什么是css?

通配符选择器
<head> /* *通配符选择器 匹配任何元素 */ *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } </head>
css样式有三种
一种是内嵌,写在head的style里面
<style> div{ /*内嵌的css*/ width: 200px; height: 200px; background: blue; } </style>
一种是外链,写在单独的.css文件里面
通过link标签(link + tab)填写路径的.css文件名即可
<head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" href=""> <title>css</title> </head>
一种是标签,直接写在标签里面
<body> <div style=" 200px;height: 200px;background: lawngreen"></div> </body>
优先级:标签样式>内嵌样式 >外链样式
因为存在三种方法,所以在开发中总会产生耦合,所以存在一个选择器的概念
优先级:id选择器>class选择器>标签选择器
选择器
用于准确的选中元素,赋予样式
选择器权重
谁的权重大,就听谁的,谁的权重大,就用谁的样式
1 class选择器
通过标签的class属性,选择对应的元素,借助类的概念,一处定义,多处使用
2 id选择器
通过标签的id属性,选择对应元素。注:id选择器唯一
3 群组选择器
可以同时选择多个标签的选择器
4 层次选择器
分为兄弟,子代,相邻,后代,四种选择器
class选择器(.class名)借助类的概念,一处定义,多处使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>css</title> <style> .wrap{ background: aqua; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="wrap">3</div> <div class="wrap">4</div> </body> </html>
id选择器(.id名)id选择器唯一
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>css</title> <style> #box{ background: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box">2</div> </body> </html>
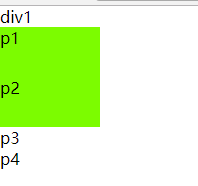
群组选择器(群组选择器 对几个有相同属性的选择器进行样式设置 两个选择器之间必须用逗号隔开)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } /*群组选择器,逗号分隔,都拥有样式属性*/ div,p{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background: lawngreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div>div1</div> <p>p1</p> <p>p2</p> <div> <p>p3</p> <p>p4</p> </div> </body> </html>
层次选择器
兄弟选择器(~)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } /*兄弟选择器 操作的对象是该元素下(下方)的所有兄弟元素*/ div~p{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background: lawngreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div>div1</div> <p>p1</p> <p>p2</p> <div> <p>p3</p> <p>p4</p> </div> </body> </html>
子代选择区(>)只会选儿子,不会选孙子
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } /*子代选择器 选择某个元素下面的子元素*/ div>p{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background: lawngreen; } </style> </head> <body> <div>div1</div> <p>p1</p> <p>p2</p> <div> <p>p3</p> <p>p4</p> </div> </body> </html>
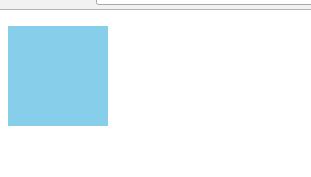
相邻选择器:(+)同级元素相邻!隔开就不行
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>选择器</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } /*相邻选择器操作的对象是该元素的同级元素选择div相邻的下一个兄弟元素 选择到紧随目标元素后的第一个元素挨着的兄弟元素 */ div+p{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background: skyblue; } </style> </head> <body> <div>div1</div> <p>p1</p> <p>p2</p> <div> <p>p3</p> <p>p4</p> </div> </body> </html>
后代选择器
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> li{ list-style: none; } /*后代选择器 之后要是后代*/ div li{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background: aqua; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <ul> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> </ul> <ol> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> </ol> </div> <ul> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> </ul> </body> </html>
复杂后代选择器 优先级的比较
1.先比id(最高位) class(中间位) tagName(个数位)
1 2 3
2.id选择器个数不相等,id越多,优先级越高
3.id选择器个数相同,则看class,class多的优先级高
4.class个数相等,就看tagName个数
伪类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>伪类选择器</title> <style> <!--顺序不能乱--> /*LoVeHAte*/ a:link{/*link 未被点击的链接*/ color: red; } a:visited{/*已被点击的链接*/ color: green; } a:hover{/*鼠标悬停其上的元素 这个一定要掌握*/ color: yellow; } a:active{/*鼠标已经再其上按下但是还没有释放的元素*/ color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="http://www.baidu.com">baidu</a> </body> </html>
重点了解hover:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background: skyblue; } div:hover{ /*div:hover 改变的是div本身*/ background: red; width: 300px; height: 200px; cursor: pointer;/*手指*/ /*cursor: default; 箭头*/ /*cursor: wait; 等待*/ /*cursor: help;*/ } div:hover p{/*div:hover p 当div被鼠标划入的时候 改变后代p*/ width: 50px; height: 30px; background: aqua; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <p></p> </div> </body> </html>

