简介
Channel类,即通道类。Channel类是可能产生事件的文件描述符封装在其中的,这里的文件描述符可以是file descriptor,可以是socket,还可以是timefd,signalfd。但实际上它不拥有fd_,不用负责将其关闭,关闭是Eventpool的事情。
Acceptor和TcpConnection通过Channel与Eventpool建立连接,而且真正的事件处理函数也都是封装在Channel类中的。
每个Channel对象自始至终只属于一个EventLoop,因此每个Channel对象都只属于某一个IO线程。
每个Channel对象自始至终只负责一个文件描述符(fd)的IO事件分发,但它并不拥有这个fd,也不会在析构的时候关闭这个fd。
Muduo用户一般不直接使用Channel,而会使用更上层的封装,如TcpConnection。
Channel的生命期由其owner calss负责管理。
Channel的成员函数都只能在IO线程调用,因此更新数据成员都不必加锁。
源码分析
Channel.h源码
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved. // http://code.google.com/p/muduo/ // // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license // that can be found in the License file. // Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com) // // This is an internal header file, you should not include this. #ifndef MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H #define MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H #include <boost/function.hpp> #include <boost/noncopyable.hpp> #include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp> #include <boost/weak_ptr.hpp> #include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h> /*个人理解:channel是一个具体来处理事件的类,它与eventloop关系紧密,主要是根据事件宏定义来调用对应的回调函数 *主要的事件有三种,读事件,写事件和结束事件 **/ namespace muduo { namespace net { class EventLoop; /// /// A selectable I/O channel. /// /// This class doesn't own the file descriptor. /// The file descriptor could be a socket, /// an eventfd, a timerfd, or a signalfd class Channel : boost::noncopyable { public: typedef boost::function<void()> EventCallback; typedef boost::function<void(Timestamp)> ReadEventCallback;//读事件的回调函数中必须有参数Timestamp Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd);//一个channel要绑定一个EventLoop和一个文件描述符,但channel无权操作fd ~Channel(); void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);//处理事件 void setReadCallback(const ReadEventCallback &cb) { readCallback_ = cb; } void setWriteCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { writeCallback_ = cb; } void setCloseCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { closeCallback_ = cb; } void setErrorCallback(const EventCallback &cb) { errorCallback_ = cb; }//设置四种回调函数 /// Tie this channel to the owner object managed by shared_ptr, /// prevent the owner object being destroyed in handleEvent. //这个函数,用于延长某些对象的生命期,使其寿命长过Channel::handleEvent()函数。 void tie(const boost::shared_ptr<void> &);//将一个shared_ptr指针的值赋给tie_ int fd() const { return fd_; } int events() const { return events_; } void set_revents(int revt) { revents_ = revt; } // used by pollers // int revents() const { return revents_; } bool isNoneEvent() const { return events_ == kNoneEvent; }//判断事件是否为0,也就是没有关注的事件 void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }//设置读事件,并将当前channel加入到poll队列当中 // void disableReading() { events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update(); } void enableWriting() { events_ |= kWriteEvent; update(); }//设置写事件,并将当前channel加入到poll队列当中 void disableWriting() { events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update(); }//关闭写事件,并将当前channel加入到poll队列当中 void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); }//关闭所有事件,并暂时删除当前channel bool isWriting() const { return events_ & kWriteEvent; }//是否关注写事件 // for Poller int index() { return index_; }//返回序号 void set_index(int idx) { index_ = idx; }//设置序号 // for debug string reventsToString() const; void doNotLogHup() { logHup_ = false; }//把挂起标志位置false EventLoop *ownerLoop() { return loop_; } void remove(); private: void update(); void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime); static const int kNoneEvent; static const int kReadEvent; static const int kWriteEvent; EventLoop *loop_; // 所属EventLoop const int fd_; // 文件描述符,但不负责关闭该文件描述符 int events_; // 需要epoll关注的事件 int revents_; // poll/epoll wait返回的需要处理的事件 int index_; // used by Poller.表示在epoll队列中的状态:1.正在队列中2.曾经在队列中3.从来没在队列中 bool logHup_; // for POLLHUP是否被挂起 boost::weak_ptr<void> tie_;//保证channel所在的类 bool tied_; bool eventHandling_; // 是否处于处理事件中 ReadEventCallback readCallback_;//当文件描述符产生读事件时,最后调用的读函数,我将它命名为channel的读函数 EventCallback writeCallback_;//当文件描述符产生写事件时,最后调用的写函数,我将它命名为channel的写函数 EventCallback closeCallback_;//当文件描述符产生关闭事件时,最后调用的关闭函数,我将它命名为channel的关闭函数 EventCallback errorCallback_;//当文件描述符产生错误事件时,最后调用的错误函数,我将它命名为channel的错误函数 }; } } #endif // MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H
Channel.cc源码
// Copyright 2010, Shuo Chen. All rights reserved. // http://code.google.com/p/muduo/ // // Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license // that can be found in the License file. // Author: Shuo Chen (chenshuo at chenshuo dot com) #include <muduo/base/Logging.h> #include <muduo/net/Channel.h> #include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h> #include <sstream> #include <poll.h> using namespace muduo; using namespace muduo::net; const int Channel::kNoneEvent = 0; const int Channel::kReadEvent = POLLIN | POLLPRI; const int Channel::kWriteEvent = POLLOUT; Channel::Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd__) : loop_(loop), fd_(fd__), events_(0), revents_(0), index_(-1),//就是kNew logHup_(true), tied_(false), eventHandling_(false) { } Channel::~Channel() { assert(!eventHandling_); } void Channel::tie(const boost::shared_ptr<void> &obj)//给tie_指针赋值,tie_指针是一个weak_ptr指针,但是给weak_ptr指针赋值的一定是一个shared_ptr指针 { tie_ = obj; tied_ = true; } void Channel::update()//把当前的channel加入到poll队列当中 { loop_->updateChannel(this); } // 调用这个函数之前确保调用disableAll // 从EventLoop中移除这个channel void Channel::remove() { assert(isNoneEvent()); loop_->removeChannel(this); } void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)//Timestamp主要用于读事件的回调函数 { boost::shared_ptr<void> guard; if (tied_) { guard = tie_.lock();//提升tie_为shared_ptr,如果提升成功,说明指向一个存在的对象 if (guard) { LOG_TRACE << "[6] usecount=" << guard.use_count(); handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime); LOG_TRACE << "[12] usecount=" << guard.use_count(); } } else { handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime); } } void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime) //暂时理解:查看epoll/或者poll返回的具体是什么事件,并根据事件的类型进行相应的处理 { eventHandling_ = true; /* if (revents_ & POLLHUP) { LOG_TRACE << "1111111111111111"; } if (revents_ & POLLIN) { LOG_TRACE << "2222222222222222"; } */ if ((revents_ & POLLHUP) && !(revents_ & POLLIN))//当事件为挂起并没有可读事件时 { if (logHup_) { LOG_WARN << "Channel::handle_event() POLLHUP"; } if (closeCallback_) closeCallback_(); } if (revents_ & POLLNVAL)//描述字不是一个打开的文件描述符 { LOG_WARN << "Channel::handle_event() POLLNVAL"; } if (revents_ & (POLLERR | POLLNVAL))//发生错误或者描述符不可打开 { if (errorCallback_) errorCallback_(); } if (revents_ & (POLLIN | POLLPRI | POLLRDHUP))//关于读的事件 { if (readCallback_) readCallback_(receiveTime); } if (revents_ & POLLOUT)//关于写的事件 { if (writeCallback_) writeCallback_(); } eventHandling_ = false; } string Channel::reventsToString() const//把事件编写成一个string { std::ostringstream oss; oss << fd_ << ": "; if (revents_ & POLLIN) oss << "IN "; if (revents_ & POLLPRI) oss << "PRI "; if (revents_ & POLLOUT) oss << "OUT "; if (revents_ & POLLHUP) oss << "HUP "; if (revents_ & POLLRDHUP) oss << "RDHUP "; if (revents_ & POLLERR) oss << "ERR "; if (revents_ & POLLNVAL) oss << "NVAL "; return oss.str().c_str(); }
Channel::tie()详解
这里是一个智能指针使用的特定场景之一,用于延长特定对象的生命期
结合例子分析,看下面的一个调用时序图
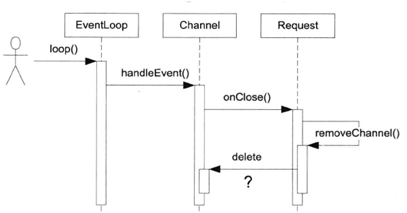
当对方断开TCP连接,这个IO事件会触发Channel::handleEvent()调用,后者会调用用户提供的CloseCallback,而用户代码在onClose()中有可能析构Channel对象,这就造成了灾难。等于说Channel::handleEvent()执行到一半的时候,其所属的Channel对象本身被销毁了。这时程序立刻core dump就是最好的结果了。
Muduo的解决办法是提供Channel::tie(const boost::shared_ptr<void>&)这个函数,用于延长某些对象(可以是Channel对象,也可以是其owner对象)的生命期,使之长过Channel::handleEvent()函数。
Muduo TcpConnection采用shared_ptr管理对象生命期的原因之一就是因为这个。
当有关闭事件时,调用流程如下:
Channel::handleEvent -> TcpConnection::handleClose ->TcpClient::removeConnection ->TcpConnection::connectDestroyed->channel_->remove()。
1、为了在Channel::handleEvent处理期间,防止因其owner对象被修改,进而导致Channel被析构,最后出现不可预估错误。 Channel::tie()的作用就是将Channel的owner对象进行绑定保护起来。
2、另外channel->remove的作用是删除channel在Poll中的地址拷贝,而不是销毁channel。channel的销毁由其owner对象决定。