通道(Channel):由 java.nio.channels 包定义的,Channel 表示 IO 源与目标打开的连接。Channel 类似于传统的“流”,只不过 Channel本身不能直接访问数据,Channel 只能与Buffer 进行交互。
Channel的顶层接口:
public interface Channel extends Closeable { public boolean isOpen(); public void close() throws IOException; }
其中只包含最基本的两个方法,如下图是从《Java NIO》截取的Channel继承树。
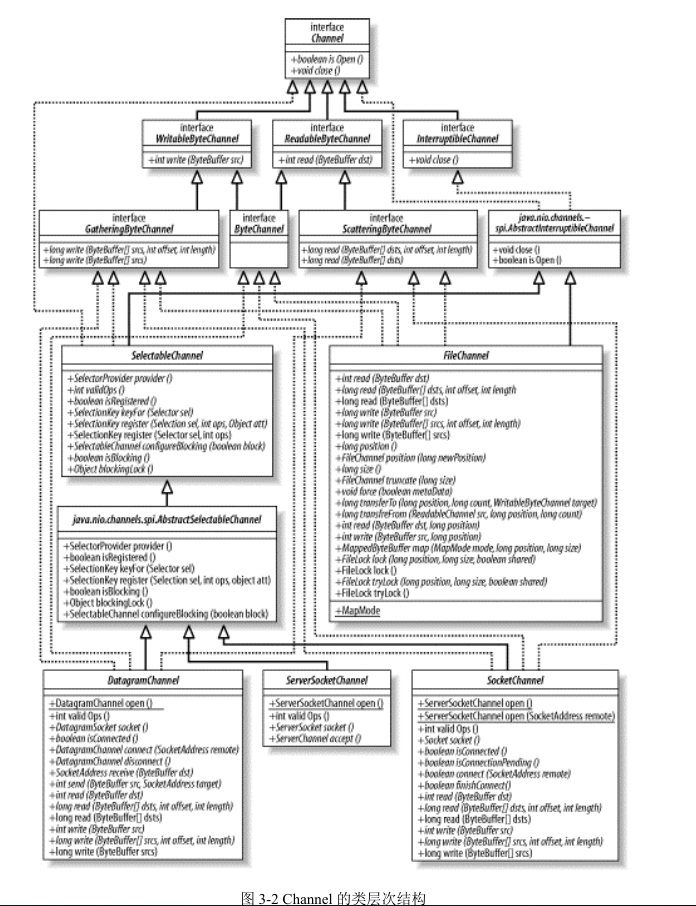
Channel可分为可读和可写,实现了对应的可读可写的Channel接口或者抽象Channel类,就可以读写兼并。
Java 为 Channel 接口提供的最主要实现类如下:
FileChannel:用于读取、写入、映射和操作文件的通道。
DatagramChannel:通过 UDP 读写网络中的数据通道。
SocketChannel:通过 TCP 读写网络中的数据。
ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的 TCP 连接,对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个 SocketChannel。
以上Channel都实现或者继承了相应的Channel读写接口或者读写抽象类,所以都是可读写的。但是因为FileChannel可以根据FileInputStream或者FileOutputStream获取,所以当根据以上类获取的FileChennel进行读或者写的时候会抛出异常。
获取Channel对象:
1. FileChannel对象的获取:
@Test
public void test() throws IOException{
//1. 使用FileInputStream获取FileChannel
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt");
FileChannel fChannel = fis.getChannel();
//2. 使用FileOutputStream获取FileChannel
FileInputStream ois = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt");
FileChannel fChannel1 = ois.getChannel();
//3, 使用RandomAccessFile对象获取
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("d:\1.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fChannel2 = raf.getChannel();
//4. FileChannel的open方法打开
FileChannel fChannel3 = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:\1.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE);
}
2. 其他三个网络Channel的获取方式:
@Test public void test2() throws IOException{ SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898)); ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); DatagramChannel datagramChannel = DatagramChannel.open(); }
Channel的读写:
1. 从Channel中读取数据到buffer
public abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException;
public abstract long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length)throws IOException;
public final long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts) throws IOException {
return read(dsts, 0, dsts.length);
}
2. 将buffer中的数据写入Channel
public abstract int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException;
public abstract long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs, int offset, int length)throws IOException;
public final long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) throws IOException {
return write(srcs, 0, srcs.length);
}
3. 如下一段文件读写的代码
public void test3() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileChannel inputChannel = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
FileChannel outputChannel = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt");
inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\1.bak.txt");
outputChannel = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = -1;
while ((len = inputChannel.read(buf)) != -1) {
buf.flip();
outputChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (outputChannel != null) {
try {
outputChannel.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
if (outputChannel != null) {
try {
outputChannel.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
if (inputChannel != null) {
try {
inputChannel.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
}
}
}
}
Channel的transferFrom和transferTo,看如下代码(为了看着简单异常直接抛出去):
public void test4() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt");
FileChannel inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\1.bak.txt");
FileChannel outputChannel = fos.getChannel();
// 直接从通道中读,在内存中分配空间,在物理内存中直接操作
// inputChannel.transferTo(0,inputChannel.size() , outputChannel);
outputChannel.transferFrom(inputChannel, 0, inputChannel.size());
}
分散(Scatter)和聚集(Gather)
1. 分散是将一个Channel中的数据写到多个顺序的buffer中,一般是传进一个buffer数组中,Channel中的数据依次写入buffer数组中的buffer当中。

2. 聚集是将多个buffer中的数据写入同一个buffer中,一般操作是一个buffer数组。

代码如下:
@Test
public void test5() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("d:\1.txt");
FileChannel inputChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\1.bak.txt");
FileChannel outputChannel = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
ByteBuffer buf3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
ByteBuffer[] bufs = { buf1, buf2, buf3 };
while (inputChannel.read(bufs) != -1) {
// 分散读取(Scattering Reads)
inputChannel.read(bufs);
for (ByteBuffer buf : bufs) {
buf.flip();
}
// 聚集写入(Gathering Writes)
outputChannel.write(bufs);
for (ByteBuffer buf : bufs) {
buf.clear();
}
}
}
Channel暂时想到这么多东西,后续有想到的再补充,开始写博客欢迎批评指正。
参看资料: 《Java NIO 中文版》