1 安装
安装
yum install samba -y
卸载
yum remove samba* -y
配置文件
安装完成后可以查看到配置文件
ls /etc/samba
会自动产生三个文件 smb.conf
# See smb.conf.example for a more detailed config file or
# read the smb.conf manpage.
# Run 'testparm' to verify the config is correct after
# you modified it.
[global]
workgroup = SAMBA #设置主机工作组
security = user #以user或share验证方式访问
passdb backend = tdbsam
printing = cups
printcap name = cups
load printers = yes
cups options = raw
[homes]
comment = Home Directories
valid users = %S, %D%w%S
browseable = No
read only = No
inherit acls = Yes
[printers]
comment = All Printers
path = /var/tmp
printable = Yes
create mask = 0600
browseable = No
[print$]
comment = Printer Drivers
path = /var/lib/samba/drivers
write list = @printadmin root
force group = @printadmin
create mask = 0664
directory mask = 0775
lmhosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
smb.conf.example 和smb.conf 类似
# This is the main Samba configuration file. For detailed information about the # options listed here, refer to the smb.conf(5) manual page. Samba has a huge # number of configurable options, most of which are not shown in this example. # # The Samba Wiki contains a lot of step-by-step guides installing, configuring, # and using Samba: # https://wiki.samba.org/index.php/User_Documentation # # In this file, lines starting with a semicolon (;) or a hash (#) are # comments and are ignored. This file uses hashes to denote commentary and # semicolons for parts of the file you may wish to configure. # # NOTE: Run the "testparm" command after modifying this file to check for basic # syntax errors. # #--------------- # Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) Notes: # # Turn the samba_domain_controller Boolean on to allow a Samba PDC to use the # useradd and groupadd family of binaries. Run the following command as the # root user to turn this Boolean on: # setsebool -P samba_domain_controller on # # Turn the samba_enable_home_dirs Boolean on if you want to share home # directories via Samba. Run the following command as the root user to turn this # Boolean on: # setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on # # If you create a new directory, such as a new top-level directory, label it # with samba_share_t so that SELinux allows Samba to read and write to it. Do # not label system directories, such as /etc/ and /home/, with samba_share_t, as # such directories should already have an SELinux label. # # Run the "ls -ldZ /path/to/directory" command to view the current SELinux # label for a given directory. # # Set SELinux labels only on files and directories you have created. Use the # chcon command to temporarily change a label: # chcon -t samba_share_t /path/to/directory # # Changes made via chcon are lost when the file system is relabeled or commands # such as restorecon are run. # # Use the samba_export_all_ro or samba_export_all_rw Boolean to share system # directories. To share such directories and only allow read-only permissions: # setsebool -P samba_export_all_ro on # To share such directories and allow read and write permissions: # setsebool -P samba_export_all_rw on # # To run scripts (preexec/root prexec/print command/...), copy them to the # /var/lib/samba/scripts/ directory so that SELinux will allow smbd to run them. # Note that if you move the scripts to /var/lib/samba/scripts/, they retain # their existing SELinux labels, which may be labels that SELinux does not allow # smbd to run. Copying the scripts will result in the correct SELinux labels. # Run the "restorecon -R -v /var/lib/samba/scripts" command as the root user to # apply the correct SELinux labels to these files. # #-------------- # #======================= Global Settings ===================================== [global] # ----------------------- Network-Related Options ------------------------- # # workgroup = the Windows NT domain name or workgroup name, for example, MYGROUP. # # server string = the equivalent of the Windows NT Description field. # # netbios name = used to specify a server name that is not tied to the hostname, # maximum is 15 characters. # # interfaces = used to configure Samba to listen on multiple network interfaces. # If you have multiple interfaces, you can use the "interfaces =" option to # configure which of those interfaces Samba listens on. Never omit the localhost # interface (lo). # # hosts allow = the hosts allowed to connect. This option can also be used on a # per-share basis. # # hosts deny = the hosts not allowed to connect. This option can also be used on # a per-share basis. # workgroup = MYGROUP server string = Samba Server Version %v ; netbios name = MYSERVER ; interfaces = lo eth0 192.168.12.2/24 192.168.13.2/24 ; hosts allow = 127. 192.168.12. 192.168.13. # --------------------------- Logging Options ----------------------------- # # log file = specify where log files are written to and how they are split. # # max log size = specify the maximum size log files are allowed to reach. Log # files are rotated when they reach the size specified with "max log size". # # log files split per-machine: log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m # maximum size of 50KB per log file, then rotate: max log size = 50 # ----------------------- Standalone Server Options ------------------------ # # security = the mode Samba runs in. This can be set to user, share # (deprecated), or server (deprecated). # # passdb backend = the backend used to store user information in. New # installations should use either tdbsam or ldapsam. No additional configuration # is required for tdbsam. The "smbpasswd" utility is available for backwards # compatibility. # security = user passdb backend = tdbsam # ----------------------- Domain Members Options ------------------------ # # security = must be set to domain or ads. # # passdb backend = the backend used to store user information in. New # installations should use either tdbsam or ldapsam. No additional configuration # is required for tdbsam. The "smbpasswd" utility is available for backwards # compatibility. # # realm = only use the realm option when the "security = ads" option is set. # The realm option specifies the Active Directory realm the host is a part of. # # password server = only use this option when the "security = server" # option is set, or if you cannot use DNS to locate a Domain Controller. The # argument list can include My_PDC_Name, [My_BDC_Name], and [My_Next_BDC_Name]: # # password server = My_PDC_Name [My_BDC_Name] [My_Next_BDC_Name] # # Use "password server = *" to automatically locate Domain Controllers. ; security = domain ; passdb backend = tdbsam ; realm = MY_REALM ; password server = <NT-Server-Name> # ----------------------- Domain Controller Options ------------------------ # # security = must be set to user for domain controllers. # # passdb backend = the backend used to store user information in. New # installations should use either tdbsam or ldapsam. No additional configuration # is required for tdbsam. The "smbpasswd" utility is available for backwards # compatibility. # # domain master = specifies Samba to be the Domain Master Browser, allowing # Samba