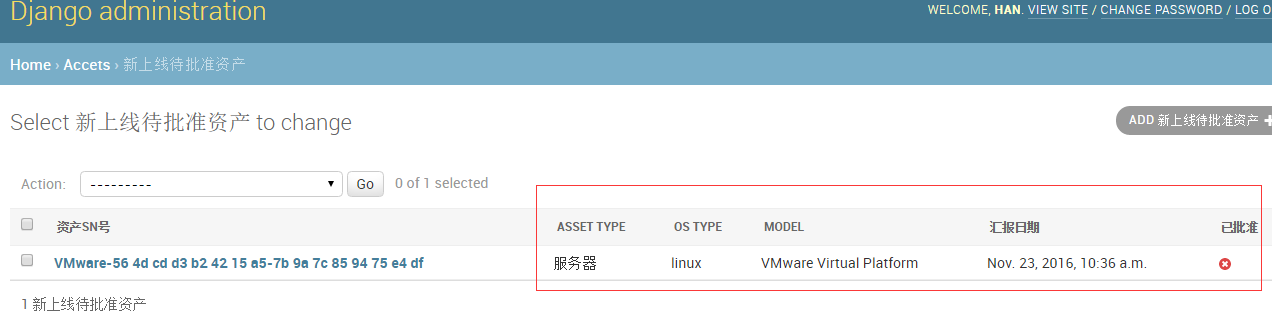
1、想在admin中增加新的字段如图:
默认django只显示 def __str__(self)里面的return的值
from django.contrib import admin # Register your models here. from accets import models class NewAssetApprovalZoneAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): #自定义一个类,必须继承 admin.ModelAdmin """增加列数据""" #list_display中的数据就是在models中设置的字段 list_display = ['sn', 'asset_type', 'os_type', 'model' ,"date", "approved"] admin.site.register(models.EventLog), admin.site.register(models.Manufactory), admin.site.register(models.Tag) admin.site.register(models.NewAssetApprovalZone,NewAssetApprovalZoneAdmin)

class NewAssetApprovalZone(models.Model): sn = models.CharField(u'资产SN号',max_length=128, unique=True) asset_type_choices = ( ('server', u'服务器'), ('switch', u'交换机'), ('router', u'路由器'), ('firewall', u'防火墙'), ('storage', u'存储设备'), ('NLB', u'NetScaler'), ('wireless', u'无线AP'), ('software', u'软件资产'), ('others', u'其它类'), ) asset_type = models.CharField(choices=asset_type_choices,max_length=64,blank=True,null=True) manufactory = models.CharField(max_length=64,blank=True,null=True) model = models.CharField(max_length=128,blank=True,null=True) ram_size = models.IntegerField(blank=True,null=True) cpu_model = models.CharField(max_length=128,blank=True,null=True) cpu_count = models.IntegerField(blank=True,null=True) cpu_core_count = models.IntegerField(blank=True,null=True) os_distribution = models.CharField(max_length=64,blank=True,null=True) os_type = models.CharField(max_length=64,blank=True,null=True) os_release = models.CharField(max_length=64,blank=True,null=True) data = models.TextField(u'资产数据') date = models.DateTimeField(u'汇报日期',auto_now_add=True) approved = models.BooleanField(u'已批准',default=False) approved_by = models.ForeignKey('UserProfile',verbose_name=u'批准人',blank=True,null=True) approved_date = models.DateTimeField(u'批准日期',blank=True,null=True) def __str__(self): return self.sn class Meta: verbose_name = '新上线待批准资产' verbose_name_plural = "新上线待批准资产"
2、增加过滤功能
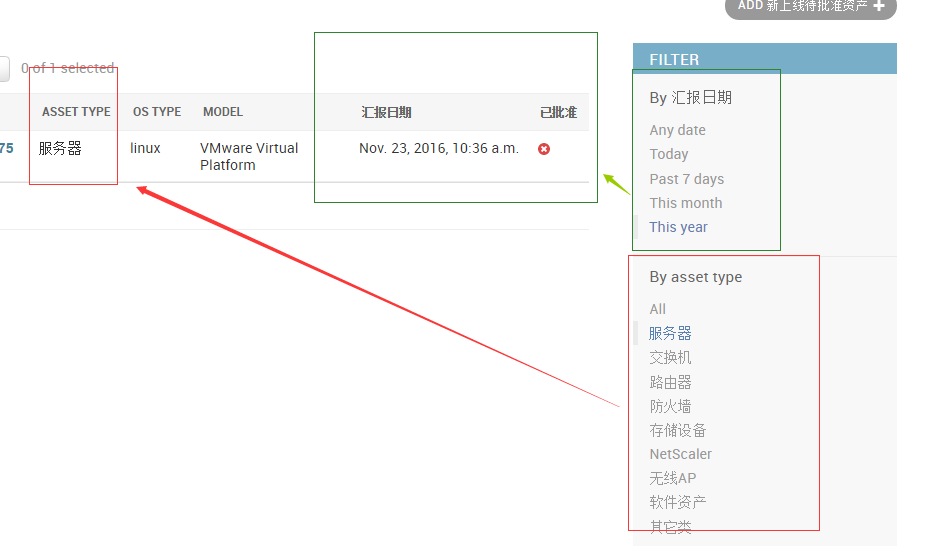
class NewAssetApprovalZoneAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): """增加列数据""" list_display = ['sn', 'asset_type', 'os_type', 'model' ,"date", "approved"] list_filter = ('date', 'asset_type' ) admin.site.register(models.Asset), admin.site.register(models.BusinessUnit), admin.site.register(models.IDC), admin.site.register(models.Server), admin.site.register(models.NetworkDevice), admin.site.register(models.NewAssetApprovalZone,NewAssetApprovalZoneAdmin)
3、只能在多对多的列中使用
 ======》
======》 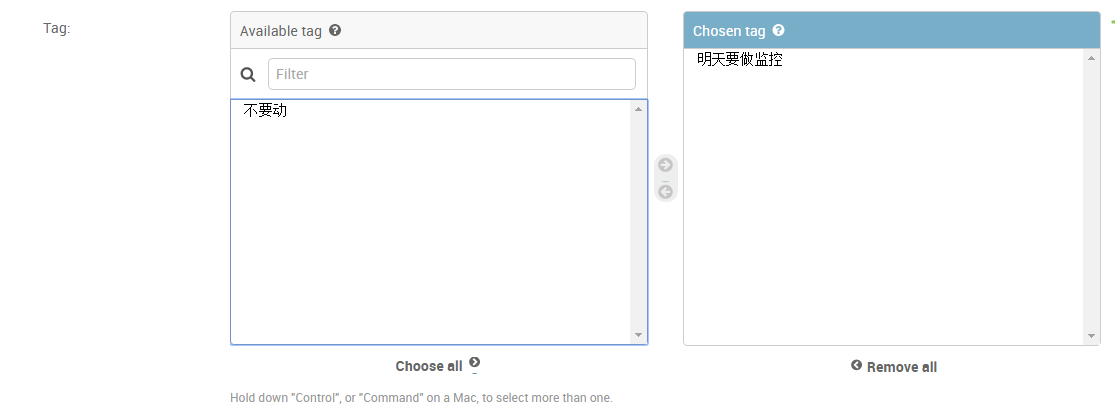
class AssetAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): list_display = ['name', 'sn', "asset_type", "create_date", "update_date" ] filter_horizontal =('tag',) admin.site.register(models.Asset,AssetAdmin), admin.site.register(models.BusinessUnit), admin.site.register(models.IDC), admin.site.register(models.Server), admin.site.register(models.NetworkDevice),
tag就是models 中 Asset的一个列
4、增加下拉框选项:
class NewAssetApprovalZoneAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin): """增加列数据""" list_display = ['sn', 'asset_type', 'os_type', 'model' ,"date", "approved"] list_filter = ('date', 'asset_type',) search_fields = ("sn", "os_type",) actions = ['apprpve_select_rows']
def apprpve_select_rows(self,*args,**kwargs):
print(args,kwargs)
#<WSGIRequest: POST '/admin/accets/newassetapprovalzone/'>, [<NewAssetApprovalZone: VMware-56 4d cd d3 b2 42 15 a5-7b 9a 7c 85 94 75 e4 df>
<WSGIRequest: POST '/admin/accets/newassetapprovalzone/'>, request对象
<NewAssetApprovalZone: VMware-56 4d cd d3 b2 42 15 a5-7b 9a 7c 85 94 75 e4 df> 在admin中选中的对象
5、自定义django用户认证
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class TestUser(AbstractBaseUser):
"""官网推荐的方法"""
user = models.OneToOneField(User)
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
#此时用户就集成了Django User的功能
这么做有一些问题
1、在admin中创建用户必须要先执行以下user这个用户,然后才能在下面创建一个用户
2、在调用的时候需要通过user字段才能调用出username的字段
调用: a = modules.UserProfile.objects.last() a.user.username
- django User深度自定义
官网文档 搜索:custom authentication
继承的User是什么鬼
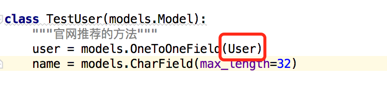
点进去瞅瞅
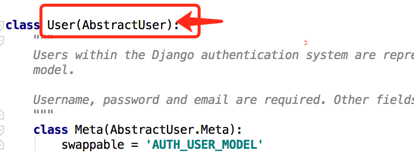
就能发现这个User就是继承的AbstractUser
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import (
BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser
)
1、我们就先导入这个 使用其中的的AbstractBaseUser
UserProfile
class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser): #自定义一个用户认证的类,继承 AbstractBaseUser,这里面会有密码字段,所以下面不用创建密码字段 """自定义用户表""" email = models.EmailField( #定义用户注册的类型为email 也可以定义为别的 verbose_name='email address', max_length=255, unique=True, ) # date_of_birth = models.DateField() name = models.CharField(max_length=64) #用户名 is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) #是不是活跃 is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) #是不是管理员 bind_hosts = models.ManyToManyField('BindHost', blank=True) host_groups = models.ManyToManyField('HostGroups', blank=True) objects = UserProfileManager() #关联UserProfileManager一个类 USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' #用户名字段 REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] # 必须要有这个字段 def get_full_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def get_short_name(self): # The user is identified by their email address return self.email def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2 return self.email def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None): "Does