流的概念和作用
流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输特性将流抽象为各种类,方便更直观的进行数据操作。
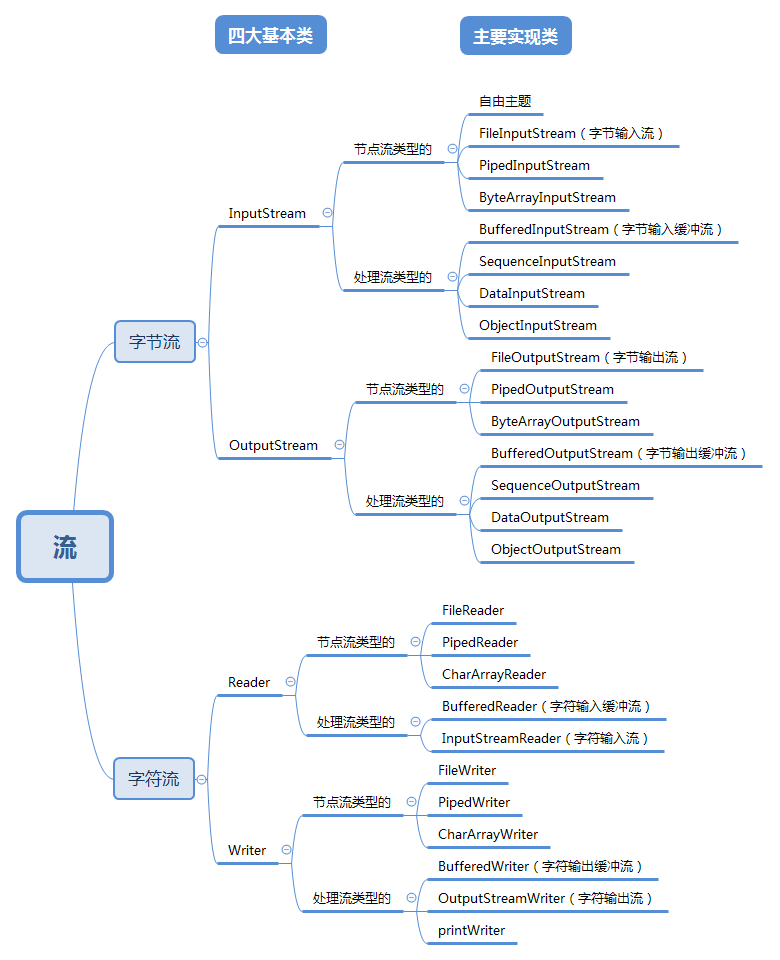
Java流类图结构:
Stream流的聚合操作
1.末端方法;都是一次性的使用,流就会关闭,不能再用此流了。
2.中间方法;会返回一个新的流对象,继续调用其他的聚合方法操作。

1 public class TestStream1 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //存整数 生产者模式 思想 5 //返回 一个 流对象 6 IntStream stream = IntStream.builder().add(11).add(22).add(33).add(44).build(); 7 // System.out.println(stream.max().getAsInt());//末端 8 // IntStream stream1 = IntStream.builder().add(11).add(22).add(33).add(44).build(); 9 // System.out.println(stream1.min().getAsInt()); 10 // System.out.println(stream.min().getAsInt()); 11 // System.out.println(stream.sum()); 12 // System.out.println(stream.average().getAsDouble()); 13 // System.out.println(stream.count()); 14 //是否 所有的 数据 都 满足条件,都满足 true,否则不成立 15 /* System.out.println(stream.allMatch(new IntPredicate() { 16 17 @Override 18 public boolean test(int value) { 19 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 20 return value > 10; 21 } 22 }));*/ 23 // System.out.println(stream.allMatch(v-> v > 10)); 24 //只要有一个元素满足条件 就 成立 true 25 // System.out.println(stream.anyMatch(v-> v > 22)); 26 //中间方法 27 // System.out.println(stream.filter(v-> v > 22).count()); 28 stream.filter(v->v>22).forEach(System.out::println); 29 30 31 } 32 33 34 35 }
File类主要用来获取文件(或目录)本身的一些信息,如文件的名字,不涉及文件的读写操作。
常用方法
对文件的操作

