_width:指定该子组件的基本宽度。
- fill_parent:指定组件的高度、宽度与父容器组件的一样。
- match_parent:与fill_parent一样,Android2.2开始推荐使用。
- warp_content:内容包裹。
- android:layout_marginBottom(下边距);
- android:layout_marginLeft(左边距);
- android:layout_marginRight(右边距):
- layout_marginTop(上边距)
对于View的尺寸,android提供了三种单位供选择使用:
- px:像素。
- dp:dpi,表示屏幕实际的像素。
- sp:会根据系统设定的字体大小进行缩放,与dp类似,通常用于设置字体。
尺寸单位选择的技巧:如果设置长度、高度等属性时可以使用dp,但是如果设置字体,推荐使用sp。在屏幕适配方面,不推荐使用px,因为使用dp或者sp,UI会根据设备的density和scaledDensity进行等比例缩放,以达到不同屏幕适配的功效,让其在不同的屏幕上看起来差不多的效果。
为了适应各种界面风格,Android提供了五种布局规范,利用这五种布局,基本上可以在设备上随心所欲的摆放任何UI组件,这五种布局分别是:
- FrameLayout(帧布局)。
- LinearLayout(线性布局)
- RelativeLayout(相对布局)。
- TableLayout(表格布局)。
- AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局)。
线性布局(LinearLayout)
LinearLayout是最常用的布局方式,在XML文件中使用<LinearLayout>标记。它会将容器里的UI组件一个一个挨着排列起来。但是LinearLayout不会换行,当UI组件超出屏幕之后,则不会被显示出来。LinearLayout有两个重要的XML属性:android:gravity(对齐方式);android:orientation(排列方式)。
android:orientation(排列方式),设定了LinearLayout中包含的UI组件的排列方式,有两个选项vertical(竖向)、horizontal(横向,默认值)
android:gravity(对齐方式),设定LinearLayout中包含UI组件的对齐方式,其选项很多,常用上(top)、下(bottom)、左(left)、右(right)。
LinearLayout布局示例:
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 tools:context=".MainActivity" android:orientation="horizontal" android:gravity="bottom"> 6 <Button 7 android:layout_weight="1" 8 android:text="button" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> 11 <Button 12 android:text="button" 13 android:layout_gravity="top" 14 android:layout_weight="1" 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> 17 <Button 18 android:text="button" 19 android:layout_weight="1" 20 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> 22 </LinearLayout>
显示效果:
帧布局(FrameLayout)
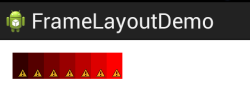
帧布局是最简单的布局方式,所有添加到这个布局中的视图都是以层叠的方式显示,并且后声明的遮挡先声明的控件。
帧布局容器为每个加入其中的组件创建一个空白的区域(称为一帧),所有每个子组件占据一帧,这些帧都会根据gravity属性执行自动对齐。
下面通过一个例子说明帧布局,以一个经典的渐变色条为例,在FrameLayout中以此添加多个TextView,赋予不同尺寸和颜色,会叠加显示。
FrameLayout示例代码:
1 <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 6 android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 7 android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 8 android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 9 tools:context=".MainActivity" > 10 11 <TextView 12 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 13 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 14 android:width="210px" 15 android:height="50px" 16 android:background="#ff0000" 17 /> 18 <TextView 19 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 20 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 21 android:width="180px" 22 android:height="50px" 23 android:background="#dd0000" 24 /> 25 <TextView 26 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 27 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 28 android:width="150px" 29 android:height="50px" 30 android:background="#bb0000" 31 /> 32 <TextView 33 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 34 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 35 android:width="120px" 36 android:height="50px" 37 android:background="#990000" 38 /> 39 <TextView 40 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 41 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 42 android:width="90px" 43 android:height="50px" 44 android:background="#770000" 45 /> 46 <TextView 47 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 48 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 49 android:width="60px" 50 android:height="50px" 51 android:background="#550000" 52 /> 53 <TextView 54 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 55 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 56 android:width="30px" 57 android:height="50px" 58 android:background="#330000" 59 /> 60 </FrameLayout>
以上示例显示效果图:
相对布局(RelativeLayout)
RelativeLayout,其内子组件的位置总是相对兄弟UI组件、父亲容器来决定的。比如UI组件A相对于UI组件B的位置进行定位,那么UI组件B需要在UI组件A之前定义。
相对布局用到的主要属性:
- android:layout_below:在某元素的下方。
- android:layout_above:在某元素的上方。
- android:layout_toLeftOf:在某元素的左边。
- android:layout_toRightOf:在某元素的右边。
- android:layout_alignXxx:控制与某元素的边界对其方式。
下面通过一个例子来说明RelativeLayout,在该布局XML中,确定一个经典的梅花布局效果,上下左右的UI组件通过中间的UI组件位置确定自己的位置。
示例代码:
1 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:gravity="top" 6 android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 7 android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 8 android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" 9 android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" 10 tools:context=".MainActivity" > 11 12 <TextView 13 android:id="@+id/view1" 14 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 15 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 16 android:text="中" 17 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 18 /> 19 <TextView 20 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 22 android:text="上" 23 android:layout_above="@id/view1" 24 android:layout_alignLeft="@id/view1" 25 /> 26 <TextView 27 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 28 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 29 android:text="下" 30 android:layout_below="@id/view1" 31 android:layout_alignLeft="@id/view1" 32 /> 33 <TextView 34 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 35 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 36 android:text="左" 37 android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/view1" 38 android:layout_alignTop="@id/view1" 39 /> 40 <TextView 41 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 42 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 43 android:text="右" 44 android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view1" 45 android:layout_alignTop="@id/view1" 46 /> 47 </RelativeLayout>
效果展示
表格布局(TableLayout)
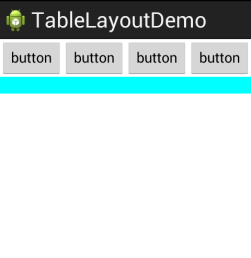
表格布局,采用行、列的形式来管理UI组件,TableLayout通过TableRow、其他UI组件来控制表格的行数和列数。
每次向TableLayout中添加一个TableRow,该TableRow就是一个表格行,TableRow也是容器,因此它也可以不断添加其他组件,没添加一个子组件,该表格就增加一列。如果直接向TableLayout中添加组件,那么这个组件将直接占用一行。
- android:collapseColumns:设置需要被隐藏的列序号。
- android:shrinkColumns:设置需要被收缩的列序号。
- android:stretchColumns:设置需要被拉伸的列序号。
注意:TableLayout中所谓的序列号是从0开始计算的。
下面用一个例子来说明TableLayout布局,代码如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <TableLayout 8 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 10 android:stretchColumns="0,1,2,3" > 11 12 <TableRow 13 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 14 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 15 16 <Button 17 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 18 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 19 android:text="button" /> 20 21 <Button 22 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 23 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 24 android:text="button" /> 25 26 <Button 27 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 28 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 29 android:text="button" /> 30 31 <Button 32 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 33 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 34 android:text="button" /> 35 </TableRow> 36 37 <EditText 38 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 39 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 40 android:background="#00ffff" /> 41 </TableLayout> 42 43 </LinearLayout>
展示效果:
绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout)
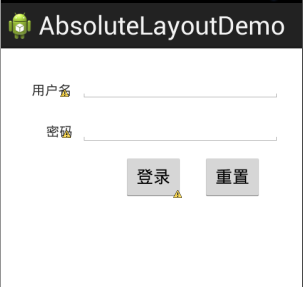
对于AbsoluteLayout,android不提供任何布局控制,而是由开发人员自己通过X坐标、Y坐标来控制组件的位置。
在AbsoluteLayout中,每个子组件都需要通过两个XML属性来确定坐标:layout_x:指定该子组件的X坐标;layout_y:指定该子组件的Y坐标。
因为此布局比较繁琐,而且在不同的屏幕上显示效果差距比较大,所以一般不推荐使用,下面通过一个简单的示例来展示AbsoluteLayout的用法
示例代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <EditText 8 android:id="@+id/editText1" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 android:layout_x="84dp" 12 android:layout_y="20dp" 13 android:ems="10" /> 14 15 <EditText 16 android:id="@+id/EditText01" 17 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 18 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 19 android:layout_x="84dp" 20 android:layout_y="66dp" 21 android:ems="10" /> 22 23 <Button 24 android:id="@+id/button1" 25 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 26 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 27 android:layout_x="214dp" 28 android:layout_y="113dp" 29 android:text="重置" /> 30 31 <Button 32 android:id="@+id/button2" 33 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 34 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 35 android:layout_x="130dp" 36 android:layout_y="113dp" 37 android:text="登录" /> 38 39 <TextView 40 android:id="@+id/textView1" 41 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 42 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 43 android:layout_x="33dp" 44 android:layout_y="36dp" 45 android:text="用户名" /> 46 47 <TextView 48 android:id="@+id/textView2" 49 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 50 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 51 android:layout_x="48dp" 52 android:layout_y="80dp" 53 android:text="密码" /> 54 55 </AbsoluteLayout>
展示效果: