一.
1.
public class EnumTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Size s=Size.SMALL;
Size t=Size.LARGE;
//s和t引用同一个对象?
System.out.println(s==t); //
//是原始数据类型吗?
System.out.println(s.getClass().isPrimitive());
//从字符串中转换
Size u=Size.valueOf("SMALL");
System.out.println(s==u); //true
//列出它的所有值
for(Size value:Size.values()){
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
enum Size{SMALL,MEDIUM,LARGE};
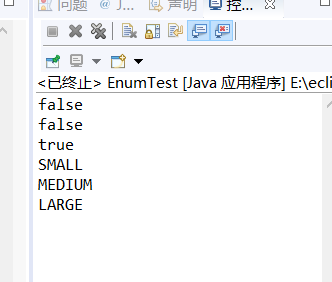
//定义枚举Size这里面包括SMALL,MEDIUM,LARRGE,这里的s为SMALL,t为LARRGE,s==t是判断t和s是否相等不相等为false,
//第二个输出他是为原始的数据类型,false 原始的数据类型有:byte、short、int、long、boolean、char、float、double。
//第三个一个普通的字符串转换成一个枚举对象,u赋值为SMALL
//values()实现将枚举类型成员以数组的形式返回,按顺序输出。
//枚举类型属于引用类型,每个具体的值都引用特定的对象 基本会了
2.
原码:是最简单的机器数表示法。用最高位表示符号位,‘1’表示负号,‘0’表示正号。其他位存放该数的二进制的绝对值。
反码:正数的反码还是等于原码,负数的反码就是他的原码除符号位外,按位取反。
补码:正数的补码等于他的原码,负数的补码等于反码+1。
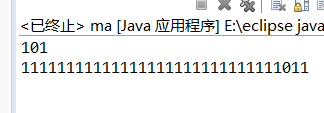
public class ma {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int i = 5;
int j = -5;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(j));
}
}
3.同名变量的屏蔽原则
在java中是不允许在同一个函数中声明同名变量的,但是可以在类中声明类的全局变量,然后在函数中声明同名的函数的局部变量;每个变量都有一个有效区域,即定义的那片区域,出了这个区域,变量将不再有效。
public class Test {
private static int Albert = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int Albert = 2;
System.out.println(Albert);
}
}
输出的结果有是2;
4.数据类型
java中有8种基本数据类型:byte、int、short、long、boolean、char、float、double
char: 2字节
复杂到简单会有数据损失
5


double计算不精确,和二进制和十进制的转化有关
6.
public class TestBigDecimal
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int X=100;
int Y=200;
System.out.println("X+Y="+X+Y);
System.out.println(X+Y+"=X+Y");
}
}

双引号里的内容会以字符串的形式出现
字符串转化为浮点型
int number = Integer.parseInt(numberString );
字符串连接
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "The sum is " + sum, "Results",JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE );
二.取反码
三.链表实现