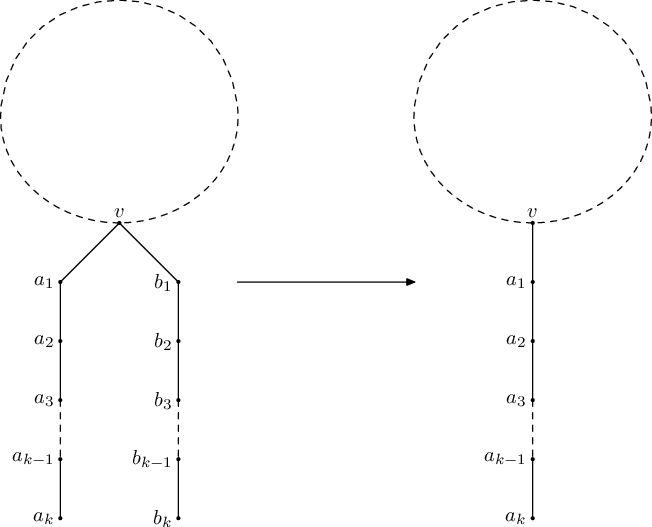
从每个叶结点开始走。如果某点连的不同子长度个数大于等于3则不存在。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 3 #include <queue> 4 #include <cstdio> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 using namespace std; 8 typedef long long ll; 9 typedef unsigned long long ull; 10 const int MAX=2e5+5; 11 set <int> edge[MAX]; 12 set <int> dis[MAX]; 13 queue <int> que; 14 bool vi[MAX]; 15 int re(int x) 16 { 17 while(x%2==0) 18 x/=2; 19 return x; 20 } 21 int solve() 22 { 23 memset(vi,false,sizeof(vi)); 24 while(!que.empty()) 25 { 26 int u=que.front(); 27 que.pop(); 28 if(vi[u]) 29 continue; 30 if(edge[u].size()==1) 31 { 32 if(dis[u].size()==1) 33 { 34 int v=*edge[u].begin(); 35 edge[u].erase(v); 36 edge[v].erase(u); 37 dis[v].insert(*dis[u].begin()+ 1 ); 38 que.push(v); 39 vi[u]=true; 40 } 41 } 42 else if(edge[u].empty()) 43 { 44 if(dis[u].size()>=3) 45 { 46 return -1; 47 } 48 if(dis[u].size()==1) 49 return re(*dis[u].begin()); 50 return re(*dis[u].begin()+*dis[u].rbegin()); 51 52 } 53 54 } 55 return -1; 56 } 57 int n; 58 int main() 59 { 60 scanf("%d",&n); 61 int i; 62 int u,v; 63 for(i=1;i<=n-1;i++) 64 { 65 scanf("%d %d",&u,&v); 66 edge[u].insert(v); 67 edge[v].insert(u); 68 } 69 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) 70 { 71 if(edge[i].size()==1) 72 { 73 que.push(i); 74 dis[i].insert(0); 75 } 76 } 77 printf("%d ",solve()); 78 }