基本使用:
http://www.jcodecraeer.com/a/anzhuokaifa/androidkaifa/2015/0106/2275.html
http://www.jianshu.com/p/1873287eed87
http://blog.csdn.net/itachi85/article/details/51190687
一个最简单的DEMO
public class OkHttp3BasicActivity extends Activity { @BindView(R.id.sn_tv) TextView tv; private OkHttpClient client ; String str = ""; private Handler handler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { super.handleMessage(msg); switch (msg.what) { case 1: tv.setText(msg.obj.toString()); break; } } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.simple_network_main); ButterKnife.bind(this); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { okrun(); } }).start(); } private void okrun() { client = new OkHttpClient(); httpUrl = httpUrl+"?"+httpArg; Request request = new Request.Builder() .url("http://publicobject.com/helloworld.txt") .build(); client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() { @Override public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) { } @Override public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException { if (!response.isSuccessful()) throw new IOException("Unexpected code " + response); str = response.body().string(); Message msg = Message.obtain(); msg.what =1; msg.obj = str; handler.sendMessage(msg); } }); } }
两个需要注意的点:
- okhttp3不能在ui线程中运行
- onresponse在子线程中,需要用handler回调才能操作ui
请求网络原理解析:
http://liuwangshu.cn/application/network/7-okhttp3-sourcecode.html
HTTP请求执行流程分析
http://www.jianshu.com/p/230e2e2988e0
OkHttp3源码详解(二整体流程)
整个实现流程如下:
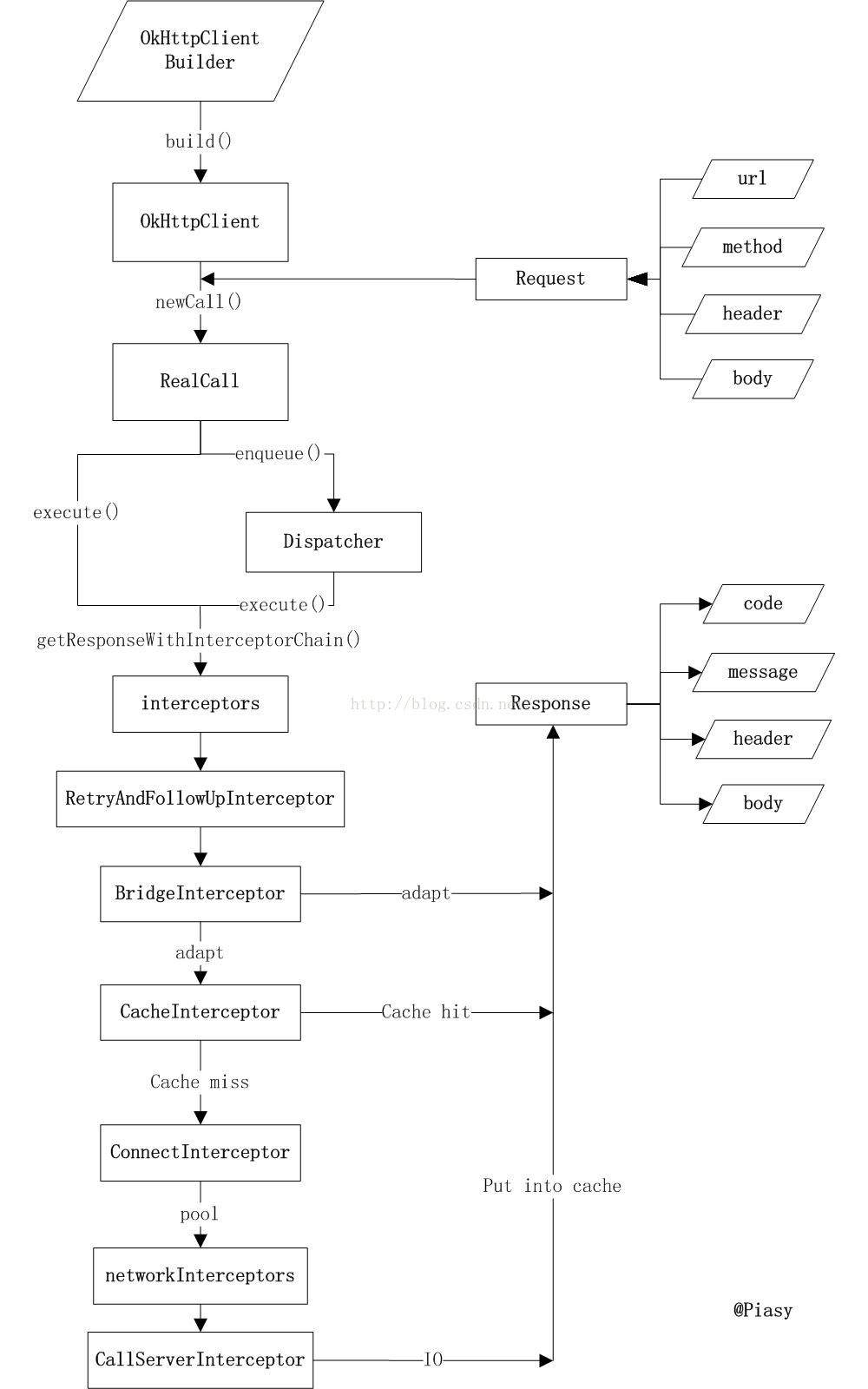
- 创建OkHttpClient对象。OkHttpClient为网络请求执行的一个中心,它会管理连接池,缓存,SocketFactory,代理,各种超时时间,DNS,请求执行结果的分发等许多内容。
- 创建Request对象。Request用于描述一个HTTP请求,比如请求的方法是"GET"还是"POST",请求的URL,请求的header,请求的body,请求的缓存策略等。
- 利用前面创建的OkHttpClient对象和Request对象创建Call对象。Call是一次HTTP请求的Task,它会执行网络请求以获得响应。OkHttp中的网络请求执行Call既可以同步进行,也可以异步进行。调用call.execute()将直接执行网络请求,阻塞直到获得响应。而调用call.enqueue()传入回调,则会将Call放入一个异步执行队列,由ExecutorService在后台执行。
如果正在运行的异步任务队列数量小于最大请求数,线程池调用execute()执行该任务,否则加入准备队列
默认情况下,这是一个不限容量的线程池。但Dispatcher会限制每个host同时执行的最大请求数量,默认为5,同时也会限制同时执行的总的最大请求数量
用户可以通过Dispatcher的构造函数来定制ExecutorService,这需要通过OkHttpClient.Builder在OkHttpClient的构建过程中间接的做到。
线程池execute()
由getResponseWithInterceptorChain()来执行网络请求,得到response
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
成功后回调CallBack的onResponse方法
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
可以看到这里对回调接口是同步调用,也就是回调方法将在后台线程中被调用。
getResponseWithInterceptorChain()加上了一系列的interceptor,然后执行chain.proceed(request)
private Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException { //构建全栈拦截器 List interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());//自定义拦截器 interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);//重试拦截器 interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));//桥接拦截器 interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));//缓存拦截器 interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));//连接拦截器 if (!retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isForWebSocket()) { interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());//用户预定义的网络拦截器 } interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor( retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isForWebSocket()));//调用服务拦截器 //内部通过责任链模式来使用拦截器 Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain( interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest); return chain.proceed(originalRequest);//获取Response }

RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor
重试与重定向拦截器,用来实现重试和重定向功能,内部通过while(true)死循环来进行重试获取Response(有重试上限,超过会抛出异常)。followUpRequest主要用来根据响应码来判断属于哪种行为触发的重试和重定向(比如未授权,超时,重定向等),然后构建响应的Request进行下一次请求。当然,如果没有触发重新请求就会直接返回Response。
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor在intercept()中首先从client取得connection pool,用所请求的URL创建Address对象,并以此创建StreamAllocation对象。
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor对重定向的响应也不会无休止的处理下去,它处理的最多的重定向级数为20次,超过20次时,它会抛异常出来。
总结一下RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor做的事情:
- 创建StreamAllocation对象,为后面流程的执行准备条件。
- 处理重定向的HTTP响应。
- 错误恢复。
BridgeInterceptor
桥接拦截器,用于完善请求头
这个Interceptor做的事情比较简单。可以分为发送请求和收到响应两个阶段来看。在发送请求阶段,BridgeInterceptor补全一些http header,这主要包括Content-Type、Content-Length、Transfer-Encoding、Host、Connection、Accept-Encoding、User-Agent,还加载Cookie,随后创建新的Request,并交给后续的Interceptor处理,以获取响应。
而在从后续的Interceptor获取响应之后,会首先保存Cookie。如果服务器返回的响应的content是以gzip压缩过的,则会先进行解压缩,移除响应中的header Content-Encoding和Content-Length,构造新的响应并返回;否则直接返回响应。
CacheInterceptor
缓存拦截器,首先根据Request中获取缓存的Response,然后根据用于设置的缓存策略来进一步判断缓存的Response是否可用以及是否发送网络请求(CacheControl.FORCE_CACHE因为不会发送网络请求,所以networkRequest一定为空)。如果从网络中读取,此时再次根据缓存策略来决定是否缓存响应。
对于CacheInterceptor.intercept(Chain chain)的分析同样可以分为两个阶段,即请求发送阶段和响应获取之后的阶段。这两个阶段由chain.proceed(networkRequest)来分割。
在请求发送阶段,主要是尝试从cache中获取响应,获取成功的话,且响应可用未过期,则响应会被直接返回;否则通过后续的Interceptor来从网络获取,获取到响应之后,若需要缓存的,则缓存起来。
关于HTTP具体的缓存策略这里暂时不再详述。
由RealCall.getResponseWithInterceptorChain()可见CacheInterceptor的cache同样来自于OkHttpClient。OkHttp已经有实现Cache的整套策略,在Cache类,但默认情况下不会被用起来,需要自己在创建OkHttpClient时,手动创建并传给OkHttpClient.Builder。
ConnectInterceptor
连接拦截器,用于打开一个连接到远程服务器。说白了就是通过StreamAllocation获取HttpStream和RealConnection对象,以便后续读写。
CallServerInterceptor
调用服务拦截器,拦截链中的最后一个拦截器,通过网络与调用服务器。通过HttpStream依次次进行写请求头、请求头(可选)、读响应头、读响应体。
CallServerInterceptor首先将http请求头部发给服务器,如果http请求有body的话,会再将body发送给服务器,继而通过httpStream.finishRequest()结束http请求的发送。
随后便是从连接中读取服务器返回的http响应,并构造Response。
如果请求的header或服务器响应的header中,Connection值为close,CallServerInterceptor还会关闭连接。
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor --->创建StreamAllocation对象,处理http的redirect,出错重试。对后续Interceptor的执行的影响:修改request及StreamAllocation。
BridgeInterceptor-------------->补全缺失的一些http header。对后续Interceptor的执行的影响:修改request。
CacheInterceptor-------------->处理http缓存。对后续Interceptor的执行的影响:若缓存中有所需请求的响应,则后续Interceptor不再执行。
ConnectInterceptor------------>借助于前面分配的StreamAllocation对象建立与服务器之间的连接,并选定交互所用的协议是HTTP 1.1还是HTTP 2。对后续Interceptor的执行的影响:创建了httpStream和connection。
CallServerInterceptor----------->处理IO,与服务器进行数据交换。对后续Interceptor的执行的影响:为Interceptor链中的最后一个Interceptor,没有后续Interceptor。
public final class RealInterceptorChain implements Interceptor.Chain { private final List<Interceptor> interceptors; private final StreamAllocation streamAllocation; private final HttpStream httpStream; private final Connection connection; private final int index; private final Request request; private int calls; public RealInterceptorChain(List<Interceptor> interceptors, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpStream httpStream, Connection connection, int index, Request request) { this.interceptors = interceptors; this.connection = connection; this.streamAllocation = streamAllocation; this.httpStream = httpStream; this.index = index; this.request = request; }
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain( interceptors, streamAllocation, httpStream, connection, index + 1, request); Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index); Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
RealInterceptorChain + Interceptor实现了装饰器模式,实现了请求/响应的串式或流式处理。只不过内层装饰器不是外层装饰器的成员变量,而是接口方法中创建的临时变量。
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException { RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain; Request request = realChain.request(); StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation(); // We need the network to satisfy this request. Possibly for validating a conditional GET. boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !request.method().equals("GET"); HttpStream httpStream = streamAllocation.newStream(client, doExtensiveHealthChecks); RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection(); return realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, httpStream, connection); }
在Http1xStram中,它利用Okio对Socket的读写操作进行封装,而创建HttpStream 对象的过程涉及到 StreamAllocation、RealConnection,代码较长,这里就不展开,这个过程概括来说,就是找到一个可用的RealConnection,再利用RealConnection 的输入输出(BufferedSource 和BufferedSink)创建HttpStream 对象,供后续步骤使用。
里我们可以看到,核心工作都由HttpStream对象完成,而HttpStream实际上利用的是 Okio,而 Okio 实际上还是用的Socket,所以没什么神秘的,只不过一层套一层,层数有点多。
其实 Interceptor 的设计也是一种分层的思想,每个Interceptor 就是一层。为什么要套这么多层呢?分层的思想在 TCP/IP 协议中就体现得淋漓尽致,分层简化了每一层的逻辑,每层只需要关注自己的责任(单一原则思想也在此体现),而各层之间通过约定的接口/协议进行合作(面向接口编程思想),共同完成复杂的任务。
个人理解:
OkHttpClient.newCall(request)进行execute或者enqueue操作
Request保存了url,method,body,head等信息
1.调用dispatcher的enqueue方法
dispatcher维护了一个类似于CachedThreadPool的线程池,比较适合执行大量的耗时比较少的任务。线程池正在运行的请求主机数小于5时则把请求加载到runningAsyncCalls中并在线程池中执行。
2.进入拦截器链
重试和重定向:处理重定向事件
bridge:完善请求头,加载cookie
Cache:读取缓存(ETAG,LastModified),判断缓存是否过期,如果未过期则直接返回,不再进入后续拦截器。如果开启网络连接则判断是否要缓存响应
Connection:建立连接
其中,Cache这里的缓存都是基于Map,key是请求中url的md5,value是在文件中查询到的缓存,页面置换基于LRU算法
建立连接后,核心工作都由HttpStream对象完成,而HttpStream实际上利用的是 Okio,而 Okio 实际上还是用的Socket
