import os
def get_testinfo(conf,index,dir):
import xlrd
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(dir+conf[index]['info_path'])
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name(conf[index]['sheetname'])
testinfo = []
for i in range(conf[0]['start_row'],conf[index]['end_row']):
testdata = worksheet.cell(i,conf[index]['testdata_col']).value
expect = worksheet.cell(i,conf[index]['expect_col']).value
tmp = testdata.split(' ')
tup = {}
for j in tmp:
tup[j.split('=')[0]] = j.split('=')[1]
tup['expect'] = expect
testinfo.append(tup)
return testinfo
def get_json(path):
import json
try:
with open(path,encoding='utf-8') as f:
contents = json.load(f)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
finally:
f.close()
return contents
root_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
path = root_dir+'\demo1130\testdata.json'
data = get_json(path)
i=0
print(get_testinfo(data,i,root_dir))
运行结果: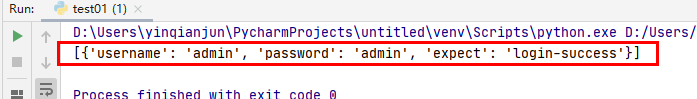
方法解释:在UI自动化中,采用分层思想,将每个模块需要调用的参数写在json中。如login:

具体用例写在excel中:
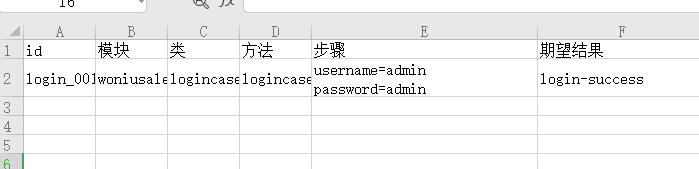
先通过get_json函数读取参数,然后将参数传入get_testinfo函数,读取对应的用例数据,最后可将用例数据传到具体模块的操作函数中。