to collate browse lists between subnets. Do not use the "domain master" # option if you already have a Windows NT domain controller performing this task. # # domain logons = allows Samba to provide a network logon service for Windows # workstations. # # logon script = specifies a script to run at login time on the client. These # scripts must be provided in a share named NETLOGON. # # logon path = specifies (with a UNC path) where user profiles are stored. # # ; security = user ; passdb backend = tdbsam ; domain master = yes ; domain logons = yes # the following login script name is determined by the machine name # (%m): ; logon script = %m.bat # the following login script name is determined by the UNIX user used: ; logon script = %u.bat ; logon path = \%LProfiles\%u # use an empty path to disable profile support: ; logon path = # various scripts can be used on a domain controller or a stand-alone # machine to add or delete corresponding UNIX accounts: ; add user script = /usr/sbin/useradd "%u" -n -g users ; add group script = /usr/sbin/groupadd "%g" ; add machine script = /usr/sbin/useradd -n -c "Workstation (%u)" -M -d /nohome -s /bin/false "%u" ; delete user script = /usr/sbin/userdel "%u" ; delete user from group script = /usr/sbin/userdel "%u" "%g" ; delete group script = /usr/sbin/groupdel "%g" # ----------------------- Browser Control Options ---------------------------- # # local master = when set to no, Samba does not become the master browser on # your network. When set to yes, normal election rules apply. # # os level = determines the precedence the server has in master browser # elections. The default value should be reasonable. # # preferred master = when set to yes, Samba forces a local browser election at # start up (and gives itself a slightly higher chance of winning the election). # ; local master = no ; os level = 33 ; preferred master = yes #----------------------------- Name Resolution ------------------------------- # # This section details the support for the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS). # # Note: Samba can be either a WINS server or a WINS client, but not both. # # wins support = when set to yes, the NMBD component of Samba enables its WINS # server. # # wins server = tells the NMBD component of Samba to be a WINS client. # # wins proxy = when set to yes, Samba answers name resolution queries on behalf # of a non WINS capable client. For this to work, there must be at least one # WINS server on the network. The default is no. # # dns proxy = when set to yes, Samba attempts to resolve NetBIOS names via DNS # nslookups. ; wins support = yes ; wins server = w.x.y.z ; wins proxy = yes ; dns proxy = yes # --------------------------- Printing Options ----------------------------- # # The options in this section allow you to configure a non-default printing # system. # # load printers = when set you yes, the list of printers is automatically # loaded, rather than setting them up individually. # # cups options = allows you to pass options to the CUPS library. Setting this # option to raw, for example, allows you to use drivers on your Windows clients. # # printcap name = used to specify an alternative printcap file. # load printers = yes cups options = raw ; printcap name = /etc/printcap # obtain a list of printers automatically on UNIX System V systems: ; printcap name = lpstat ; printing = cups # --------------------------- File System Options --------------------------- # # The options in this section can be un-commented if the file system supports # extended attributes, and