说明:这是基于同事的培训材料做的练习,记录下来,以作日后自己coding分析和改进
1.准备
pom.xml
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId> <version>4.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>14.0</version> </dependency>
Dish.java
package com.example.demo; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; /** * Created by Administrator on 2019/9/7. */ @Data @AllArgsConstructor public class Dish { private int calories; private String name; }
List<Dish> list;
list = Lists.newArrayList(
new Dish( 1,"aa"),
new Dish(13,"bb"),
new Dish(7,"cc"),
new Dish( 6,"aa"),
new Dish(9,"dd"),
new Dish(1,"ee"),
new Dish( 3,"aa"),
new Dish(1,"ff"),
new Dish(1,"gg")
);
2.stream的创建
Integer[] ints={1,2};
List<Integer> list2=Lists.newArrayList(ints);
List<String> collect3 = list2.stream().map(o -> "1" + o).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> collect4 = Stream.of(1,2).map(o -> "1" + o).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> collect5 = Stream.of(ints).map(o -> "1" + o).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> collect6 = Stream.of(list2).map(o -> "1" + o).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect3);
System.out.println(collect4);
System.out.println(collect5);
System.out.println(collect6);
输出:
[11, 12]
[11, 12]
[11, 12]
[1[1, 2]]
3.list转map并排序
list排序参照java8排序 java8 list转Map报错Collectors.toMap :: results in "Non-static method cannot be refernced from static context"
TreeMap<String, String> collect1 = list.stream() .collect(Collectors.toMap(Dish::getName, o -> "", (key1, key2) -> key2, TreeMap<String, String>::new)); //Map中的value自己o->o或者Function.identity()
System.out.println(collect1);
输出:{aa=, bb=, cc=, dd=, ee=, ff=, gg=}
4.list转linkedList
LinkedList<Dish> collect2 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));
输出:[Dish(calories=1, name=aa), Dish(calories=13, name=bb), Dish(calories=7, name=cc), Dish(calories=6, name=aa), Dish(calories=9, name=dd), Dish(calories=1, name=ee), Dish(calories=3, name=aa), Dish(calories=1, name=ff), Dish(calories=1, name=gg)]
5.filter筛选,map映射,sorted排序,limit截断流,collect的使用
List<String> collect = list.stream() .filter(d ->d.getCalories() < 9) .sorted(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories).reversed()) .map(d->d.getName()) .limit(3)
输出:[cc, aa, aa]
打印日志:
List<String> collect = list.stream() .filter(d ->{ System.out.println("filter "+d.getName()); return d.getCalories() < 9;}) .sorted(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories).reversed()) .map(d->{ System.out.println("map "+d.getName()); return d.getName(); }) .limit(3) .collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
输出:
filter aa
filter bb
filter cc
filter aa
filter dd
filter ee
filter aa
filter ff
filter gg
map cc
map aa
map aa
[cc, aa, aa]
//不排序
Stream在迭代的时候称为内部迭代,会进行一系列的优化,并不会将前面的执行完再进行后面的操作,它会进行全面的评估,执行最优迭代,前面的操作都不会执行,直到最后的collect方法调用时,这称为惰性执行.(你在某些情况下甚至可以使用parallelStream(),它会根据你cpu核数并行计算.)
List<Dish> list; list = Lists.newArrayList( new Dish( 1,"aa"), new Dish(13,"bbc"), new Dish(7,"cc"), new Dish( 6,"aa"), new Dish(9,"dd"), new Dish(1,"ee"), new Dish( 3,"aa"), new Dish(1,"ff"), new Dish(1,"gg") ); List<String> collect = list.stream() .filter(d ->{ System.out.println("filter "+d.getName()); return d.getCalories() < 9;}) // .sorted(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories).reversed()) .map(d->{ System.out.println("map "+d.getName()); return d.getName(); }) .limit(3) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(collect);
输出:
filter aa
map aa
filter bbc
filter cc
map cc
filter aa
map aa
[aa, cc, aa]
比如:这里filter只进行了4次就找够了,map也只进行了三次,他们是并行进行的
6.skip,distinct,flatMap的使用
//distinct
List<String> collect7 = list.stream().map(Dish::getName).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect7);
输出:[aa, bb, cc, dd, ee, ff, gg]
//skip
List<String> collect7 = list.stream().map(Dish::getName).distinct().skip(3).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(collect7);
输出:[dd, ee, ff, gg]
//Map
String[] words=new String[]{"hello","world"};
List<String[]> collect8 = Arrays.stream(words).map(w -> w.split("")) .distinct() .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(collect8));
输出:[["h","e","l","l","o"],["w","o","r","l","d"]]
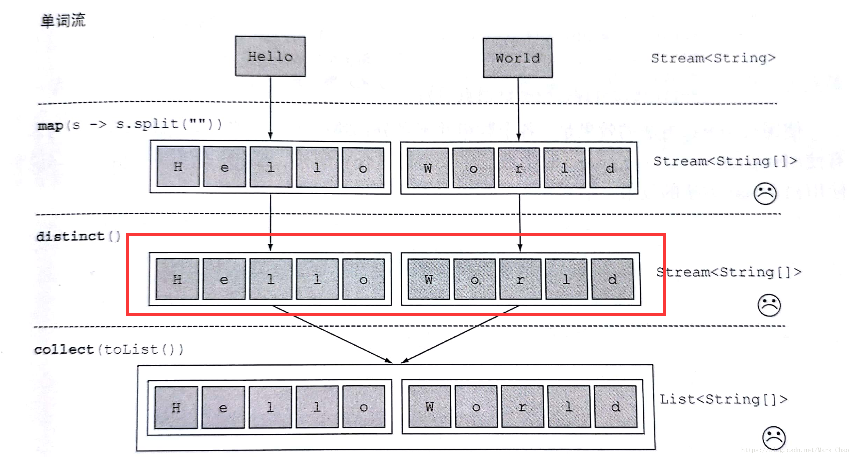
//flatmap对流扁平化处理
List<String> collect8 = Arrays.stream(words).map(w -> w.split("")) .flatMap(Arrays::stream) .distinct() .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(collect8));
输出:["h","e","l","o","w","r","d"]

7.终结操作:
7.1 匹配anyMatch,allMatch,oneMatch
anyMatch,只有找到第一个匹配的就退出并返回true
if(Stream.of(9,5,8,6,5,9,8,3,1,0,8,2).anyMatch(o->o==8)){ System.out.println("find the item"); };
输出:find the item
allMatch,匹配所有元素才返回true
if(Stream.of(9,5,8,6,5,9,8,3,1,0,8,2).allMatch(o->o==8)){ System.out.println("success"); }else { System.out.println("failure"); };
输出:failure
noneMatch,所有元素都不匹配才返回true,否则false
if(Stream.of(9,5,8,6,5,9,8,3,1,0,8,2).noneMatch(o->o==11)){ System.out.println("success"); }else { System.out.println("failure"); };
输出:false
7.2查找findAny,findFirst
findAny,返回任意一个,注意是否为null的判断,关于Optional参考理解、学习与使用 Java 中的 Optional
Optional<Integer> any = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).filter(o -> o < 2).findAny(); if(any.isPresent()) System.out.println(any.get());
输出:1
findFirst,找到第一个符合条件的,如找到第一个平方能被4整除的值
Optional<Integer> any = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).map(o->o*o).filter(o -> o%4==0).findAny(); if(any.isPresent()) System.out.println(any.get());
输出:64
相比于findAny,findFirst在并行上有更多的限制,如果不关心找到哪个元素,推荐用findAny。与limit(1)不同,它们是终结操作,不需要collect
8.归约操作
8.1求和(广义归约)
归约操作是指将流中的所有元素反复组合起来,得到一个值。比如,将流中的元素求和:int sum = numbers.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b);为什么说是反复组合起来?
求和归约操作中是将指定的初始值0(reduce方法的第一个参数)与流中的第一个元素相加(表达为reduce的第二个参数BinaryOperator,我们传递是Lambda表达式(a, b) -> a + b)得到一个中间值后与流中的第二个元素相加,直至流中的所有元素都被累加完,得到最终的求和结果。
Integer reduce = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b); System.out.println(reduce);//64
只传一个参数
Optional<Integer> reduce = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).reduce((a, b) -> a + b); if(reduce.isPresent()) System.out.println(reduce.get());//64
也可以这样
Optional<Integer> reduce = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).reduce(Integer::sum); if(reduce.isPresent()) System.out.println(reduce.get());//64
也可以
Integer collect9 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.reducing(0,//初始值 Dish::getCalories, //转换函数 Integer::sum));//累积函数 System.out.println(collect9);//42
预定义归约:
Integer collect9 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Dish::getCalories));
System.out.println(collect9);
更简洁的用法:
int sum = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum(); System.out.println("sum===="+sum);//sum====42
8.2求最大值
Optional<Integer> reduce = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).reduce(Integer::max); if(reduce.isPresent()) System.out.println(reduce.get());//9
也可以
Optional<Dish> collect9 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories))); Optional<Dish> collect10 = list.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories)); if(collect9.isPresent()) System.out.println(collect9.get());//Dish(calories=13, name=bb)
8.3求最小值
Optional<Integer> reduce = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).reduce(Integer::min); if(reduce.isPresent()) System.out.println(reduce.get());//0
8.4其它归约函数count
Long collect9 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.counting()); long count = list.stream().count(); System.out.println(collect9);
8.5 join连接
String collect11 = list.stream().map(Dish::getName).collect(Collectors.joining()); System.out.println(collect11);//aabbccaaddeeaaffgg String collect12 = list.stream().map(Dish::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("--", "start:", ":end")); System.out.println(collect12);//start:aa--bb--cc--aa--dd--ee--aa--ff--gg:end
8.6 groupingBy
Map<String, List<Dish>> collect13 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Dish::getName)); System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(collect13)); System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(list));
输出:
{"gg":[{"calories":1,"name":"gg"}],"ff":[{"calories":1,"name":"ff"}],"ee":[{"calories":1,"name":"ee"}],"dd":[{"calories":9,"name":"dd"}],"cc":[{"calories":7,"name":"cc"}],"bb":[{"calories":13,"name":"bb"}],"aa":[{"calories":1,"name":"aa"},{"calories":6,"name":"aa"},{"calories":3,"name":"aa"}]}
[{"calories":1,"name":"aa"},{"calories":13,"name":"bb"},{"calories":7,"name":"cc"},{"calories":6,"name":"aa"},{"calories":9,"name":"dd"},{"calories":1,"name":"ee"},{"calories":3,"name":"aa"},{"calories":1,"name":"ff"},{"calories":1,"name":"gg"}]
只要统计个数
Map<String, Long> collect13 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Dish::getName, Collectors.counting()));
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(collect13));
输出:{"gg":1,"ff":1,"ee":1,"dd":1,"cc":1,"bb":1,"aa":3}
9并行执行
int sum = Stream.of(9, 5, 8, 6, 5, 9, 8, 3, 1, 0, 8, 2).parallel().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum(); System.out.println("sum===="+sum);//42
数据并行处理,只需要在原来的基础上加一个parallel()就可以开启~。顺便提一下这里parallel()开启的底层并行框架是fork/join,默认的并行数是Ncpu个。