the user have a specific permission?" # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always return True def has_module_perms(self, app_label): "Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?" # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always return True @property def is_staff(self): "Is the user a member of staff?" # Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff return self.is_admin
2、UserProfileManager (创建用户使用的类)
class UserProfileManager(BaseUserManager): #创建用户使用的类 def create_user(self, email, name, password=None): """ Creates and saves a User with the given email, date of birth and password. """ if not email: #确认要有email raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') user = self.model( email=self.normalize_email(email), #判断邮件地址是否合法 # date_of_birth=date_of_birth, name=name ) user.set_password(password) #加密密码 user.save(using=self._db) return user def create_superuser(self, email, name, password): #通过命令行创建时会调用这里 """ Creates and saves a superuser with the given email, date of birth and password. """ user = self.create_user( email, password=password, name=name, ) user.is_admin = True #把用户类型admin 定义为True user.save(using=self._db) return user
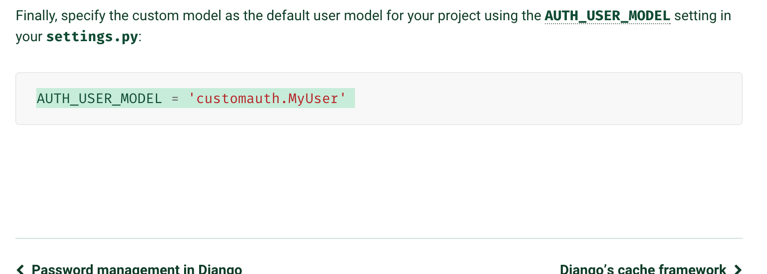
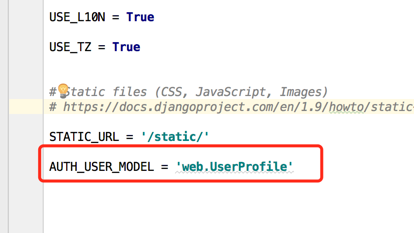
3、让Django用自己写的这个UserProfile的用户认证,需要在setting中增加一个字段
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'customauth.MyUser'
4、然后就执行
python3 manage.py makemigrations
如果之前执行创建过用户,就要把之前的User删除
成功以后,进入amdin中,看到用户的密码是密文的,但是自己添加是明文的,所以我们输入密码django就不能识别了。、
5、然后再写一个文件将django官网中的一段代码粘贴过来
名字随便起就可以
from django import forms from django.contrib import admin from django.contrib.auth.models import Group from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin as BaseUserAdmin from django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashField from web.models import UserProfile #导入自定义的用户表 class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm): #创建用户 """A form for creating new users. Includes all the required fields, plus a repeated password.""" password1 = forms.CharField(label='Password', widget=forms.PasswordInput) #输入两次密码 password2 = forms.CharField(label='Password confirmation', widget=forms.PasswordInput) class Meta: model = UserProfile #这里指定之前自定义的UserProfile fields = ('email', 'name','is_admin','bind_hosts', 'host_groups', ) #创建用户的时候需要输入的内容 - 1 def clean_password2(self): # Check that the two password entries match password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1") password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2") if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2: raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don't match") return password2 def save(self, commit=True): # Save the provided password in hashed format user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False) user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"]) if commit: user.save() return user class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm): #修改用户记录的时候显示的东西 """A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on the user, but replaces the password field with admin's password hash display field. """ password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField() class Meta: model = UserProfile fields = ('email', 'password', 'name', 'is_active', 'is_admin') def clean_password(self): # Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value. # This is done here, rather than on the field, because the # field does not have access to the initial value return self.initial["password"] class UserAdmin(BaseUserAdmin): # The forms to add and change user instances form = UserChangeForm add_form = UserCreationForm # The fields to be used in displaying the User model. # These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin # that reference specific fields on auth.User. list_display = ('email', 'name', 'is_admin') #显示字段 list_filter = ('is_admin','name') #过滤字段 fieldsets = ( (None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}), ('Personal info', {'fields': ('name',)}), ('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_admin', 'bind_hosts', 'host_groups',)}), #点击修改用户时候显示的字段 ) # add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin # overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user. add_fieldsets = ( (None, { 'classes': ('wide',), 'fields': ('email', 'name', 'password1', 'password2','bind_hosts', 'host_groups')} #创建新用户是需要填写那些字段内容 - 2 ), ) search_fields = ('email',) ordering = ('email',) filter_horizontal = ('bind_hosts','host_groups') #可以拖拽的格式 # Now register the new UserAdmin... admin.site.register(UserProfile, UserAdmin) # ... and, since we're not using Django's built-in permissions, # unregister the Group model from admin. admin.site.unregister(Group)
6、在admin.py中注册custom_user_admin
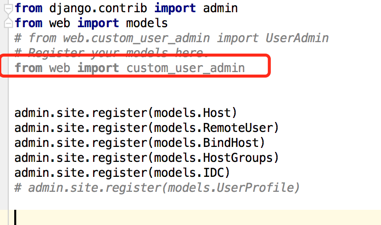
7、然后将django这个用户认证可以用到我们的自己的业务中
a、在最后粘贴的新文件中导入UserProfile用户类
b、 UserCreationForm 类中
fields = ('email', 'name','is_admin','bind_hosts', 'host_groups', ) #创建用户的时候需要输入的内容 - 1
c、UserAdmin 类中
fieldsets = (
(None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}),
('Personal info', {'fields': ('name',)}),
('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_admin', 'bind_hosts', 'host_groups',)}), #点击修改用户时候显示的字段
add_fieldsets = (
(None, {
'classes': ('wide',),
'fields': ('email', 'name', 'password1', 'password2','bind_hosts', 'host_groups')} #创建新用户是需要填写那些字段内容 - 2
),
)