官方API地址:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/modules.html
前面几节课写的user.js就称为一个module,这样做的原因是:由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。每个模块又是独立的store,拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
下面以在根store对象动态注册模块为例来对module做演示:
store.vue代码:
<template>
<div>
<a-input :value="inputValue" @input="handlerInput"></a-input>
<p>{{ inputValue }} -> lastLetter is {{ inputValueLastLetter }}</p>
<p>appName: {{ appName }}, appNameWithVersion : {{ appNameWithVersion }}</p>
<p>userName : {{ userName }}, firstLetter is : {{ firstLetter }}</p>
<button @click="handleChangeAppName">修改appName和user.js中的userName</button>
<p>动态给state增加appVersion: {{ appVersion }}</p>
<button @click="handleActionChangeAppName">通过Action修改appName</button>
<button @click="registerModule">动态注册模块</button>
<p v-for="(li, index) in todoList" :key="index">{{ li }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import AInput from "_c/AInput.vue";
import AShow from "_c/AShow.vue";
//变量的解构赋值
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
import { stat } from "fs";
export default {
name: "store",
data() {
return {
inputValue: ""
};
},
components: {
AInput: AInput,
AShow: AShow
},
computed: {
//ES6展开操作符 mapState展开会形成一个对象 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
appName: state => state.appName,
appVersion: state => state.appVersion,
userName: state => state.user.userName,
todoList: state => (state.todo ? state.todo.todoList : [])
}),
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
// ...mapGetters(["appNameWithVersion"]),
appNameWithVersion() {
//通过属性访问getters,Getter 会暴露为 store.getters 对象,可以以属性的形式访问这些值:
return this.$store.getters.appNameWithVersion;
},
...mapGetters(["firstLetter"]),
inputValueLastLetter() {
return this.inputValue.substr(-1, 1);
}
},
methods: {
handlerInput(val) {
this.inputValue = val;
},
//
...mapMutations([
"SET_USER_NAME", //将 `this.SET_USER_NAME()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('SET_USER_NAME')`
"SET_APP_NAME" //将 `this.SET_APP_NAME()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('SET_APP_NAME')`
]),
...mapActions([
"updateAppName" //将 `this.updateAppName()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('updateAppName')`
]),
handleChangeAppName() {
this.SET_APP_NAME({
appName: "newAppName"
});
this.SET_USER_NAME({
userName: "shuyujie"
});
this.$store.commit("SET_APP_VERSION");
},
handleActionChangeAppName() {
//第一种调用Action的方法
//this.$store.dispatch('updateAppName')
//第二种调用Action的方法
this.updateAppName();
},
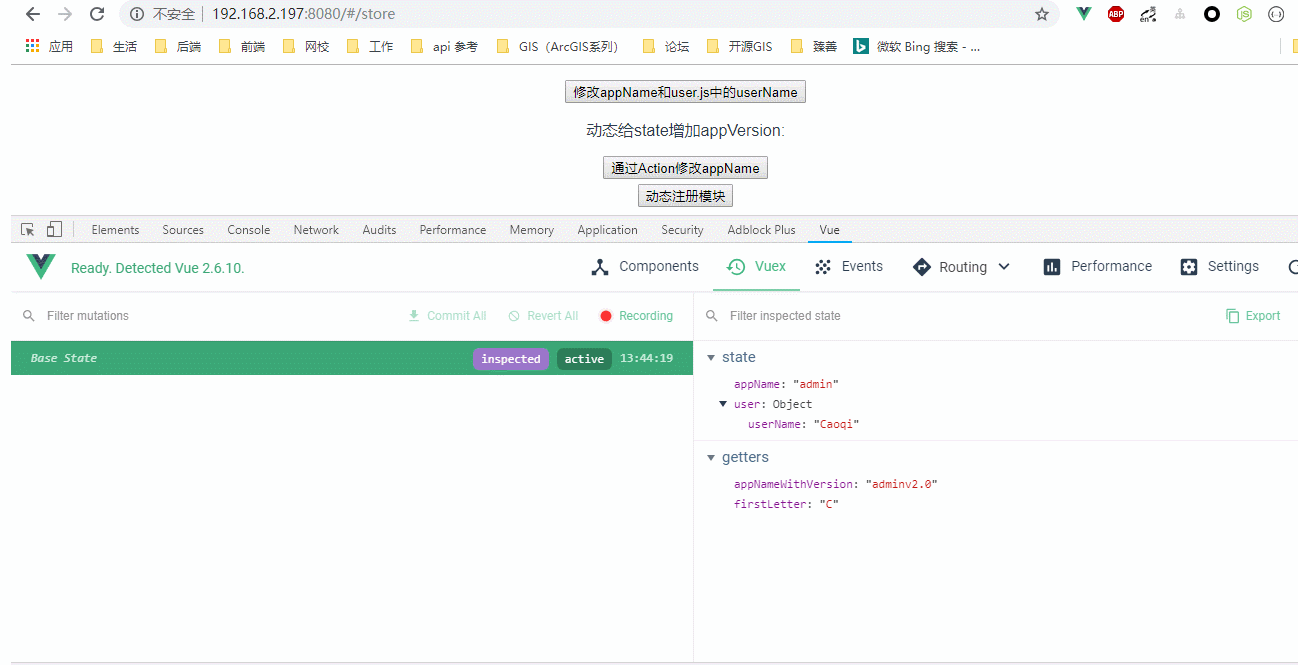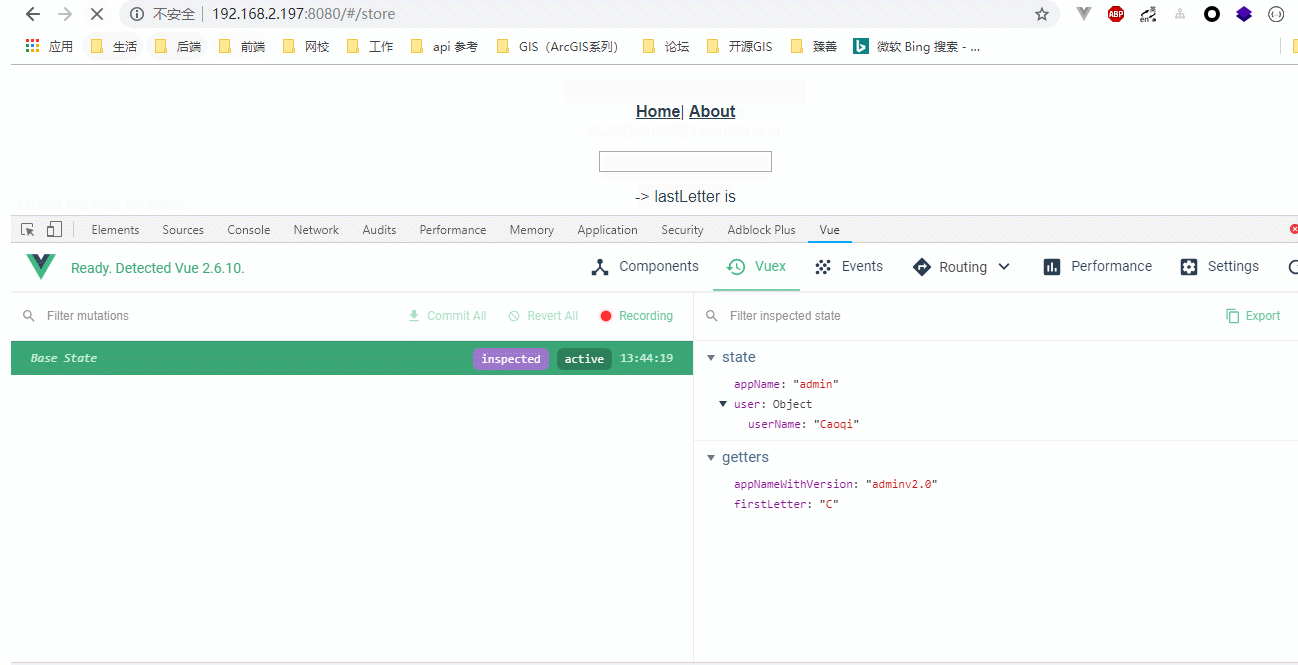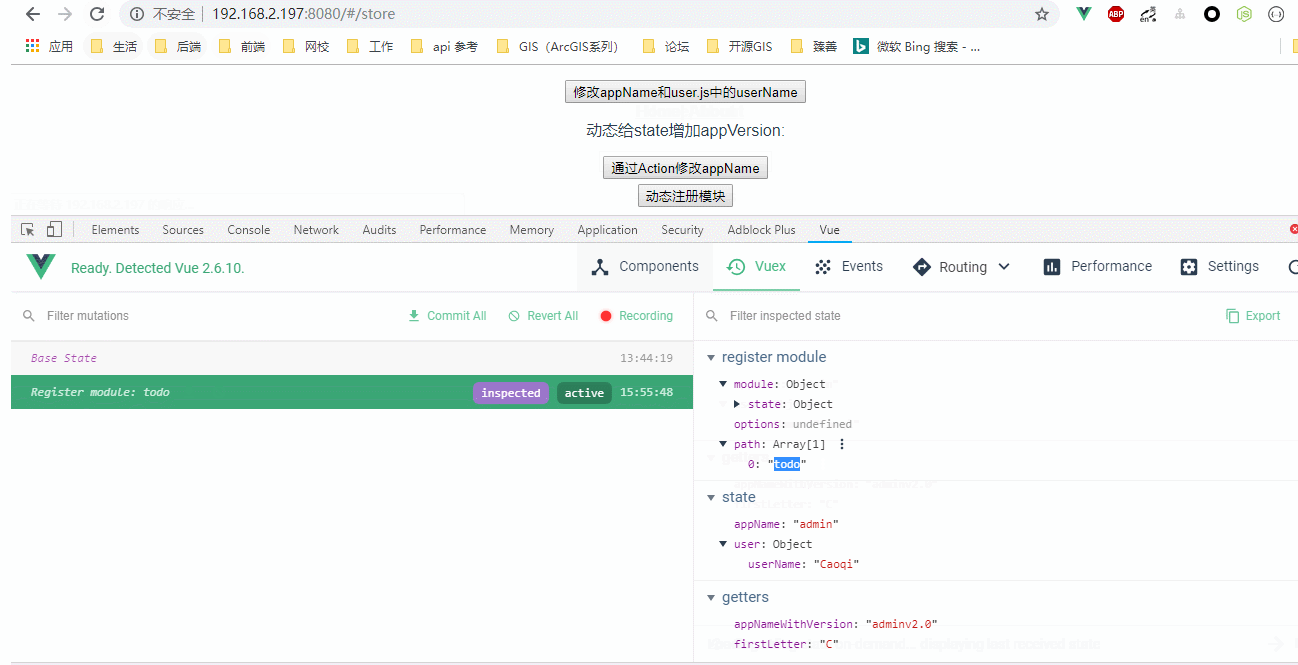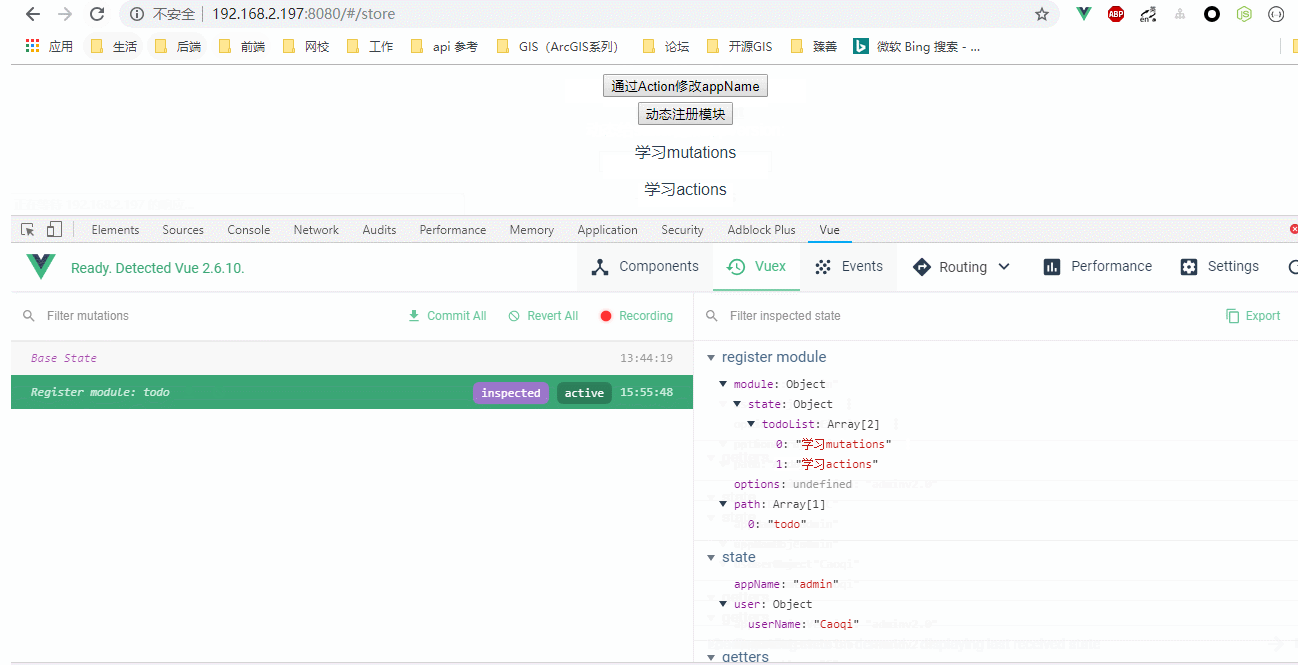
registerModule() {
this.$store.registerModule( "todo", {
state: {
todoList: ["学习mutations", "学习actions"]
}
});
}
}
};
</script>
效果图:
若给user动态一个模块,则store.vue组件代码:
<template>
<div>
<a-input :value="inputValue" @input="handlerInput"></a-input>
<p>{{ inputValue }} -> lastLetter is {{ inputValueLastLetter }}</p>
<p>appName: {{ appName }}, appNameWithVersion : {{ appNameWithVersion }}</p>
<p>userName : {{ userName }}, firstLetter is : {{ firstLetter }}</p>
<button @click="handleChangeAppName">修改appName和user.js中的userName</button>
<p>动态给state增加appVersion: {{ appVersion }}</p>
