207.课程表
现在你总共有 n 门课需要选,记为 0 到 n-1。在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 例如,想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 ,我们用一个匹配来表示他们: [0,1]给定课程总量以及它们的先决条件,判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?
示例 1:输入: 2, [[1,0]],输出: true,解释: 总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0。所以这是可能的。
示例 2:输入: 2, [[1,0],[0,1]]输出: false,解释: 总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要先完成课程 0;并且学习课程 0 之前,你还应先完成课程 1。这是不可能的。
分析:这个问题相当于查找一个循环是否存在于有向图中,可使用BFS/DFS,本体先使用BFS,易于理解。如何判断一门课程能够学习--这门课程不用先修课程,或者先修课程已经完成,我们将已经修完的课程直接抛弃参与以后的讨论。一门课程的先修课程数即使‘’入度‘,当入度为0时,就说明这门课程可以完成,所以我们首先创建一个degree数组存储每门课程的入度。当一个有向图中不存在环,那么刚开始时肯定有一个入度为0,即没有先修课程的课程。我们以此课程进行广度遍历。没遍历到一门课程,那么说明此条路径可达,那么这门课程的入度减一,如果入度变为0,说明此课程不在环内,待完成课程数减一。最后查看待完成课程是否为0.如何实现遍历呢,使用队列,先进先出
实例:degree[] = {0 ,0 ,1, 1, 2, 1}
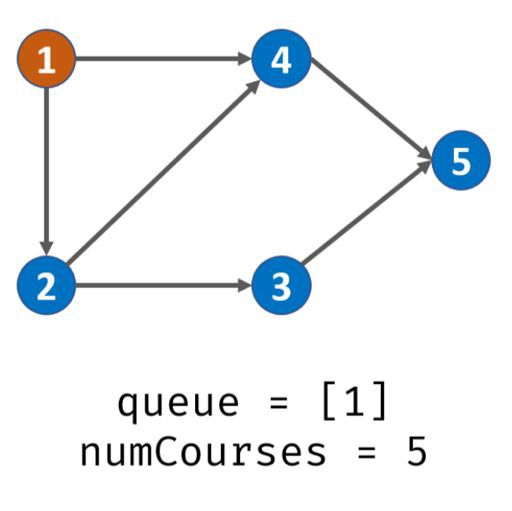
以课程1为出发点遍历有序图,将课程1放入队列。此时栈内:1
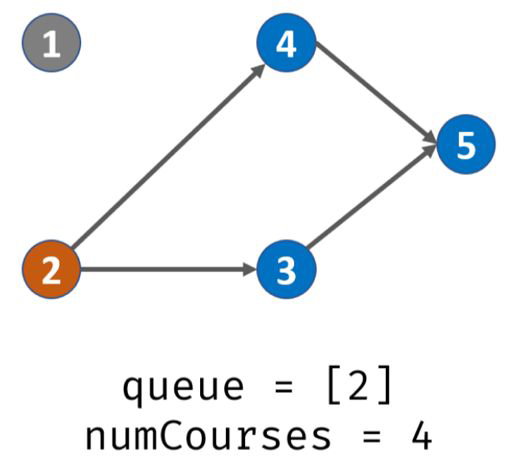
出栈,遍历prerequisites[][],发现课程2的先修课程是1,那么就将degree[2] -1,此时degree[2]=0,那么说明2入度为0,可完成,入栈。此时栈内:2
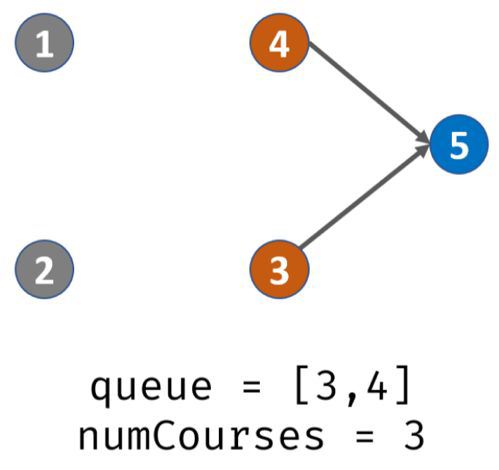
出栈,遍历prerequisites[][],发现课程3的先修课程是2,那么就将degree[3 ]-1,此时degree[3]=0,那么说明3入度为0,可完成,入栈。此时栈内:3

(此处不用出栈,因为还在以课程2为入度的循环内)遍历prerequisites[][],发现课程4的先修课程是2,那么就将degree[4] -1,此时degree[4]=1,那么说明4入度为0,可完成,入栈。此时栈内:3,4
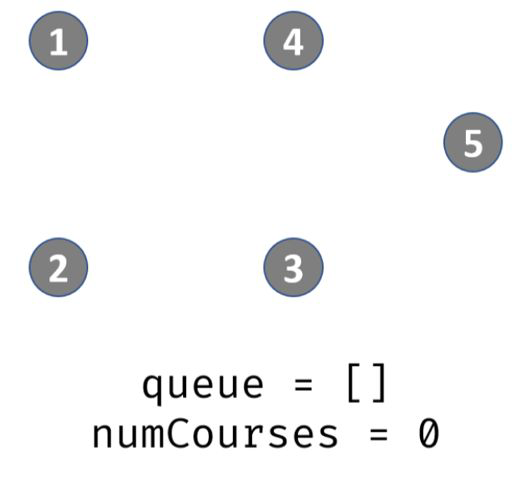
出栈,遍历prerequisites[][],发现课程5的先修课程是3,那么就将degree[5 ]-1,此时degree[5]=1,那么说明5入度为1,不可完成。此时栈内:4
出栈,遍历prerequisites[][],发现课程5的先修课程是4,那么就将degree[5 ]-1,此时degree[5]=0,那么说明5入度为0,可完成。入栈,此时栈内:5
出栈,遍历prerequisites[][],发现没有以5为先修课程的,那么结束循环。此时队列也为空,那么结束循环。判断此时待修课程是否为0;
1 class Solution { 2 public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) { 3 //计算入度数组 4 int[] degree = new int[numCourses]; 5 for(int[] cp : prerequisites){ 6 degree[cp[0]]++; 7 } 8 //存放入度为0课程 9 LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList(); 10 //找出入度为0的课程 11 for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++){ 12 if(degree[i]==0) queue.addLast(i); 13 } 14 //找到下一个入度为0的 15 while(!queue.isEmpty()){ 16 //出栈,能够完成的课程 17 Integer pre = queue.removeFirst(); 18 numCourses--; 19 for(int[] req : prerequisites){ 20 if(req[1] != pre) continue; 21 degree[req[0]]--; 22 if(degree[req[0]] == 0) queue.addLast(req[0]); 23 } 24 } 25 return numCourses==0; 26 } 27 }
208.实现Trie(前缀树)
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个操作。
示例:
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // 返回 true
trie.search("app"); // 返回 false
trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // 返回 true
分析:Trie根节点不存入值
1.Trie节点结构:一个int[26]数组来存储字符值,一个boolean类型is_end判断是否以该字符结尾。下图表示leet在树中的表示。
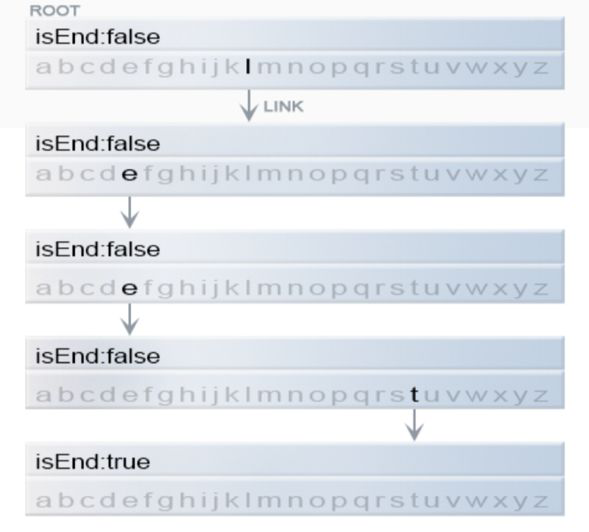
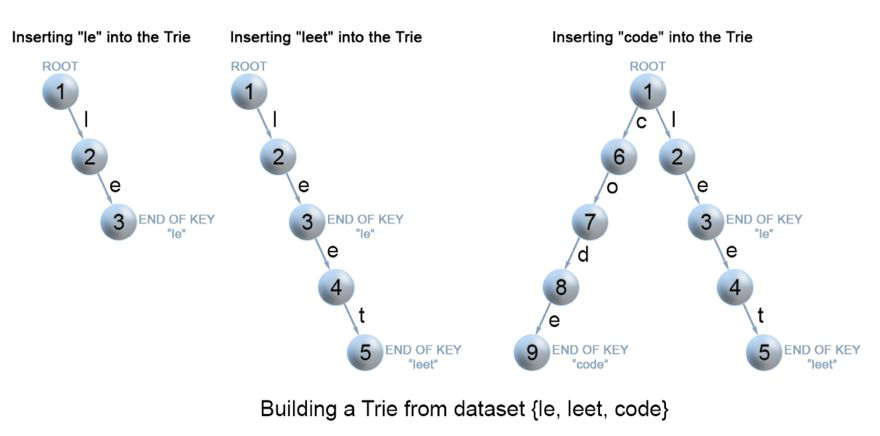
2.插入:插入一个值,从根部开始搜索字符值,存在两种情况:
链接存在:继续向下搜索
链接不存在:创建新节点,直到达到插入值最后一个字符,将末尾字符is_end设置为true
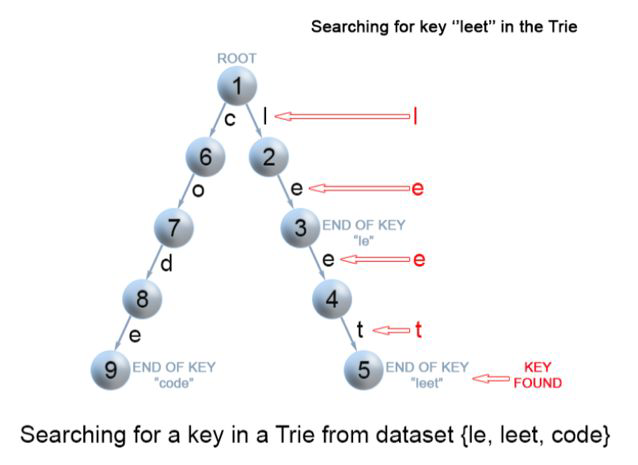
3.查找:
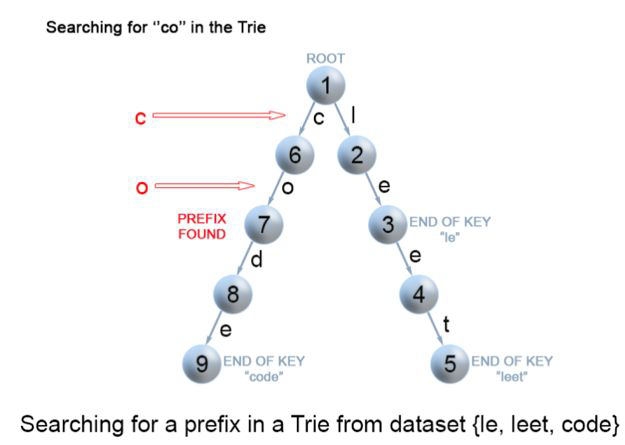
4.前缀
1 class TrieNode{ 2 TrieNode[] chiled;//记录孩子节点 3 boolean is_end; 4 TrieNode(){ 5 chiled = new TrieNode[26];//一个孩子节点有2266个分支,即一层树有26各分支 6 is_end = false; 7 } 8 } 9 class Trie { 10 TrieNode root;//根节点,不存值 11 /** Initialize your data structure here. */ 12 public Trie() { 13 root = new TrieNode(); 14 } 15 16 /** Inserts a word into the trie. */ 17 public void insert(String word) { 18 TrieNode node = root; 19 for(int i=0;i<word.length();i++){ 20 char c = word.charAt(i); 21 if(node.chiled[c-'a']==null){//如果该层该字符位置为空,则新建一个 22 node.chiled[c-'a'] = new TrieNode(); 23 } 24 node = node.chiled[c-'a'];//指向下一层 25 } 26 node.is_end = true;//字符串最后一个字符那层的位置is_end=true 27 } 28 29 /** Returns if the word is in the trie. */ 30 public boolean search(String word) { 31 TrieNode node = root; 32 for(int i=0;i<word.length();i++){ 33 char c= word.charAt(i); 34 if(node.chiled[c-'a'] == null){//判断是否存在 35 return false; 36 } 37 node = node.chiled[c-'a']; 38 } 39 return node.is_end;//判断结尾 40 } 41 42 /** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */ 43 /** 44 *serach和startWith区别在于是否判断结尾is_end,startWith是只要字符存在就行 45 */ 46 public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { 47 TrieNode node = root; 48 for(int i=0;i<prefix.length();i++){ 49 char c= prefix.charAt(i); 50 if(node.chiled[c-'a'] == null){//判断是否存在 51 return false; 52 } 53 node = node.chiled[c-'a']; 54 } 55 return true; 56 } 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such: 61 * Trie obj = new Trie(); 62 * obj.insert(word); 63 * boolean param_2 = obj.search(word); 64 * boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix); 65 */
215.数组中最K个最大元素
示例 1:输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2,输出: 5
示例 2:输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4,输出: 4
分析:排序,输出nums[length-K],快排O(NlogN);复杂度不咋地,看了题解使用堆排序,维持一个大小为K的小顶堆,那么堆顶就是答案,如果大于堆顶且堆满就加入,反之不操作,复杂度为O(NlogK)。
1 class Solution { 2 public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { 3 //利用最小堆,创建k+1的size,遍历数组进行添加,并poll一个 4 PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue(k+1); 5 for(int num : nums){ 6 heap.add(num); 7 if(heap.size() > k){ 8 heap.poll(); 9 } 10 } 11 return heap.poll(); 12 } 13 }
221.最大正方形
在一个由 0 和 1 组成的二维矩阵内,找到只包含 1 的最大正方形,并返回其面积。
示例:
输入: 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 输出: 4
分析:动态规划,建立一个二维数组dp[i][j],在左上角矩阵中由matrix[i-1][j-1]参与构成的最大正方形边长。
如果matrix[i-1][j-1]='1' => dp[i][j] = min{dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i][j-1] } +1。否则 dp[i][j]=0。

1 class Solution { 2 public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) { 3 if(matrix.length == 0) return 0; 4 int rl = matrix.length; 5 int cl = matrix[0].length; 6 int[][] dp = new int[rl+1][cl+1]; 7 int maxLen = 0; 8 for(int i=1;i<=rl;i++){ 9 for(int j=1;j<=cl;j++){ 10 if(matrix[i-1][j-1] == '1'){ 11 dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1], Math.min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]))+1; 12 maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, dp[i][j]); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 return maxLen*maxLen; 17 } 18 }
226.翻转二叉树
示例:
输入:
4
/
2 7
/ /
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/
7 2
/ /
9 6 3 1
分析:递归
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { 12 if(root == null){ 13 return root; 14 } 15 TreeNode leftNode = invertTree(root.left); 16 TreeNode rightNode = invertTree(root.right); 17 root.left = rightNode; 18 root.right = leftNode; 19 return root; 20 } 21 }
迭代
class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return null; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); TreeNode temp = node.left; node.left = node.right; node.right = temp; if(node.left!=null) queue.add(node.left); if(node.right!=null) queue.add(node.right); } return root; } }
234.回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:输入: 1->2输出: false
示例 2:输入: 1->2->2->1输出: true
分析:1.快慢指针,指向中间。2.将前半段倒序。3.遍历比较
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } 7 * } 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { 11 if(head == null || head.next == null) return true; 12 ListNode cur = head; 13 ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next, pre = null, prepre = null; 14 while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){ 15 pre = slow;//先保存slow 16 slow = slow.next; 17 fast = fast.next.next; 18 //先移动再反转 19 pre.next = prepre; 20 prepre = pre; 21 } 22 ListNode p2 = slow.next;//右边 23 slow.next = pre; 24 ListNode p1 = fast == null ? slow.next : slow;//如果是奇数个,则跳过中间节点 25 while(p1 != null){ 26 if(p1.val != p2.val) 27 return false; 28 p1 = p1.next; 29 p2 = p2.next; 30 } 31 return true; 32 } 33 }
