这是尾插法单链表,单链表比较适合用来做队列和栈,因为在链表的头和尾时的增删改查的时间复杂度为O(1),而在链表内部的增删改查的平均时间复杂度为O(n)。
#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" //提供malloc()和free() #include "string.h" #include "time.h" //提供strcpy(),time()等 //1.用结构体创建链表节点 //一个用来存放数据,另一个存放指针 struct Node { int data; //数据域 struct Node* next; //指针域(指向节点的指针) }; //2.全局定义链表头尾指针,方便调用 struct Node* head = NULL; struct Node* end = NULL; //3.向链表添加数据 void AddListTill(int a ) { //创建一个节点 struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); //此处注意强制类型转换 //节点数据进行赋值 temp->data = a; temp->next = NULL; //连接分两种情况1.一个节点都没有2.已经有节点了,添加到尾巴上 if(NULL == head) { head = temp; //end=temp; } else { end->next=temp; //end=temp; //尾结点应该始终指向最后一个 } end=temp; //尾结点应该始终指向最后一个 } //4.遍历链表并输出 void ScanList() { struct Node *temp = head; //定义一个临时变量来指向头 while (temp != NULL) { printf("%d ",temp->data); temp = temp->next; //temp指向下一个的地址 即实现++操作 } } //5.查找指定的数据是否在链表内 struct Node* FindNode(int a ) { struct Node *temp = head; while(temp != NULL) { if(a == temp->data) { return temp; } temp = temp->next; } //没找到 return NULL; } //6.删除链表 void FreeList() { struct Node *temp = head; //定义一个临时变量来指向头 while (temp != NULL) { struct Node* pt = temp; temp = temp->next; //temp指向下一个的地址 即实现++操作 free(pt); //释放当前 } //头尾清空,不然下次的头就接着0x10 head = NULL; end = NULL; } //7.在指定位置处插入数据 void AddListRand(int index,int a) { if (NULL == head) { printf("链表没有节点 "); return; } struct Node* pt = FindNode(index); if(NULL == pt) //没有此节点 { printf("没有指定节点 "); return; } //有此节点 //创建临时节点,申请内存 struct Node* temp =(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); //节点成员进行赋值 temp->data = a; temp->next = NULL; //连接到链表上 1.找到的节点在尾部 2.找到的节点在中间 if (pt == end) { //尾巴的下一个指向新插入的节点 end->next = temp; //新的尾巴 end = temp; } else { //先连后面 (先将要插入的节点指针指向原来找到节点的下一个) temp->next = pt->next; //后连前面 pt->next = temp; } } //8.删除链表末尾数据 void DeleteListTail() { if (NULL == end) { printf("链表为空,无需删除 "); return; } //链表不为空 //链表有一个节点 if (head == end) { free(head); head = NULL; end = NULL; } else { //找到尾巴前一个节点 struct Node* temp = head; while (temp->next != end) { temp = temp->next; } //找到了,删尾巴 //释放尾巴 free(end); //尾巴迁移 end=temp; //尾巴指针为NULL end->next = NULL; } } //9.删除链表的第一个数据 void DeleteListHead() { //记住旧头 struct Node* temp = head; //链表检测 if (NULL == head) { printf("链表为空 "); return; } head = head->next; //头的第二个节点变成新的头 free(temp); } //10.删除链表指定的数据 void DeleteListRand(int a) { //链表判断 是不是没有东西 if(NULL == head) { printf("链表没东西 "); return; } //链表有东西,找这个节点 struct Node* temp = FindNode(a); if(NULL == temp) { printf("查无此点 "); return; } //找到了,且只有一个节点 if(head == end) { free(head); head = NULL; end = NULL; } else if(head->next == end) //有两个节点 { //看是删除头还是删除尾 if(end == temp) { DeleteListTail(); } else if(temp == head) { DeleteListHead(); } } else//多个节点 { //看是删除头还是删除尾 if(end == temp) DeleteListTail(); else if(temp == head) DeleteListHead(); else //删除中间某个节点 { //找要删除temp前一个,遍历 struct Node* pt = head; while(pt->next != temp) { pt=pt->next; } //找到了 //让前一个直接连接后一个 跳过指定的即可 pt->next = temp->next; free(temp); } } } //主函数 void main() { struct Node *pFind; srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int i; //创建20个节点 for(i = 0; i < 20; i++) AddListTill(i); //添加数据 //AddListTill(rand()); AddListRand(4,86); //在指定位置4增加节点14 //DeleteListHead(); //删除一个头结点 //DeleteListTail(); //删除一个尾结点 DeleteListRand(4); //删除4节点 ScanList(); //遍历输出链表 //FreeList(); //删除链表 pFind = FindNode(5); //查找5节点 if (pFind != NULL) { printf("找到%d ",pFind->data); //找到节点并且输出该节点数据 } else { printf("No Find! "); } }
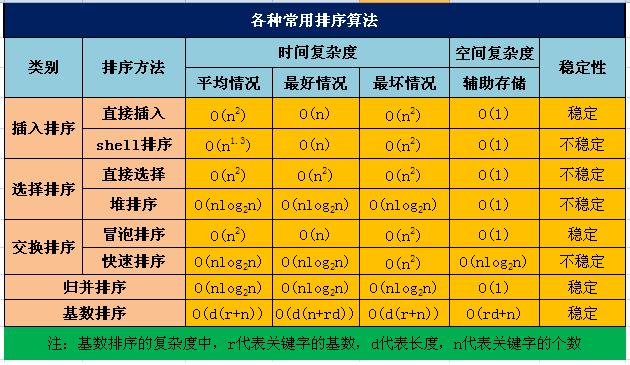
以下是排序算法的时间和空间复杂度表: