继承条件下构造方法的调用
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c = new Child();
}
}

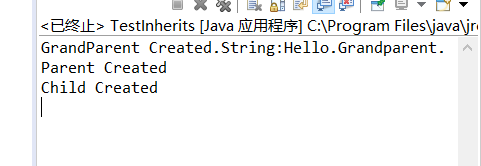
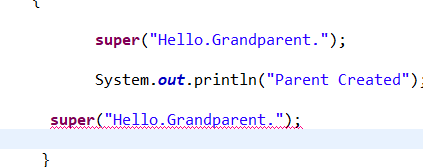
通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
子类拥有父的成员变量和成员方法,如果不调用,则从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法得不到正确的初始化。不能反过来调用也是这个原因,因为父类根本不知道子类有什么变量而且这样一来子类也得不到初始化的父类变量,导致程序运行出错!
class A{}
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new A());
}
}

示例中,main方法实际上调用的是:
public void println(Object x),这一方法内部调用了String类的valueOf方法。
valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() +"@" +
Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:
public native int hashCode();
神奇的加号
public class Fruit
{
public String toString()
{
return "Fruit toString.";
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Fruit f=new Fruit();
System.out.println("f="+f);
// System.out.println("f="+f.toString());
}
}

在“+”运算中,当任何一个对象与一个String对象,连接时,会隐式地调用其toString()方法,默认情况下,此方法返回“类名 @ + hashCode”。为了返回有意义的信息,子类可以重写toString()方法。
方法覆盖要求子类与父类的方法一模一样,否则就是方法重载(overload)!
class Mammal{
public void display() {
System.out.println("mamall");
}
}
class De extends Mammal{
public void display() {
super.display();
System.out.println("de");
}
}
class Cd extends Mammal{
public void display() {
System.out.println("cd");
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mammal a=new Mammal();
a.display();
De d=new De();
d.display();
Cd c=new Cd();
c.display();
}
}

(1)覆盖方法的允许访问范围不能小于原方法。
(2)覆盖方法所抛出的异常不能比原方法更多。
(3)声明为final方法不允许覆盖。
例如,Object的getClass()方法不能覆盖。
(4)不能覆盖静态方法。
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}

public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
System.out.println(parent.myValue);
System.out.println(child.myValue);
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
System.out.println(parent.myValue);
System.out.println(child.myValue);
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
System.out.println(parent.myValue);
System.out.println(child.myValue);
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
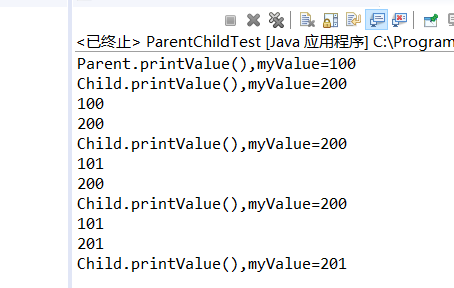
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
这个特性实际上就是面向对象“多态”特性的具体表现。
如果子类与父类有相同的字段,则子类中的字段会代替或隐藏父类的字段,子类方法中访问的是子类中的字段(而不是父类中的字段)。如果子类方法确实想访问父类中被隐藏的同名字段,可以用super关键字来访问它。
如果子类被当作父类使用,则通过子类访问的字段是父类的!