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
示例 1:输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1;输出: 3,解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
示例 2:输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4;输出: 5,解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
分析:递归,从根节点开始。如果存在公共祖先,所以要么是根节点,要么在左子树或右子树。如果根节点已经包含待求值中的某一值,则根节点一定是最早公共祖先(一个节点先遍历到,另一个节点是其祖先)。遍历过程中,存在三种情况:
- 如果左子树中没有待求值,但右子树中返回了某一节点值,则可判断右子树中存在公共子节点,而递归操作就可以达到查找到最早公共子节点的作用
- 如果左子树中返回每一节点,而右子树中为空,与上述情况相同
- 如果左右子树均有返回节点,则可判断左右子树中应分别有一个待求节点,故此时的根节点一定是最早公共祖先。
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { 12 if(root == null || root == p || root == q){ 13 return root; 14 } 15 //根据当前节点寻找左右子树 16 TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); 17 TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); 18 //如果左子树有一个,右子树也找到一个,则返回当前节点 19 if(left!=null&&right!=null){ 20 return root; 21 } 22 //左子树没有,那么去右子树找 23 if(left == null) return right; 24 //与上述相反 25 if(right == null) return left; 26 return null; 27 } 28 }
238.除自身以外数组的乘积
给定长度为 n 的整数数组 nums,其中 n > 1,返回输出数组 output ,其中 output[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积。
示例:输入: [1,2,3,4],输出: [24,12,8,6]
说明: 请不要使用除法,且在 O(n) 时间复杂度内完成此题。
分析:暴力法不可取,O(N^2)。乘积 = 当前数左边乘积 * 当前数右边乘积。设置一数组,一次从头到尾遍历原数组存入左边乘值,一次从未到头遍历原数组存入右边乘值。例如:[1,2,3,4]
从前往后:[1,1*1, 2*1, 2*3]
从后往前:[1*2*3*4,1*1 * 3*4,2*1 * 4,2*3]
1 class Solution { 2 public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) { 3 int[] res = new int[nums.length]; 4 int k = 1; 5 for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ 6 res[i] = k;//[1,1,2,6] 7 k *= nums[i];//[1,2,6,24]给下次乘值使用,这样就是i左边的乘值 8 } 9 k = 1; 10 for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){ 11 res[i] *= k;//[24,12,8,6] 12 k *= nums[i];//[24,24,12,4] i右边的乘值 13 } 14 return res; 15 } 16 }
239.滑动窗口最大值
给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
示例:
输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3,输出: [3,3,5,5,6,7]
解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
提示:你可以假设 k 总是有效的,在输入数组不为空的情况下,1 ≤ k ≤ 输入数组的大小。
分析:双向链表:剑指Offer;
Step1.使用一个双端队列存储滑窗内元素的下标。
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
queue
Step2.若queue为空,说明刚开始滑动,将num第一个元素的索引压入队列中。
