出处:arxiv 2016 尚未出版
Motivation
根据文字描述来合成相片级真实感的图片是一项极具挑战性的任务。现有的生成手段,往往只能合成大体的目标,而丢失了生动的细节信息。StackGAN分两步来完成生成目标:Stage-I从文字中生成低分辨率的大体框架和基本色彩,Stage-II以文字和Stage-I中生成的基本框架图为输入,生成高分辨率的具体细节。运用StackGAN可以生成当前state_of_art的256*256分辨率的文字转换图像。训练数据集采用了CUB and Oxford-102。
Introduction
现有工作中,[20][22]可以利用GAN根据文字描述生成低分辨率64*64的图片。为了克服这一困难,作者描述了StackGAN怎样将任务分解为两步来达到目标。
Model
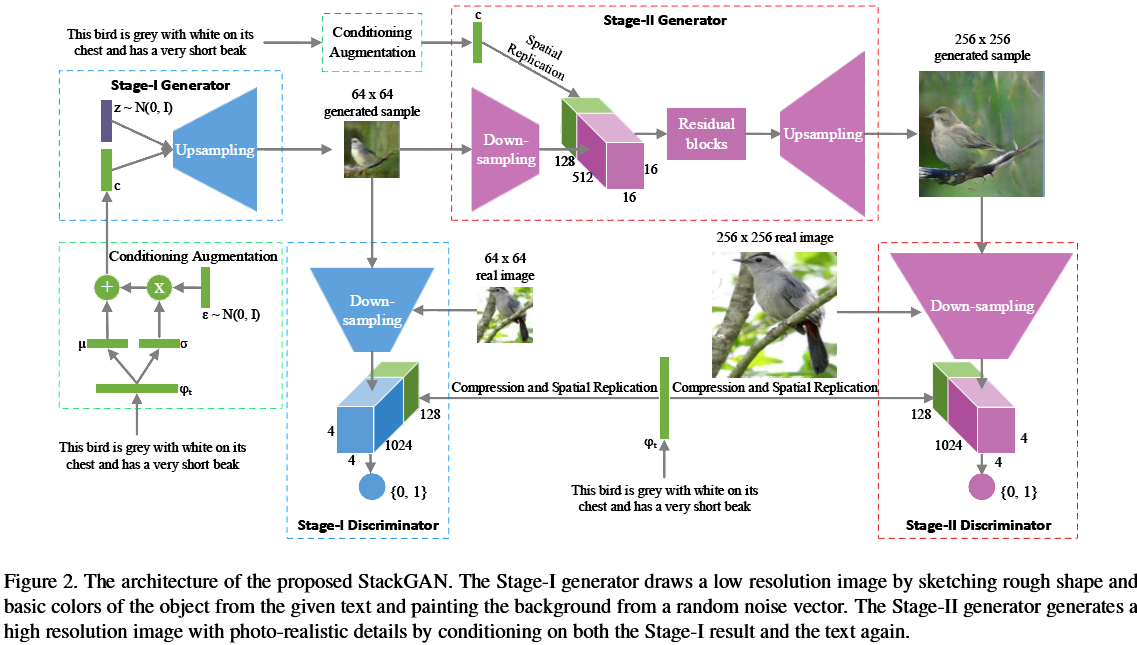
Stage-I GAN
对G来说,输入的文字描述被一个训练好的非线性转换器(nonlinearly transformed)Encoder $phi$转化为隐变量(text-embeding),通常来说,该隐变量的维度相当高,通常大于100维,在G学习时对连续性有影响。因此作者提出一种扩张机制(augmentation),来为G产生更多的条件变量。作者构建一个特殊的高斯分布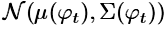 ,从中进行随机采样,The proposed formulation encourages robustness to small perturbations along the conditioning manifold, and
,从中进行随机采样,The proposed formulation encourages robustness to small perturbations along the conditioning manifold, and
thus yields more training pairs given a small number of image-text pairs。并且在训练过程中,作者使用KL距离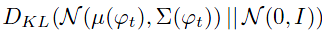
作为正则项来增强流型的平滑性同时避免overfitting。
损失函数:
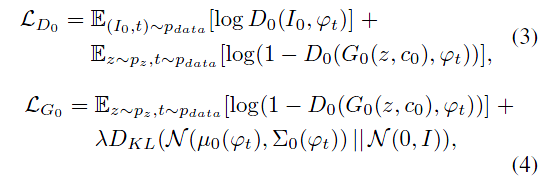
stage-II GAN:
把前一阶段生成的低分辨率图像和文字描述作为输入,模型致力于弥补上阶段丢失的细节信息
损失函数:
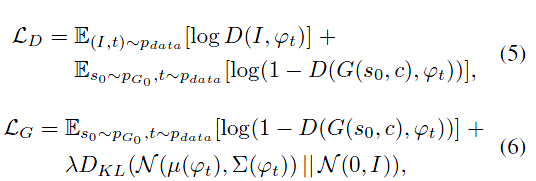
其中$S_0$是上阶段生成的低分辨率图,随机变量Z没有出现在这个一生成阶段中。两个阶段都共享了训练好的词向量encoder,但是后面接的连接层不同,产生的平均数和方差数不同,因此能比1阶段生成更详细的信息(这段转得很生硬,我也不懂为什么这样就能产生更丰富的信息)。
其他:
数据集:CUB and Oxford-102采用了【21】提供的标签,每张图片提供10个标注
评估指标:使用了【26】推荐的Inception score 来评价生成质量
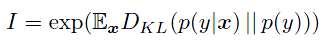
其中,x是生成的样本,y是label predicted by the Inception model【28】
不足之处:个人认为没有对多目标生成进行研究,这方面如果有所突破将会是篇好的paper。
pytoch 源码地址:https://github.com/hanzhanggit/StackGAN
后续论文:
StackGAN++: Realistic Image Synthesis with Stacked Generative Adversarial Networks
AttnGAN: Fine-Grained Text to Image Generation with Attentional Generative Adversarial Networks
[20] S. Reed, Z. Akata, S. Mohan, S. Tenka, B. Schiele, and
H. Lee. Learning what and where to draw. In NIPS, 2016. 1,
2, 3, 5, 6, 7
[21]S. Reed, Z. Akata, B. Schiele, and H. Lee. Learning deep
representations of fine-grained visual descriptions. In CVPR,
2016.
[22] S. Reed, Z. Akata, X. Yan, L. Logeswaran, B. Schiele, and
H. Lee. Generative adversarial text-to-image synthesis. In
ICML, 2016. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7
[26] T. Salimans, I. J. Goodfellow, W. Zaremba, V. Cheung,
A. Radford, and X. Chen. Improved techniques for training
gans. In NIPS, 2016. 2, 5
[28] C. Szegedy, V. Vanhoucke, S. Ioffe, J. Shlens, and Z. Wojna.
Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In
CVPR, 2016. 5