those attributes are enabled (usually via the # "user_xattr" mount option). These options allow the administrator to specify # that DOS attributes are stored in extended attributes and also make sure that # Samba does not change the permission bits. # # Note: These options can be used on a per-share basis. Setting them globally # (in the [global] section) makes them the default for all shares. ; map archive = no ; map hidden = no ; map read only = no ; map system = no ; store dos attributes = yes #============================ Share Definitions ============================== [homes] comment = Home Directories browseable = no writable = yes ; valid users = %S ; valid users = MYDOMAIN\%S [printers] comment = All Printers path = /var/spool/samba browseable = no guest ok = no writable = no printable = yes # Un-comment the following and create the netlogon directory for Domain Logons: ; [netlogon] ; comment = Network Logon Service ; path = /var/lib/samba/netlogon ; guest ok = yes ; writable = no ; share modes = no # Un-comment the following to provide a specific roaming profile share. # The default is to use the user's home directory: ; [Profiles] ; path = /var/lib/samba/profiles ; browseable = no ; guest ok = yes # A publicly accessible directory that is read only, except for users in the # "staff" group (which have write permissions): ; [public] ; comment = Public Stuff ; path = /home/samba ; public = yes ; writable = no ; printable = no ; write list = +staff
samba 软件目录结构
/etc/samba/smb.conf #samba服务的主要配置文件
/etc/samba/lmhosts #samba服务的域名设定,主要设置IP地址对应的域名,类似linux系统的/etc/hosts
/etc/samba/smbusers #samba服务设置samba虚拟用户的配置文件
/var/log/samba #samab服务存放日志文件
/var/lib/samba/private/{passdb.tdb,secrets.tdb} #存放samba的用户账号和密码数据库文档
2 配置
2.1 找到win的工作组
转到Windows PC并启动命令提示符。输入命令:
> net config workstation
从输出中我们可以清楚地看到工作站域指向' WORKGROUP '。稍后将在Linux机器上对其进行配置。

2.2 设置smb.conf
先复制一份
cp smb.conf smb.conf.copy
编辑smb.conf
vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = Samba Server %v #samba服务注释
netbios name = centos-8
security = user
map to guest = bad user
dns proxy = no
[ttt]
path = /myweb
browsable =yes
writable = yes
guest ok = yes
;read only = no #共享文件可读,不能与writable共用
2.3 全局参数设置
#全局设置参数 [global] config file = /etc/samba/smb.conf.%U #可以让你使用另一个配置文件来覆盖缺省的配置文件。如果文件 不存在,则该项无效。 workgroup = WORKGROUP #工作组名称 server string = Samba Server Version %v #主机的简易说明 netbios name = MYSERVER #主机的netBIOS名称,如果不填写则默认服务器DNS的一部分,workgroup和netbios name名字不要设置成一样 interfaces = lo eth0 192.168.12.2/24 192.168.13.2/24 #设置samba服务器监听网卡,可以写网卡名称或IP地址,默认注释 hosts allow = 127. 192.168.12. 192.168.13. #设置允许连接到samba服务器的客户端,默认注释 hosts deny =192.168.12.0/255.255.255.0 #设置不允许连接到samba服务器的客户端,默认注释 log level =1 #日志文件安全级别,0~10级别,默认0 log file = /var/log/samba/%m #产生日志文件的命名,默认以访问者IP地址命名 max log size = 50 #日志文件最大容量50,默认50,单位为KB,0表示不限制
2.3.1 security = share
#设置用户访问samba服务器的验证方式 ,一共四种验证方式。
1. share:用户访问Samba Server不需要提供用户名和口令, 安全性能较低。
2. user:Samba Server共享目录只能被授权的用户访问,由Samba Server负责检查账号和密码的正确性。账号和密码要在本Samba Server中建立。
3. server:依靠其他Windows NT/2000或Samba Server来验证用户的账号和密码,是一种代理验证。此种安全模式下,系统管理员可以把所有的Windows用户
和口令集中到一个NT系统上,使用Windows NT进行Samba认证, 远程服务器可以自动认证全部用户和口令,如果认证失败,Samba将使用用户级安全模式作为替代的方式。
4. domain:域安全级别,使用主域控制器(PDC)来完成认证。
2.3.2 passdb backend = tdbsam
#定义用户后台类型
1、smbpasswd:使用SMB服务的smbpasswd命令给系统用户设置SMB密码
2、tdbsam:创建数据库文件并使用pdbedit建立SMB独立用户,smbpasswd –a username建立samba用户并设置密码,不过建立samba用户
必须先建立系统用户,也可以使用pdbedit命令来建立samba用户:
pdbedit –a username:新建Samba账户。
pdbedit –x username:删除Samba账户。
pdbedit –L:列出Samba用户列表,读取passdb.tdb数据库文件。
pdbedit –Lv:列出Samba用户列表的详细信息。