css文字属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /*设置网页字体*/ /*html{*/ /*font-size: 20px;*/ /*}*/ /*font-family 字体类型浏览器默认的字体是微软雅黑,字体中有多个字体的时候,如果前面的字体没有就使用后面的字体*/ .box1{ font-family: Arial,Algerian; } /* font-size 字体大小 单位 px rem % em px 谷歌浏览器默认字体大小16px,最小是12px rem 相对于html(根标签)的字体大小 em 等于父级的字体尺寸——相对于父级字体大小而言的 % 相对于父容器中字体的%调整 这个要知道 */ .box2{ font-size: 32px; } .box3{ font-size: 12px; } .box4{ font-size: 2rem; } .box5{ font-size: 2em; } /* font-weight 字体粗细 关键字 normal 默认字体 lighter 较细 bold 加粗 这个要知道 bolder 很粗 给值 只能100-900的整百数 400相当于正常的 700相当于bold */ .box6{ font-weight: lighter; } .box7{ font-weight: 700; } /* font-style 字体类型 normal 默认 文字正常 italic 文字斜体(属性) oblique 文字斜体 */ .box8{ font-style: italic; } /* color 文字颜色 关键字 英文单词 red green 16进制(0-9 a-f) #5544aa #54a #abd456 #dddddd #ddd rgb(0-255,0-255,0-255) r red g green b blue rgba(0-255,0-255,0-255,0-1) r red g green b blue a alpha(透明度) 0 完全透明 1 完全不透明 */ .box9{ /*color: red;*/ color: rgb(255,25,10); } .box10{ /*color: #29aa60;*/ color: rgba(255,25,10,0.5); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box2"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box3"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box4"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box5"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box6"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box7"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box8"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box9"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div class="box10"> hello word 123 你好</div> <div style="font-size: 20px"> 1<div style="font-size: 2em">2</div> </div> </body> </html>
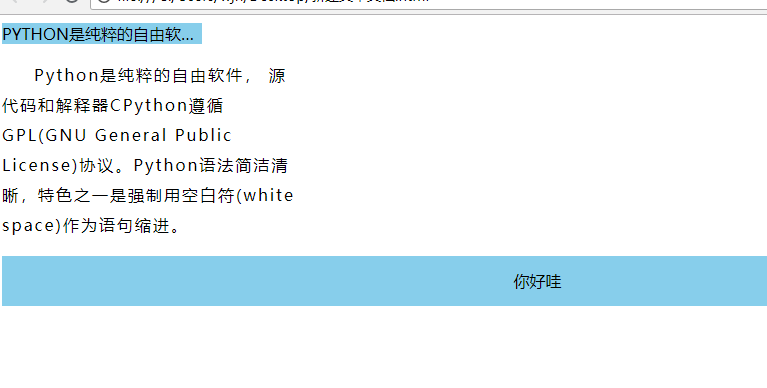
css文本属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> /* white-space: 换行方式 normal 正常换行 nowrap 不换行 */ div{ width: 200px; background: skyblue; white-space: nowrap; /*超出隐藏*/ overflow: hidden; /*省略号*/ text-overflow: ellipsis; } /* text-indent 首行缩进(em) line-height 行高 ***** letter-spacing 字距 word-spacing 词距 */ .box{ width: 300px; text-indent: 2em; line-height: 30px; letter-spacing: 2px; } /* div中的文字垂直居中:line-height:值。值等于div的高度。 line-height: 80px; text-align 文本水平对齐方式 left 默认值 向左对其 right center ***** */ .box1{ text-align: center; } /* text-transform 文本大小写 none 默认值 无转换发生 uppercase 转换成大写 lowercase 转换成小写 capitalize 将英文单词的首字母大写 */ div{ text-transform: uppercase; } </style> </head> <body> <div> Python是纯粹的自由软件, 源代码和解释器CPython遵循 GPL(GNU General Public License)协议。Python语法简洁清晰,特色之一是强制用空白符(white space)作为语句缩进。 </div> <p class="box"> Python是纯粹的自由软件, 源代码和解释器CPython遵循 GPL(GNU General Public License)协议。Python语法简洁清晰,特色之一是强制用空白符(white space)作为语句缩进。 </p> <p class="box1" style="background: skyblue;height: 50px;line-height: 50px;"> 你好哇 </p> </body> </html>
css背景
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> div{ width: 600px; height: 400px; /*background-color: skyblue;*/ /*background-image: url("img/0.jpg");*/ /*background-repeat: no-repeat;*/ /*background-repeat: repeat-x;*/ /*background-repeat: repeat-y;*/ /*background-size: contain;*/ /*background-position: 90px;*/ background: skyblue url("img/0.jpg") no-repeat center center/300px 300px; /*background: color image repeat position/size*/ } /* background-color 背景色 background-image 背景图片 background-repeat 背景平铺 repeat 平铺 默认 repeat-x 平铺x repeat-y 平铺y np-repeat 不平铺 注意:只有背景图片的宽高小于被设置的元素的宽高,才会有平铺效果 background-position 背景位置 x轴 y轴 x轴 left center right y轴 top center bottom 如果只给一个值,默认在x轴,y轴默认center(50%) % px background-size 背景大小 % px 给一个值的时候,默认x轴,y轴默认auto auto会等比缩放 cover 等比例缩放直到铺满x,y轴 可以铺满整个框 但是不一定能看到完整的图片 contain 等比例缩放x轴或者y轴其中的一个方向 不一定铺满 但是可以看到整个图片 */ </style> </head> <body> <div></div> </body> </html>