排序相关的算法复杂度分析
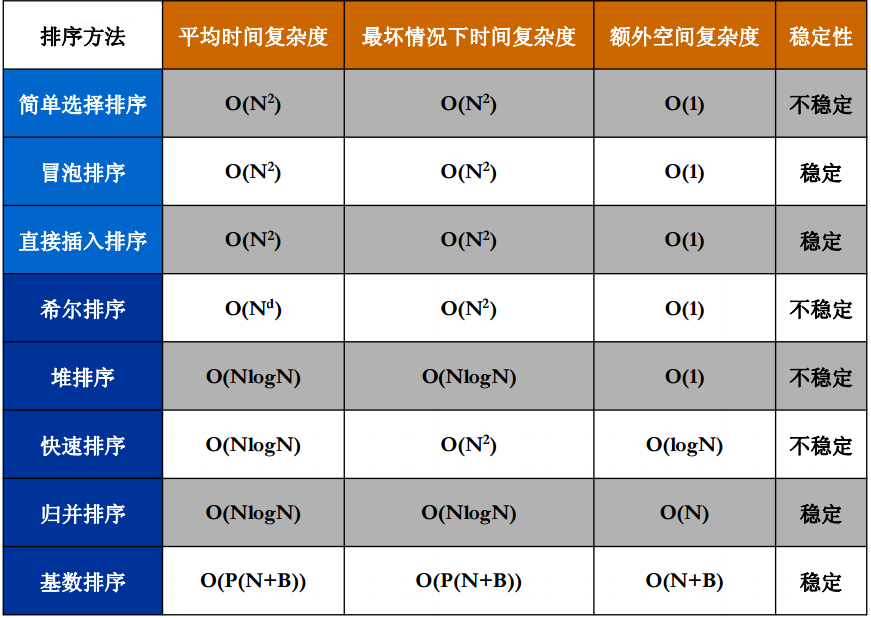
下边分别实现下各个算法
简单选择排序
1 //简单选择排序 2 void Select_Sort(int a[], int n) 3 { 4 int min; 5 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 6 { 7 int index = i; 8 min = a[i]; 9 for(int j = i; j < n; j++) 10 { 11 if(a[j] < min) 12 { 13 min = a[j]; 14 index = j; 15 } 16 } 17 swap(a[i], a[index]); 18 } 19 }
这里简单选择排序之所以不稳定是因为交换的时候会打乱顺序,例如 5,4,5,1,6。第一次交换后会是1,4,5,5,6.已经破坏了稳定性。
算法复杂度很明显是O(n^2);
冒泡排序
1 // 冒泡排序 2 void Bubble_Sort(int a[], int n) 3 { 4 for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) 5 { 6 int flag = 0; 7 for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) 8 { 9 if(a[j] > a[j+1]) 10 { 11 swap(a[j], a[j+1]); 12 flag = 1; 13 } 14 } 15 16 if(flag == 0) return ; 17 } 18 }
冒泡排序中有两点需要注意的。第一它与简单选择排序相比其最好的时间复杂度是O(n)。第二 它是稳定性的算法,因为它每次只交换相邻的元素。
只交换相邻的元素这个特点也让它可以使用于链表这个数据结构。
插入排序:
1 //插入排序 2 void Insertion_Sort(int a[], int n) 3 { 4 for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) 5 { 6 int tmp = a[i]; 7 int j; 8 for(j = i-1; (j >= 0) && (a[j] > tmp); j--) 9 { 10 a[j+1] = a[j]; 11 } 12 a[j+1] = tmp; 13 } 14 }
插入排序最好的情形也是O(n)。
希尔排序就不实现了,这个排序的时间复杂度与具体的间隔选取之间有关。
堆排序(伪代码):
1 //堆排 2 int main(void) 3 { 4 int a[] = {2,33,6,88,55,33,4,5,67,1,25}; 5 vector<int> heap(a, a + sizeof(a)/sizeof(int)); 6 Build(heap); 7 vector<int>s; 8 int maxindex = heap.size(); 9 for(int i = 0; i < maxindex; i++) 10 { 11 s.push_back(heap[0]); 12 swap(heap[0],heap[heap.size()-1]); 13 heap.pop_back(); 14 int index = 0; 15 while((2*index+1) < heap.size()) 16 { 17 int min_index = index; 18 if(heap[min_index] > heap[2*index+1]) 19 { 20 min_index = 2 * index + 1; 21 } 22 if((2 * index + 2) < heap.size()) 23 { 24 if(heap[min_index] > heap[2*index + 2]) 25 min_index = 2 * index + 2; 26 } 27 swap(heap[min_index], heap[index]); 28 if(index == min_index) 29 break; 30 else 31 index = min_index; 32 } 33 34 } 35 36 return 0; 37 } 38 39 void Build(vector<int> &heap) 40 { 41 int index = 0; 42 int max = heap.size() / 2 -1; 43 44 for(int i = max; i >= 0; i--) 45 { 46 int index = i; 47 while((2*index+1) < heap.size()) 48 { 49 int min_index = index; 50 if(heap[min_index] > heap[2*index+1]) 51 { 52 min_index = 2 * index + 1; 53 } 54 if((2 * index + 2) < heap.size()) 55 { 56 if(heap[min_index] > heap[2*index + 2]) 57 min_index = 2 * index + 2; 58 } 59 swap(heap[min_index], heap[index]); 60 if(index == min_index) 61 break; 62 else 63 index = min_index; 64 } 65 } 66 return ;
堆排序是基于选择排序的思想上提出的。这里利用实现更快的寻找最大最小值。其复杂度为O(nlgn)。它与简单选择排序相比编码较繁琐。
快速排序
1 void Quick_sort(int a[], int begin, int end) 2 { 3 if(begin >= end) 4 return ; 5 int slot = end; 6 int first = begin, last = slot-1; 7 while(1) 8 { 9 while((a[first] <= a[slot]) && (first < end)) 10 first++; 11 while((a[last] > a[slot]) && (last > 0)) 12 last--; 13 if(first < last) 14 swap(a[first], a[last]); 15 else 16 break; 17 } 18 swap(a[first],a[slot]); 19 20 Quick_sort(a, begin, first-1); 21 Quick_sort(a, first+1, end); 22 }
快排比较排序中平均速度最快的一种,但是如果选择的主元不合适,会退化为n^2的复杂度。
归并排序
1 void Divide_conquer_sort(int a[], int begin, int end) 2 { 3 if(begin >= end) 4 return ; 5 int mid = (begin + end) / 2; 6 Divide_conquer_sort(a,begin, mid); 7 Divide_conquer_sort(a, mid+1,end); 8 vector<int> store; 9 int first_begin = begin, second_begin = mid+1; 10 11 while((first_begin <= mid) && (second_begin <= end)) 12 { 13 if(a[first_begin] < a[second_begin]) 14 { 15 store.push_back(a[first_begin]); 16 first_begin++; 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 store.push_back(a[second_begin]); 21 second_begin++; 22 } 23 } 24 25 while(first_begin <= mid) 26 store.push_back(a[first_begin++]); 27 while(second_begin <= end) 28 store.push_back(a[second_begin++]); 29 for(int i = 0; i < store.size(); i++) 30 a[i+begin] = store[i]; 31 }
归并排序相对于快排没有选择主元的问题,相应的也就没有最坏时间那么一说。其实还有一种使用空间是O(1)的归并排序,实现起来要稍微复杂点。