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
queue
| 0 |
Step3.遍历num下一个元素num[1]=3,
①先判断当前索引位置减去队列最左边元素是否>=size,如果是,那么说明随着滑窗滑动,当前滑窗内的最大值滑出去了,已经不再这个滑窗内,这是需要将队列最左边元素弹出。(队列最左边为滑窗内最大值索引,判断是否有效)
②将当前元素与队列最右边的索引处的数组值对比,如果当前元素大于队列最右边对应的值,则将队列最右边的值弹出,直到找到对应值比当前元素值大的。(队列左边是最大的值,随着上述操作,会逐渐更新队列,滑出去或者新添加的值更大的话将会更新队列,保证队头对应值最大)
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1 |
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 |
---输出4
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 2 | 3 |
---输出4
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 4 |
---输出6
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 4 | 5 |
---输出6
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 4 | 5 |
---输出6
| value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
--当前索引处位置(7)-队列最左边(4)=size(3)--》滑出
| 4 | 5 | 7 |
--
| 5 | 7 |
--输出5
补充:队头是存储最大值的索引,队头被弹出的情况:新来的比队内所有数都大、队头不在当前子数组中。新来成员时,判断是否有老成员太老了和新成员是否比其他老成员大(循环比,大一个弹一个,直到队列为空或者比老成员小)。队内情况:索引由小到大,因为位于当前元素前面并且小的被淘汰了。
1 class Solution { 2 public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { 3 if(nums==null||nums.length==0) return nums; 4 int len = nums.length; 5 int[] res = new int[len-k+1]; 6 int index = 0; 7 ArrayDeque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();//队列存储的是索引值 8 for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ 9 if(queue.isEmpty()){ 10 queue.add(i);//刚开始时 11 } 12 if(i-queue.peekFirst()>=k){ 13 queue.pollFirst();//将太老的老成员提出 14 } 15 while(!queue.isEmpty() && nums[i]>=nums[queue.peekLast()]){ 16 queue.pollLast(); 17 } 18 queue.addLast(i); 19 if(i>=k-1){//k-1个元素开始,就要输出了 20 res[index++] = nums[queue.peekFirst()]; 21 } 22 } 23 return res; 24 } 25 }
240.搜索二维矩阵Ⅱ
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target。该矩阵具有以下特性:每行的元素从左到右升序排列。每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例:
现有矩阵 matrix 如下:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
给定 target = 5,返回 true。给定 target = 20,返回 false。
分析:矩阵特点:左上角最小,右下角最大。本题从左下角遍历,如果大于当前元素,则向右寻找,反之,向上寻找。复杂度O(n+m)。
1 class Solution { 2 public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) { 3 if(matrix == null || matrix.length ==0 || matrix[0].length == 0){ 4 return false; 5 } 6 int m = matrix.length; 7 int n = matrix[0].length; 8 int row = m-1, col = 0; 9 while(row >= 0 && col <= n-1){ 10 if(matrix[row][col] == target){ 11 return true; 12 }else if(matrix[row][col] < target){ 13 col++; 14 }else{ 15 row--; 16 } 17 } 18 return false; 19 } 20 }