上一篇我们学习和实现了CART(分类回归树),不过主要是针对离散值的分类实现,下面我们来看下连续值的cart分类树如何实现
思考连续值和离散值的不同之处:
二分子树的时候不同:离散值需要求出最优的两个组合,连续值需要找到一个合适的分割点把特征切分为前后两块
这里不考虑特征的减少问题
切分数据的不同:根据大于和小于等于切分数据集
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value,threshold): retDataSet = [] if threshold == 'lt': for featVec in dataSet: if featVec[axis] <= value: retDataSet.append(featVec) else: for featVec in dataSet: if featVec[axis] > value: retDataSet.append(featVec) return retDataSet
选择最好特征的最好特征值
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 bestGiniGain = 1.0; bestFeature = -1;bsetValue="" for i in range(numFeatures): #遍历特征 featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#得到特征列 uniqueVals = list(set(featList)) #从特征列获取该特征的特征值的set集合 uniqueVals.sort() for value in uniqueVals:# 遍历所有的特征值 GiniGain = 0.0 # 左增益 left_subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value,'lt') left_prob = len(left_subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet)) GiniGain += left_prob * calGini(left_subDataSet) # print left_prob,calGini(left_subDataSet), # 右增益 right_subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value,'gt') right_prob = len(right_subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet)) GiniGain += right_prob * calGini(right_subDataSet) # print right_prob,calGini(right_subDataSet), # print GiniGain if (GiniGain < bestGiniGain): #比较是否是最好的结果 bestGiniGain = GiniGain #记录最好的结果和最好的特征 bestFeature = i bsetValue=value return bestFeature,bsetValue
生成cart:总体上和离散值的差不多,主要差别在于分支的值要加上大于或者小于等于号
def createTree(dataSet,labels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] # print dataSet if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): return classList[0]#所有的类别都一样,就不用再划分了 if len(dataSet) == 1: #如果没有继续可以划分的特征,就多数表决决定分支的类别 return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat,bsetValue = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) # print bestFeat,bsetValue,labels bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] if bestFeat==-1: return majorityCnt(classList) myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = list(set(featValues)) subLabels = labels[:] # print bsetValue myTree[bestFeatLabel][bestFeatLabel+'<='+str(round(float(bsetValue),3))] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, bsetValue,'lt'),subLabels) myTree[bestFeatLabel][bestFeatLabel+'>'+str(round(float(bsetValue),3))] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, bsetValue,'gt'),subLabels) return myTree
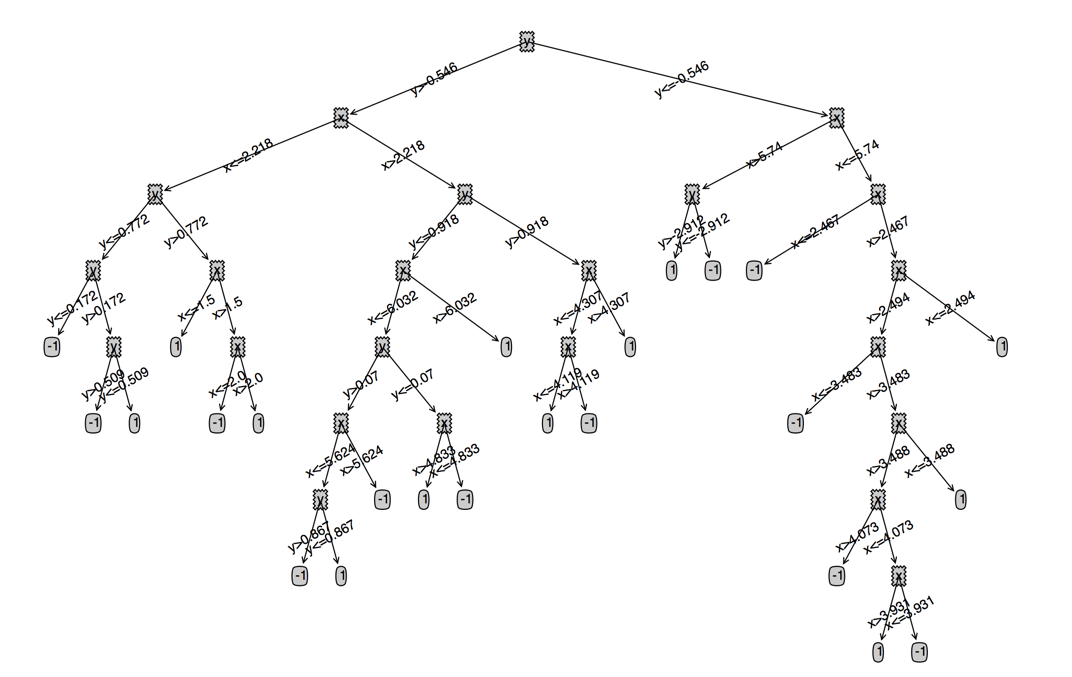
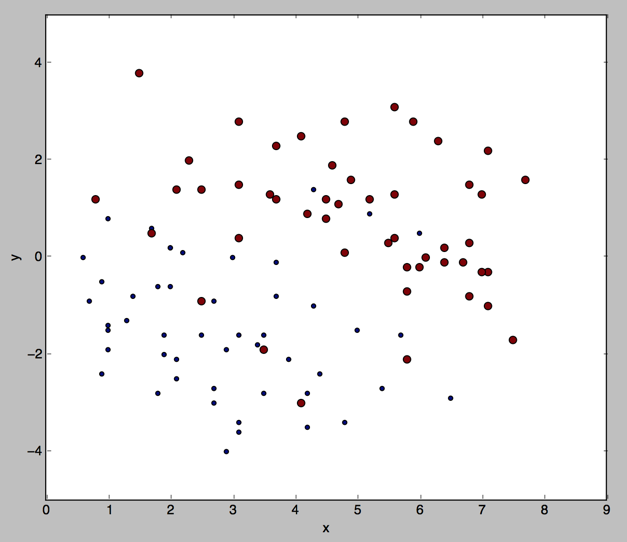
我们看下连续值的cart大概是什么样的(数据集是我们之前用的100个点的数据集)