注意一下 range 的用法。查一下 range 函数并理解它
在第 22 行(我的答案),你可以直接将 elements 赋值为 range(0, 6) ,而无需使用 for 循环?
在 python 文档中找到关于列表的内容,仔细阅读一下,除了 append 以外列表还支持哪些操作?
我的答案
32.0 基础练习
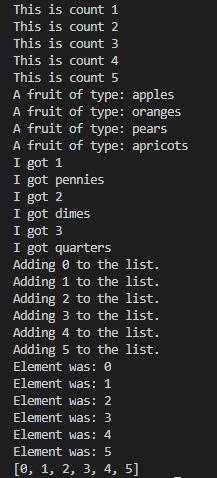
1 the_count = [1,2,3,4,5] 2 fruits = ['apples', 'oranges', 'pears', 'apricots'] 3 change = [1, 'pennies', 2, 'dimes', 3, 'quarters'] 4 5 # this first kind of for-loop goes through a list 6 7 for number in the_count: 8 print(f"This is count {number}") 9 10 # same as above 11 12 for fruit in fruits: 13 print(f"A fruit of type: {fruit}") 14 15 # also we can go through mixed lists too 16 # notice we have to use {} since we don't know what's in it 17 18 for i in change: 19 print(f"I got {i}") 20 21 # we can also build lists, first start with an empty one 22 elements = [] 23 24 #then use the range function to do 0 to 5 counts 25 26 for i in range(0,6): 27 print(f"Adding {i} to the list.") 28 # append is a function that lists understand 29 elements.append(i) 30 31 # now we can print them out too 32 for i in elements: 33 print(f"Element was: {i}") 34 35 #自己加的,看elements结果 36 print(elements)
32.1 range 的用法
最简单的变法就是查看帮助文档了,还记得我们用过的两种方法么?
( ↓↓↓↓ 刮开查看 ↓↓↓↓ )

Python3 range() 函数返回的是一个可迭代对象(类型是对象),而不是列表类型, 所以打印的时候不会打印列表。
Python3 list() 函数是对象迭代器,可以把range()返回的可迭代对象转为一个列表,返回的变量类型为列表。
range(stop) range(start, stop[, step])
创建 range 函数的实例 range 函数会返回一个数字序列。它最多接受 3 个参数
- start:启始值(被包含),默认是 0
- stop:结束值(不包含),必填
- step:步长,默认是1,不可为0,例如:range(0, 5) 等价于 range(0, 5, 1)
1 >>>range(5) 2 range(0, 5) 3 >>> for i in range(5): 4 ... print(i) 5 ... 6 0 7 1 8 2 9 3 10 4 11 >>> list(range(5)) 12 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] 13 >>> list(range(0)) 14 [] 15 >>>
有两个参数或三个参数的情况(第二种构造方法)::
1 >>>list(range(0, 30, 5)) 2 [0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25] 3 >>> list(range(0, 10, 2)) 4 [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] 5 >>> list(range(0, -10, -1)) 6 [0, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, -6, -7, -8, -9] 7 >>> list(range(1, 0)) 8 [] 9 >>> 10 >>>
32.2 不使用 for-loop ,直接为 elements 赋值为 range(6)
1 the_count = [1,2,3,4,5] 2 fruits = ['apples', 'oranges', 'pears', 'apricots'] 3 change = [1, 'pennies', 2, 'dimes', 3, 'quarters'] 4 5 # this first kind of for-loop goes through a list 6 7 for number in the_count: 8 print(f"This is count {number}") 9 10 # same as above 11 12 for fruit in fruits: 13 print(f"A fruit of type: {fruit}") 14 15 # also we can go through mixed lists too 16 # notice we have to use {} since we don't know what's in it 17 18 for i in change: 19 print(f"I got {i}") 20 21 # we can also build lists, first start with an empty one 22 elements = [] 23 24 #then use the range function to do 0 to 5 counts 25 26 elements = list(range(0,6)) 27 28 # now we can print them out too 29 for i in elements: 30 print(f"Element was: {i}") 31 32 #自己加的,看elements结果 33 print(elements)
需要为range(0,6)加上list才是需要的elements列表