1 public class TestFile { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 4 // File 5 //文件 : 6 File f1 = new File("d:/data"); 7 File f = new File(f1,"x.txt"); 8 // File f = new File("d:/data","x.txt"); 9 // File f = new File("d:\data\x.txt"); 10 // File f = new File("./x.txt"); 11 System.out.println(f.exists()); 12 //新建文件 13 f.createNewFile();// 14 //判断文件是否存在 15 System.out.println(f.exists()); 16 //文件名字 17 System.out.println(f.getName()); 18 //文件的路径:根据指定的 文件路径不同显示不同,可以显示 绝对的也可以显示相对的 19 System.out.println(f.getPath()); 20 //绝对路径 21 System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()); 22 //父路径 23 System.out.println(f.getParent()); 24 //文件 是否 可读,可写 25 System.out.println(f.canRead()); 26 System.out.println(f.canWrite()); 27 //判断 是否是文件 28 System.out.println(f.isFile()); 29 //最后修改的时间 30 long time = f.lastModified(); 31 System.out.println(time); 32 //格式化 33 //DateFormat -> SimpleDateFormat 34 System.out.println(DateFormat.getDateInstance().format(time)); 35 //文件的长度:文件内容的字节数 36 long len = f.length();// 37 System.out.println(len); 38 //删除文件 39 f.delete(); 40 System.out.println(f.exists()); 41 42 } 43 44 }
对目录的操作

