Queue表示对象的先进先出集合。实现了ICollection接口,可以由数组或链表两种形式实现,在.NET中是以数组的形式实现的。
概念
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表头(head)进行删除操作,而在表尾(tail)进行插入操作。
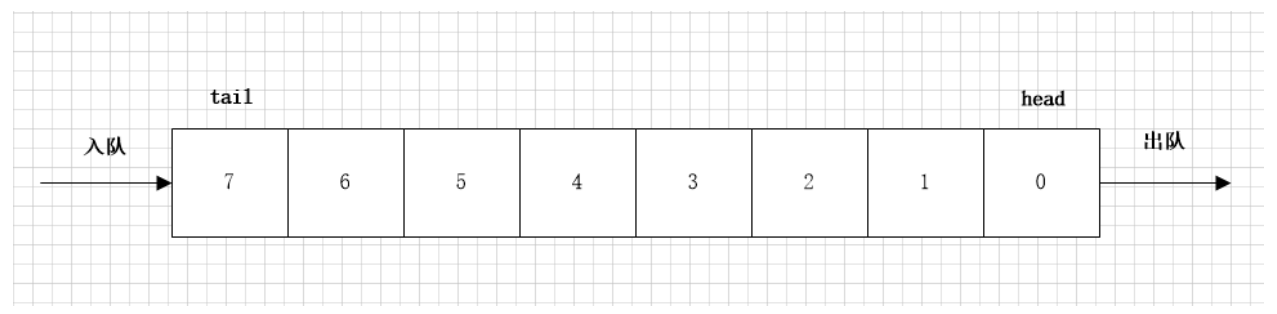
队列的数据元素又称为队列元素。在队列中插入一个队列元素称为入队,从队列中删除一个队列元素成为出队。因为队列只允许在一段插入,在另一端删除,所以只有最早进入队列的元素才能最先从队列中删除,故队列又称为先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)线性表
队列可以分为顺序队列和循环队列,.NET中为了提高空间的利用率,采用的是循环队列。
循环队列
为充分利用向量空间,克服”假溢出”(由于入队和出队操作中,头尾指针只增加不减小,致使被删元素的空间永远无法重新利用)现象的方法是:将向量空间想象为一个首尾相接的圆环,并称这种向量为循环向量。存储在其中的队列称为循环队列(Circular Queue)。概念图如下:
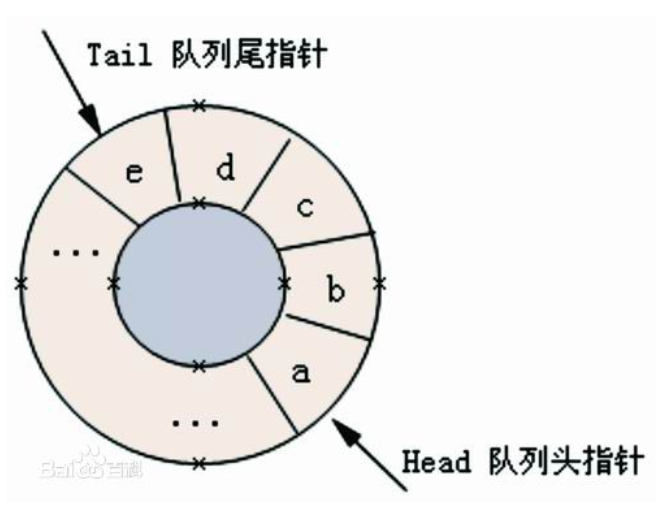
循环队列中,由于入队时尾指针向前追赶头指针;出队时头指针向前追赶尾指针,造成空队列和满队列时头尾指针均相等。因此,无法通过条件front==rear来判别队列是”空”还是”满”,.NET使用一下方法判断空队列和满队列(实际.NET中,队列的长度时自动扩容的):
(1)私有成员_size = 0时,为空队列。
(2)_size == _array.Length时(_array为Queue内部维护的实际数据数组),为满队列,这个时候会进行自动扩容(新建一个2倍于原容量的数组)。
而出队入队的位置,也要用取模的方式计算,因为可能出现数组尾部到头部的循环,如下
_head = (_head + 1) % _array.Length;
属性和变量
/// <summary> /// 内部维护的数组,实际进行数据的存放 /// </summary> private Object[] _array; /// <summary> /// First valid element in the MyQueue 表头 /// </summary> private int _head; /// <summary> /// Last valid element in the MyQueue 表尾 /// </summary> private int _tail; /// <summary> /// Number of elements. 队列元素数量 /// </summary> private int _size; public virtual int Count { get { return _size; } } private int _growFactor; // 100 == 1.0, 130 == 1.3, 200 == 2.0 private int _version; [NonSerialized] private Object _syncRoot; private const int _MinimumGrow = 4; private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 32;
构造函数
public MyQueue(int capacity, float growFactor) { if (capacity < 0) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(); if (!(growFactor >= 1.0 && growFactor <= 10.0)) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(); _array = new Object[capacity]; _head = 0; _tail = 0; _size = 0; _growFactor = (int)(growFactor * 100); }
新增及扩容
入队 // Adds obj to the tail of the MyQueue. public virtual void EnMyQueue(Object obj) { //这时候需要扩容 if (_size == _array.Length) { //使用_growFactor计算新的容量 int newcapacity = (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_growFactor / 100); if (newcapacity < _array.Length + _MinimumGrow) { newcapacity = _array.Length + _MinimumGrow; } SetCapacity(newcapacity); } //尾部指针位置赋值 _array[_tail] = obj; //循环队列,要进行余数运算 _tail = (_tail + 1) % _array.Length; _size++; _version++; } //设置队列的容量 private void SetCapacity(int capacity) { Object[] newarray = new Object[capacity]; if (_size > 0) { if (_head < _tail) //正序的情况直接复制 { Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _size); } else { //先把头部到数组结束的数据复制 Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _array.Length - _head); //再复制0到尾部的数据 Array.Copy(_array, 0, newarray, _array.Length - _head, _tail); } } _array = newarray; _head = 0; //_size == capacity尾部设置为0,这样下次新增的时候是需要扩容的 _tail = (_size == capacity) ? 0 : _size; _version++; }
出队和清空
// Removes the object at the head of the MyQueue and returns it. If the MyQueue // is empty, this method simply returns null. public virtual Object DeMyQueue() { if (Count == 0) throw new InvalidOperationException(); //返回出队对象 Object removed = _array[_head]; //指向设置为空 _array[_head] = null; //重新获取新的队列头部位置 _head = (_head + 1) % _array.Length; _size--; _version++; return removed; } // Removes all Objects from the MyQueue. public virtual void Clear() { if (_head < _tail) Array.Clear(_array, _head, _size); else { Array.Clear(_array, _head, _array.Length - _head); Array.Clear(_array, 0, _tail); } _head = 0; _tail = 0; _size = 0; _version++; }
查询
public virtual bool Contains(Object obj) { //从同步开始遍历,遍历次数为_size int index = _head; int count = _size; while (count-- > 0) { if (obj == null) { if (_array[index] == null) return true; } else if (_array[index] != null && _array[index].Equals(obj)) { return true; } //求模方式获取下个位置 index = (index + 1) % _array.Length; } return false; } internal Object GetElement(int i) { return _array[(_head + i) % _array.Length]; }