<button @click="handleActionChangeAppName">通过Action修改appName</button>
<button @click="registerModule">动态注册模块</button>
<p v-for="(li, index) in todoList" :key="index">{{ li }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import AInput from "_c/AInput.vue";
import AShow from "_c/AShow.vue";
//变量的解构赋值
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
import { stat } from "fs";
export default {
name: "store",
data() {
return {
inputValue: ""
};
},
components: {
AInput: AInput,
AShow: AShow
},
computed: {
//ES6展开操作符 mapState展开会形成一个对象 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
appName: state => state.appName,
appVersion: state => state.appVersion,
userName: state => state.user.userName,
todoList: state => (state.user.todo ? state.user.todo.todoList : [])
}),
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
// ...mapGetters(["appNameWithVersion"]),
appNameWithVersion() {
//通过属性访问getters,Getter 会暴露为 store.getters 对象,可以以属性的形式访问这些值:
return this.$store.getters.appNameWithVersion;
},
...mapGetters(["firstLetter"]),
inputValueLastLetter() {
return this.inputValue.substr(-1, 1);
}
},
methods: {
handlerInput(val) {
this.inputValue = val;
},
//
...mapMutations([
"SET_USER_NAME", //将 `this.SET_USER_NAME()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('SET_USER_NAME')`
"SET_APP_NAME" //将 `this.SET_APP_NAME()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('SET_APP_NAME')`
]),
...mapActions([
"updateAppName" //将 `this.updateAppName()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('updateAppName')`
]),
handleChangeAppName() {
this.SET_APP_NAME({
appName: "newAppName"
});
this.SET_USER_NAME({
userName: "shuyujie"
});
this.$store.commit("SET_APP_VERSION");
},
handleActionChangeAppName() {
//第一种调用Action的方法
//this.$store.dispatch('updateAppName')
//第二种调用Action的方法
this.updateAppName();
},
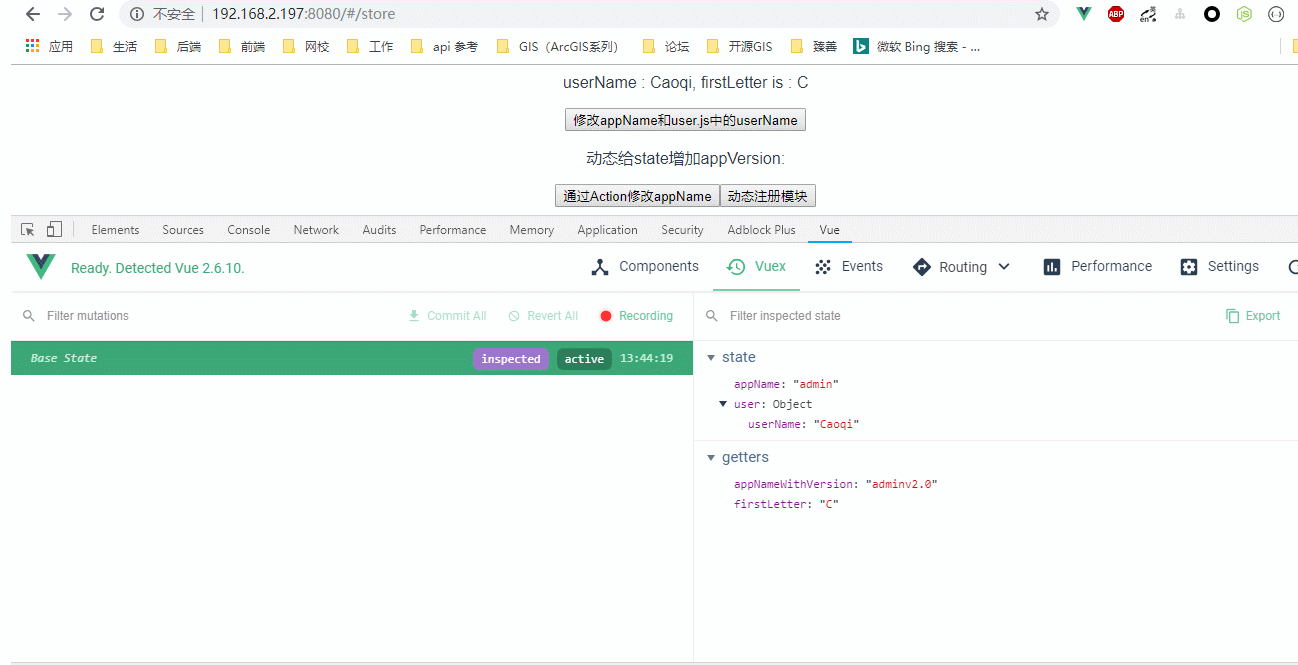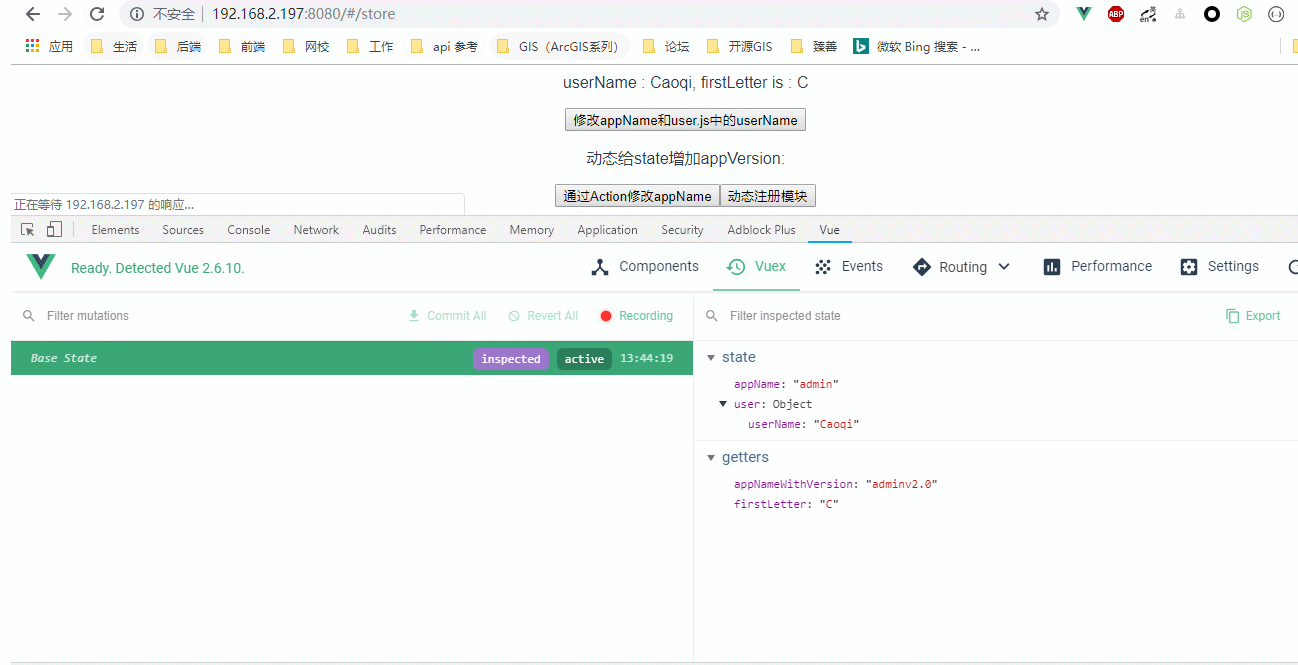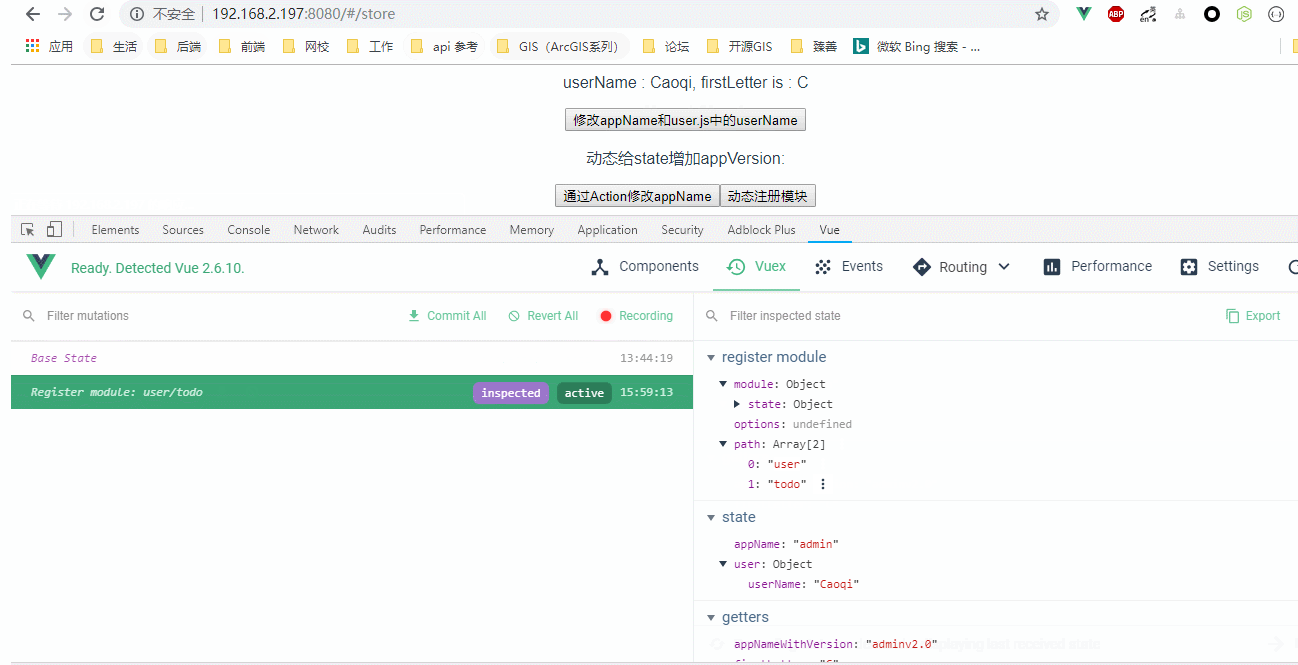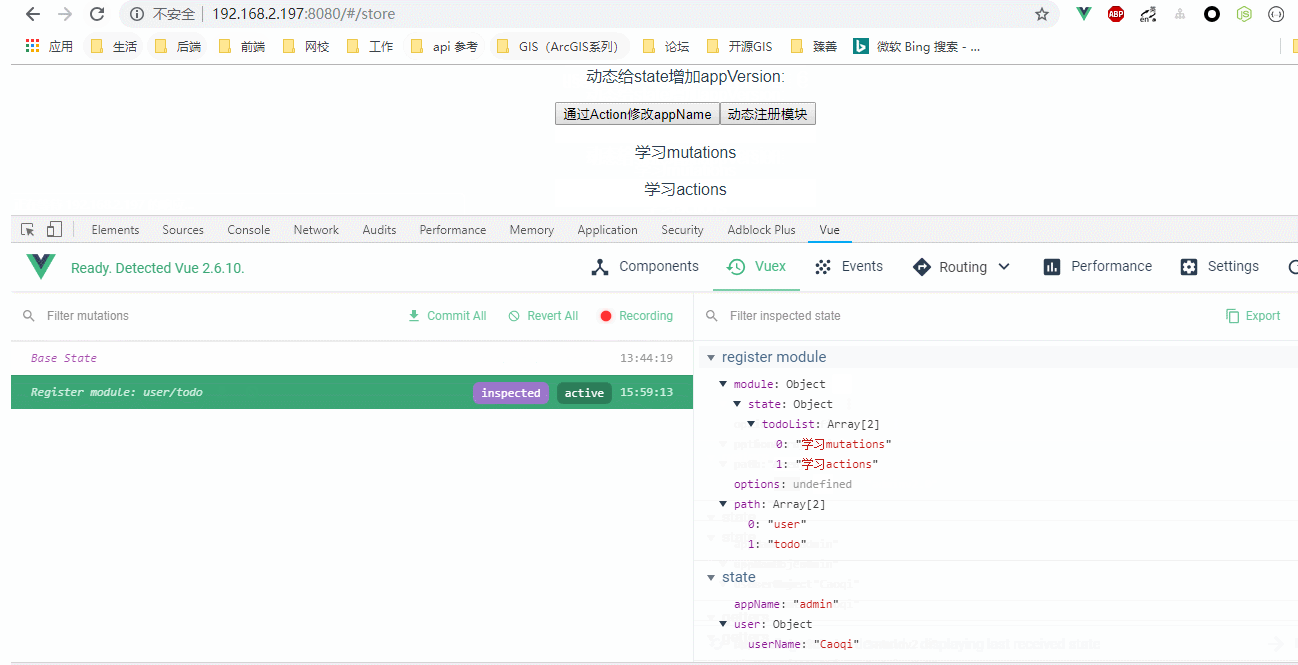
registerModule() {
this.$store.registerModule(["user", "todo"], {
state: {
todoList: ["学习mutations", "学习actions"]
}
});
}
}
};
</script>
效果图:
此外需要注意的是,若模块使用了命名空间(namespaced:true),则访问模块中定义的模块时候需要采用这种方式:
...mapMutations("user/xxx",[ "SET_USER_NAME", //将 `this.SET_USER_NAME()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('SET_USER_NAME')` "SET_APP_NAME" //将 `this.SET_APP_NAME()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('SET_APP_NAME')` ])