1 public class TestFile1 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // File目录 5 File f = new File("d:/data"); 6 // File f = new File("d:/data2/data3"); 7 System.out.println(f.exists()); 8 //是否 是目录 9 System.out.println(f.isDirectory()); 10 //建立目录 11 // f.mkdir(); 12 //建立目录 包括 父目录 13 // f.mkdirs(); 14 //获得 目录下 的 子目录 和文件的 名称 的数组 15 String [] str1 = f.list(); 16 Arrays.stream(str1).forEach(System.out::println); 17 //FilenameFilter文件名过滤器 18 String [] str2 = f.list(new FilenameFilter() { 19 20 @Override 21 public boolean accept(File dir, String name) { 22 // 把扩展名 是 java的过滤出来 23 return name.endsWith("java"); 24 } 25 }); 26 String [] str3 = f.list((d,name)->name.endsWith("java")); 27 28 System.out.println("------------------------"); 29 Arrays.stream(str2).forEach(System.out::println); 30 System.out.println("------------------------"); 31 //----------------------------------------------------- 32 File[] fl1 = f.listFiles(); 33 for(File ff:fl1) { 34 if(ff.isFile()) { 35 System.out.println(ff.getName()); 36 }else { 37 System.out.println(ff.getPath()); 38 } 39 } 40 //FileFilter过滤器 41 File[] fl2 = f.listFiles(new FileFilter() { 42 43 @Override 44 public boolean accept(File pathname) { 45 //把扩展名 是 java的过滤出来 46 return pathname.getName().endsWith("java"); 47 } 48 }); 49 System.out.println("------------------------"); 50 for(File ff:fl2) { 51 if(ff.isFile()) { 52 System.out.println(ff.getName()); 53 }else { 54 System.out.println(ff.getPath()); 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 }
序列化是写,反序列化是读
按照流的数据类型:分为字节流和字符流
按照方向:输入和输出
按照功能:节点流和处理流
处理流(过滤流,包装流):套接(包装)在节点流之上的,提供更丰富的功能或提高效率。
字节流
字节流由2个抽象类定义:
InputStream:所有字节输入流的父类
void close():关闭此输入流并释放与该留关联的所有系统资源
OutputStream:所有字节输出流的父类
void close():关闭此输出流并释放与该留关联的所有系统资源
文件流
FileInputStream
read(byte[]): 返回读到的字节数
read(,,) :(存入的字节数组,存入的起始位置,存入几个字节)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // FileInputStream 文件 输入流 //1 创建流对象 File f = new File("d:/data/a.txt"); FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(f); //把字节流转换成字符流 //转换字符流 // InputStreamReader ir = new InputStreamReader(fin); //2读 /* int temp ; while((temp = fin.read())!= -1) { System.out.print((char)temp); }*/ // byte [] b = new byte[(int)f.length()]; byte [] b = new byte[fin.available()];//获得流中的字节数 //把文件的内容 读入 到 b中 // fin.read(b); // (存入的字节数组,存入的起始位置,存入几个字节) fin.read(b, 1, 2);// ab String s = new String(b,"gbk"); System.out.println(s); //3.关 fin.close(); /*ir.close();*/ // ir.close(); }
FileOutputStream
write(byte[]):写一个字节数组
write(b, 2, 2):(数组,起始位置,字节数)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // FileOutputStream 写 输出 //String s = "hello"存到 d:/data/b.txt //1 true追加 ,false覆盖 吗,默认 false FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("d:/data/b.txt",false); //2写 String s = "hello"; byte [] b = s.getBytes(); // fout.write(b[0]);//写一字节 // fout.write(b);//写一个字节数组 , // (数组,起始位置,字节数) fout.write(b, 2, 2); //3.关 fout.close(); }
缓冲流
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream,默认8192字节,提供了缓冲区,提高效率
public class TestFileInputOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) { // 复制图片 /* //1 。创建对象 FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("d:/data/aoteman.jpg"); FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("d:/data/aotemannew.jpg"); BufferedInputStream bfin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);//缓冲流 提供了 板车 8192字节 BufferedOutputStream bfout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);// 提供了汽车 8192字节 //2读和写 int temp; while((temp = bfin.read())!=-1) { bfout.write(temp); } bfout.flush();//强制写入 //3 bfin.close(); bfout.close();*/ //---------------------------------------------------- FileInputStream fin = null; FileOutputStream fout = null; BufferedInputStream bfin = null; BufferedOutputStream bfout = null; try { fin = new FileInputStream("d:/data/aoteman.jpg"); fout = new FileOutputStream("d:/data/aotemannew.jpg"); bfin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);//缓冲流 提供了 板车 8192字节 bfout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);// 提供了汽车 8192字节 int temp; while((temp = bfin.read())!=-1) { bfout.write(temp); } bfout.flush();//强制写入 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(bfin != null) { bfin.close(); } if(bfout != null) { bfout.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
数据流
提供了 使用 Java的不同数据类型 的方式 读和写。
public class TestDateOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // DataOutputStream数据流 //-------------写-------------------------- //1 // DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/data/stu.txt")); FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("d:/data/stu.txt"); DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(fout); //2.写 int [] no = {11,22,33}; String [] name = {"aa","bb","cc"}; for(int i = 0; i < no.length; i++) { dout.writeInt(no[i]); dout.writeUTF(name[i]); } //3. dout.close(); //---------------读------------------------- FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("d:/data/stu.txt"); DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(fin); for(int i = 0; i < no.length; i++) { System.out.println(din.readInt()); System.out.println(din.readUTF()); } din.close(); } }
ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream
永久性的存储对象,需要实现Serializable接口
序列化:把对象以二进制的形式存储起来。
反序列化:把对象以二进制流的形式从文件中还原