pdbedit –c “[D]” –u username:暂停该Samba用户的账号。
pdbedit –c “[]” –u username:恢复该Samba用户的账号。
2.2.3 ldapsam:
基于LDAP服务进行账户验证
username map = /etc/samba/smbusers #配合/etc/samba/smbusers文件设置虚拟用户
2.4 共享文件设置参数
[share] #自定义共享名称 comment = This is share software #共享描述 path = /home/testfile #共享目录路径 browseable = yes/no #设置共享是否可浏览,如果no就表示隐藏,需要通过IP+共享名称进行访问 writable = yes/no #设置共享是否具有可写权限 read only = yes/no #设置共享是否具有只读权限 admin users = root #设置共享的管理员,如果security =share 时,引项无效,多用户中间使用逗号隔开,例如admin users = root,user1,user2 valid users = username #设置允许访问共享的用户,例如valid users = user1,user2,@group1,@group2(多用户或组使用逗号隔开,@group表示group用户组) invalid users = username #设置不允许访问共享的用户 write list = username #设置在共享具有写入权限的用户,例如例如write list = user1,user2,@group1,@group2(多用户或组使用逗号隔开,@group表示group用户组) public = yes/no #设置共享是否允许guest账户访问 guest ok = yes/no #功能同public 一样 create mask = 0700 #创建的文件权限为700 directory mode = 0700 #创建的文件目录为 700
2.5 不需要账号密码访问的共享(security = share )
ls -ld /home/smbuser/ #查看共享文件权限
chmod 777 /home/smbuser/ #分配共享文件最大权限
testparm #检查smb.conf配置文件是否有语法错误
netstat -tlnp | grep mbd #查看samba端口,TCP端口139,445 UDP端口 137,138
vim /etc/samba/smb.conf #设置smb.conf配置文件

[global] workgroup = WORKGROUP #设置主机工作组 server string = Samba Server Version %v #samba服务注释 log level = 1 #设置日志文件安全级别为1 log file = /var/log/samba/%m #设置日志文件名称,%m以IP地址为名称 max log size = 50 #设置日志文件最大容量50KB,0表示不限制 security = share #以share验证方式访问 passdb backend = tdbsam #定义用户后台类型 load printers = no #关闭打印共享功能 cups options = raw #打印机选项 [usershare] comment = Home Directories #共享文件描述 path = /home/shareuser #共享路径 browseable = yes #共享文件可以浏览 writable = yes #共享文件可写 ; read only = yes #共享文件可读,不能与writable共用 guest ok = yes #允许guest用户访问
在linux操作需要进行挂载
yum -y install samba-client #在线安装samba-client才能使用smbclient命令
smbclient -L //192.168.2.234 #查看samba服务器共享目录
mount -t cifs //192.168.2.234/usershare /mnt/share #挂载
2.6 需要输入账号和密码访问的共享(security = user)
标注:创建samba用户之前必须先创建系统用户,系统用户和samba用户名一样,但密码可以设置成不一样
useradd test01 #创建系统用户test01
useradd test02 #创建系统用户test02
passwd test01 #设置系统用户test01密码
passwd test01 #设置系统用户test02密码
smbpasswd -a test01 #把系统用户test01添加为samba用户并设置samba用户登录密码
smbpasswd -a test02 #把系统用户test02添加为samba用户并设置samba用户登录密码
pdbedit –L #查看samba用户
mkdir /home/{smbadmin01,smbuser01} #home创建两个共享目录
chmod 777 /home/{smbadmin01,smbuser01} #目录分配最高权限
vim /etc/samba/smb.conf #设置smb.conf配置文件

[global] workgroup = WORKGROUP #设置主机工作组 server string = Samba Server Version %v #samba服务注释 log level = 1 #设置日志文件安全级别为1 log file = /var/log/samba/%m #设置日志文件名称,%m以IP地址为名称 max log size = 50 #设置日志文件最大容量50KB,0表示不限制 security = user #以user验证方式访问 passdb backend = tdbsam #定义用户后台类型 load printers = no #关闭打印共享功能 cups options = raw #打印机选项 [usershare] comment = Home Directories #共享文件描述 path = /home/smbuser01 #共享路径 browseable = yes #共享文件可以浏览 read only = yes #共享文件可读,不能与writable共用 valid users = test01,test02 #设置允许访问共享用户 [adminshare] comment = Home Directories #共享文件描述 path = /home/smbadmin01 #共享路径 browseable = yes #共享文件可以浏览 writable = yes #共享文件可写 create make = 0664 #设置用户创建文件权限0664 directory make = 0775 #设置用户创建目录权限0775 write list = test01 #设置允许访问共享具有写入权限的用户
3 使用
启动
systemctl start smb.service
设为开机启动
systemctl enable smb.service
重启
systemctl restart smb.service
组成Samba运行的有两个服务,一个是SMB,另一个是NMB;SMB是Samba 的核心启动服务,主要负责建立 Linux Samba服务器与Samba客户机之间的对话, 验证用户身份并提供对文件和打印系统的访问,只有SMB服务启动,才能实现文件的共享,监听139 TCP端口;而NMB服务是负责解析用的,类似与DNS实现的功能,NMB可以把Linux系统共享的工作组名称与其IP对应起来,如果NMB服务没有启动,就只能通过IP来访问共享文件,监听137和138 UDP端口。
systemctl start nmb
设为开机启动
systemctl enable nmb.service
查看状态
systemctl status smb.service
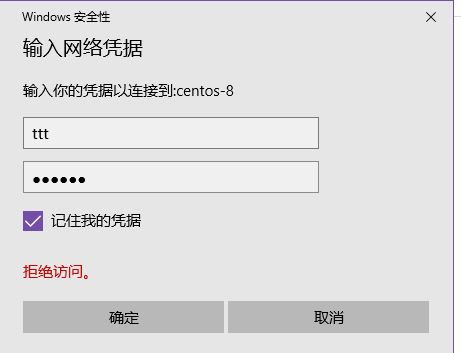
win连接
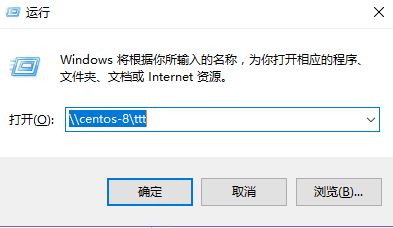
输入密码
参考阅读
