外观模式:
为子系统中的一组接口提供一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得子系统更加容易使用。
1、 由外观类,负责组合子系统方法,对外提供组合完毕的接口和服务。外部不需要了解具体的组合方式和子系统的内容
一、示例UML图
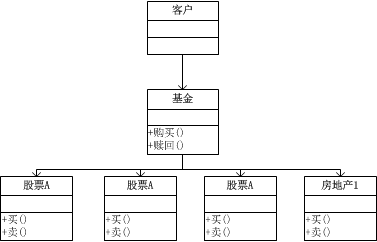
基金提供 “保本服务”和“高回报高风险服务”,客户只需要选择需要的服务即可,不必去关注组合购买股票的方式,由专业的基金组织进行组合。
二、外观模式UML图
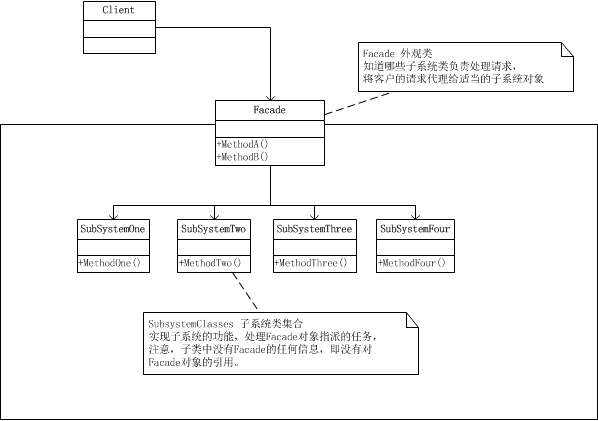
三、示例代码

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace 外观模式 7 { 8 class Program 9 { 10 static void Main(string[] args) 11 { 12 Facade f = new Facade(); 13 14 Console.WriteLine("散户A(2000元):"); 15 f.MethodA(); 16 17 Console.WriteLine(); 18 19 Console.WriteLine("中户B(十万元):"); 20 f.MethodB(); 21 22 Console.Read(); 23 } 24 } 25 26 #region 外观类 27 /// <summary> 28 /// 外观类,必须知道所有子系统的方法和属性,然后进行组合,以备外界调用 29 /// 此外观类,对外部只暴露两个组合方式:保本、高回报 两种组合方式,外界不需要知道具体购买的哪只股票 30 /// </summary> 31 public class Facade 32 { 33 SubSystemOne one; 34 SubSystemTwo two; 35 SubSystemThree three; 36 SubSystemFour four; 37 38 public Facade() 39 { 40 //此处为什么不将 四个子系统抽象出来?这就需要根据实际情况而定了, 41 //例如 股票、房地产、或者国债 他们的处理方式不同,无法抽象。 42 //强制抽象可能会违反【里氏替换原则】。 43 one = new SubSystemOne(); 44 two = new SubSystemTwo(); 45 three = new SubSystemThree(); 46 four = new SubSystemFour(); 47 } 48 49 //组合方式一:如小散户,金额 一万以下,的股票购买方式(以保本的方式为主) 50 public void MethodA() 51 { 52 //保本 53 one.MethodOne(); 54 two.MethodTwo(); 55 four.MethodFour(); 56 } 57 58 //组合方式二:中型客户,保本30%,其余70%作为风险投资,收取高额回报。 59 public void MethodB() 60 { 61 two.MethodTwo(); 62 three.MethodThree(); 63 } 64 } 65 #endregion 66 67 #region 子系统的类 68 public class SubSystemOne 69 { 70 public void MethodOne() 71 { 72 Console.WriteLine("子系统方法一"); 73 } 74 } 75 public class SubSystemTwo 76 { 77 public void MethodTwo() 78 { 79 Console.WriteLine("子系统方法二"); 80 } 81 } 82 public class SubSystemThree 83 { 84 public void MethodThree() 85 { 86 Console.WriteLine("子系统方法三"); 87 } 88 } 89 public class SubSystemFour 90 { 91 public void MethodFour() 92 { 93 Console.WriteLine("子系统方法四"); 94 } 95 } 96 #endregion 97 }
四、使用场景:
1、系统设计初期阶段:有意识的将不同的两个层分离
2、开发阶段:在系统重构演变过程中,增加外观接口,减少彼此之间的依赖。
3、在维护一个遗留的大型系统时,为新功能增加外观类,新功能就不必关注原有系统内部的构造和逻辑。