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 5 import java.io.Serializable; 6 7 class Student implements Serializable{ 8 9 /** 10 * 字节码文件中存储的那个版本号, 不显示指定,系统会自动随机一个 11 */ 12 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 13 private int no; 14 private String name; 15 private int age; 16 public int getNo() { 17 return no; 18 } 19 public void setNo(int no) { 20 this.no = no; 21 } 22 public String getName() { 23 return name; 24 } 25 public void setName(String name) { 26 this.name = name; 27 } 28 29 } 30 public class TestObjectStream { 31 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 32 // 创建对象 33 Student guojing = new Student(); 34 guojing.setNo(11); 35 guojing.setName("郭靖"); 36 //序列化 把对象 以二进制流 的形式存储起来。------------------------------------------------------- 37 //1 38 /*// ObjectOutputStream obj = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/data/obj.txt")); 39 FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("d:/data/obj.txt"); 40 ObjectOutputStream obj = new ObjectOutputStream(fout); 41 //2写 42 obj.writeObject(guojing); 43 //3. 44 obj.close();*/ 45 //反序列化 把对象 以二进制流的形式 从文件中还原----------------------------------------------------- 46 //1 47 FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("d:/data/obj.txt"); 48 ObjectInputStream objin = new ObjectInputStream(fin); 49 //2读 50 Student stu = (Student)objin.readObject(); 51 System.out.println(stu.getNo()+","+stu.getName()); 52 //3. 53 objin.close(); 54 55 } 56 57 }
打印输出字节流
PrintStream

1 public class TestPrintStream { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 4 /*// TODO Auto-generated method stub 5 System.out.println("hello"); 6 System.err.println("abc");*/ 7 //PrintStream 8 //把读到的文件 的内容 在控制台上打印输出 9 //System.out 10 //1 11 FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("d:/data/a.txt"); 12 //2读 13 byte [] b = new byte[fin.available()]; 14 fin.read(b); 15 //3. 16 fin.close(); 17 //-----------------打印到控制台------------------------------ 18 //System.out控制台输出 System.in控制台输入 19 PrintStream print = new PrintStream(System.out); 20 print.println(new String(b,"gbk")); 21 print.close(); 22 } 23 24 }
字符流
抽象父类
Reader
Writer
子类:
1.文件字符流(节点流)
FileReader
FileWriter

1 public class TestReader1 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 4 // 逆序写入 5 //读----------------------------- 6 File f = new File("d:/data/a.txt"); 7 FileReader fr = new FileReader(f); 8 int temp; 9 StringBuffer sf = new StringBuffer(); 10 while((temp = fr.read())!= -1) { 11 sf.append((char)temp);//连接 12 } 13 fr.close(); 14 //写------------------------------ 15 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:/data/b.txt"); 16 //反转 17 String s = sf.reverse().toString(); 18 fw.write(s);//写入 19 fw.close(); 20 } 21 22 }
2.字符缓冲流
BufferedReader
BufferedWriter

1 public class TestReader { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 4 // FileReader------------读------------------------- 5 //1 6 FileReader fr = new FileReader("d:/data/a.txt"); 7 BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(fr); 8 //2读 9 String s = null; 10 while((s = bfr.readLine())!= null) { 11 System.out.println(s); 12 } 13 14 /*int temp ; 15 while((temp = fr.read())!= -1) { 16 System.out.print((char)temp); 17 }*/ 18 //3. 19 fr.close(); 20 //FileWriter---------------写---------------------------- 21 /* FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:/data/b.txt"); 22 String s = "hello"; 23 fw.write(s); 24 fw.close();*/ 25 26 } 27 28 }
3.打印输出流
PrintWriter

1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 5 import java.io.PrintWriter; 6 7 public class TestPrintWriter { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // PrintWriter 11 /* PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("d:/data/num.txt"); 12 for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { 13 // System.out.println(i); 14 pw.println("数字:"+i); 15 } 16 pw.close();*/ 17 //----------------循环写入内容------------------------ 18 //1 19 // System.in 20 /* BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 21 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("d:/data/namenew.txt"); 22 String s; 23 while(true) { 24 s = br.readLine();//读一行 25 if(s.equals("q")) { 26 break; 27 } 28 pw.println(s); 29 } 30 br.close(); 31 pw.close(); 32 */ 33 //自动资源释放 34 try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 35 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("d:/data/namenew.txt");){ 36 37 String s; 38 while(true) { 39 s = br.readLine();//读一行 40 if(s.equals("q")) { 41 break; 42 } 43 pw.println(s); 44 } 45 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } catch (IOException e) { 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 } 51 52 }
