DOM4J 是一个 Java 的 XMLAPI,是 JDOM 的升级品,用来 读写 XML 文件的
一、DOM4J 解析 XML 的步骤
1) 创建 SAXReader 对象
2) 调用 read 方法
3) 获取根元素
4) 通过迭代器遍历直接节点
二、 四种解析 XML 的特点
1)DOM 解析:
形成了树结构,有助于更好的理解、掌握,且代码容易编写。
解析过程中,树结构保存在内存中,方便修改。
2)SAX 解析:
采用事件驱动模式,对内存耗费比较小。 适用于只处理 XML 文件中的数据时
3)JDOM 解析:
仅使用具体类,而不使用接口。 API 大量使用了 Collections 类。
4)DOM4J 解析: JDOM 的一种智能分支,它合并了许多超出基本 XML 文档表
示的功能。
它使用接口和抽象基本类方法。
具有性能优异、灵活性好、功能强大和极端易用的特点。
是一个开放源码的文件
public class Book { //私有属性 private String name; private String author; private double price; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public Book(String name, String author, double price) { super(); this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; } public Book() { super(); } }
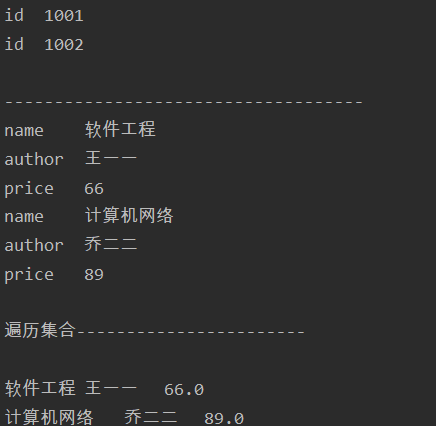
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <books> 3 <book id="1001"> 4 <name>软件工程</name> 5 <author>王一一</author> 6 <price>66</price> 7 </book> 8 <book id="1002"> 9 <name>计算机网络</name> 10 <author>乔二二</author> 11 <price>89</price> 12 </book> 13 </books>
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 import org.dom4j.Attribute; 7 import org.dom4j.Document; 8 import org.dom4j.DocumentException; 9 import org.dom4j.Element; 10 import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader; 11 12 import com.bjsxt.entity.Book; 13 14 public class TestDOM4J { 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws DocumentException { 16 // 1) 创建SAXReader对象 17 SAXReader reader=new SAXReader(); 18 // 2) 调用read方法 19 Document doc=reader.read(new File("book.xml")); 20 // 3) 获取根元素 21 Element root=doc.getRootElement();//books 22 // 4) 通过迭代器遍历直接节点 23 for(Iterator<Element> iteBook=root.elementIterator();iteBook.hasNext();){ 24 Element bookEle=iteBook.next(); 25 //System.out.println(bookEle.getName()); 26 //得到book的属性 27 for(Iterator<Attribute> iteAtt=bookEle.attributeIterator();iteAtt.hasNext();){ 28 Attribute att=iteAtt.next(); 29 System.out.println(att.getName()+" "+att.getText()); 30 } 31 } 32 33 System.out.println(" ------------------------------------"); 34 List<Book> bookList=new ArrayList<Book>(); 35 for(Iterator<Element> iteBook=root.elementIterator();iteBook.hasNext();){ 36 //创建Book对象 37 Book book=new Book(); 38 Element bookEle=iteBook.next();//得到每一个book 39 //使用for循环继续遍历 40 for(Iterator<Element> subBookEle=bookEle.elementIterator();subBookEle.hasNext();){ 41 //得到每一个子元素 42 Element subEle=subBookEle.next(); 43 System.out.println(subEle.getName()+" "+subEle.getText()); 44 /** 45 * 封装成Book对象 46 * */ 47 //获取节点的名称 48 String nodeName=subEle.getName();//name,author,price 49 //使用switch判断 50 switch (nodeName) { 51 case "name": 52 book.setName(subEle.getText()); 53 break; 54 case "author": 55 book.setAuthor(subEle.getText()); 56 break; 57 case "price": 58 book.setPrice(Double.parseDouble(subEle.getText())); 59 break; 60 } 61 62 } 63 //添加到集合中 64 bookList.add(book); 65 } 66 67 //遍历集合 68 System.out.println(" 遍历集合----------------------- "); 69 for (Book b : bookList) { 70 System.out.println(b.getName()+" "+b.getAuthor()+" "+b.getPrice()); 71 } 72 } 73 }