Persistent Bookcase
time limit per test 2 seconds
memory limit per test 512 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn't take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1 to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
- 1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.
- 2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.
- 3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
- 4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got 'A' in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
Output
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
Examples
input
Copy
2 3 31 1 13 24 0
output
Copy
140
input
Copy
4 2 63 22 2 23 33 22 2 23 2
output
Copy
213324
input
Copy
2 2 23 22 2 1
output
Copy
21
Note
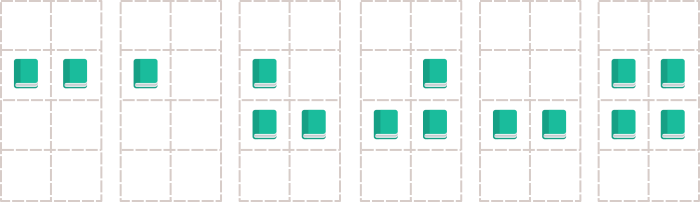
This image illustrates the second sample case.
题意:
现在有一个N*M的书架,有Q个操作,对于每个操作,输入opt:
如果opt==1,那么输入x,y,如果第x行第y列无书,则放一本书。
如果opt==2,那么输入x,y,如果第x行第y列有书,则取走那本书。
如果opt==3,那么输入x,将第x行有书的取走,无书的位置放一本。
如果opt==4,那么输入k,表示把书架的情况恢复为第k次操作后的样貌,k在当前操作之前。
思路:
注意到整体操作顺序为有根树,可以DFS回溯处理,对于书架上的书个数情况,可以直接用bitset。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
#define ALL(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define repd(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define pll pair<long long ,long long>
#define gbtb ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define MS0(X) memset((X), 0, sizeof((X)))
#define MSC0(X) memset((X), '�', sizeof((X)))
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define eps 1e-6
#define gg(x) getInt(&x)
#define chu(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]"<<endl
#define du3(a,b,c) scanf("%d %d %d",&(a),&(b),&(c))
#define du2(a,b) scanf("%d %d",&(a),&(b))
#define du1(a) scanf("%d",&(a));
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
ll powmod(ll a, ll b, ll MOD) {a %= MOD; if (a == 0ll) {return 0ll;} ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b & 1) {ans = ans * a % MOD;} a = a * a % MOD; b >>= 1;} return ans;}
void Pv(const vector<int> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%d", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("
");}}}
void Pvl(const vector<ll> &V) {int Len = sz(V); for (int i = 0; i < Len; ++i) {printf("%lld", V[i] ); if (i != Len - 1) {printf(" ");} else {printf("
");}}}
inline void getInt(int *p);
const int maxn = 1010;
const int manq = 1e5 + 10;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*** TEMPLATE CODE * * STARTS HERE ***/
bitset<maxn> a[maxn], p;
int n, m;
int q;
int op[manq];
int x[manq];
int y[manq];
std::vector<int> son[manq];
int ans[manq];
void dfs(int u, int now)
{
for (auto v : son[u]) {
if (op[v] == 1) {
if (a[x[v]][y[v]] == 0) {
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 1;
ans[v] = now + 1;
dfs(v, now + 1);
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 0;
} else {
ans[v] = now ;
dfs(v, now );
}
} else if (op[v] == 2) {
if (a[x[v]][y[v]] == 1) {
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 0;
ans[v] = now - 1;
dfs(v, now - 1);
a[x[v]][y[v]] = 1;
} else {
ans[v] = now ;
dfs(v, now );
}
} else if (op[v] == 3) {
ans[v] = now - a[x[v]].count();
a[x[v]] ^= p;
ans[v] += a[x[v]].count();
dfs(v, ans[v]);
a[x[v]] ^= p;
} else if (op[v] == 4) {
ans[v] = ans[x[v]];
dfs(v, ans[v]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen("D:\code\text\input.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("D:\code\text\output.txt","w",stdout);
du3(n, m, q);
repd(i, 1, m) {
p.set(i);
}
repd(i, 1, q) {
du1(op[i]);
if (op[i] <= 2) {
du2(x[i], y[i]);
} else {
du1(x[i]);
}
if (op[i] <= 3) {
son[i - 1].push_back(i);
} else {
son[x[i]].push_back(i);
}
}
dfs(0, 0);
repd(i, 1, q) {
printf("%d
", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
inline void getInt(int *p)
{
char ch;
do {
ch = getchar();
} while (ch == ' ' || ch == '
');
if (ch == '-') {
*p = -(getchar() - '0');
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
*p = *p * 10 - ch + '0';
}
} else {
*p = ch - '0';
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
*p = *p * 10 + ch - '0';
}
}
}