FreeRTOS Heap简易分析
- 架构:Cortex-M3
- 版本:FreeRTOS V9.0.0
- 前言:队列、任务、信号量等都是需要内存来保存的,FreeRTOS提供了五种分配内存的方式。
1.Heap1.c
直接找到heap1.c来分析
可以看到,代码并不多,至少能说明heap1的分配内存方式应该是很简单的。
从代码中可以看出,heap1只有分配,没有释放。
那么我们具体看分配函数pvPortMalloc:
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize )
{
void *pvReturn = NULL;
static uint8_t *pucAlignedHeap = NULL;
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number of bytes. */
#if( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT != 1 )
{
if( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK )
{
/* Byte alignment required. */
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) );
}
}
#endif
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
if( pucAlignedHeap == NULL )
{
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) &ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) );
}
/* Check there is enough room left for the allocation. */
if( ( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) &&
( ( xNextFreeByte + xWantedSize ) > xNextFreeByte ) )/* Check for overflow. */
{
/* Return the next free byte then increment the index past this
block. */
pvReturn = pucAlignedHeap + xNextFreeByte;
xNextFreeByte += xWantedSize;
}
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize );
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 )
{
if( pvReturn == NULL )
{
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void );
vApplicationMallocFailedHook();
}
}
#endif
return pvReturn;
}
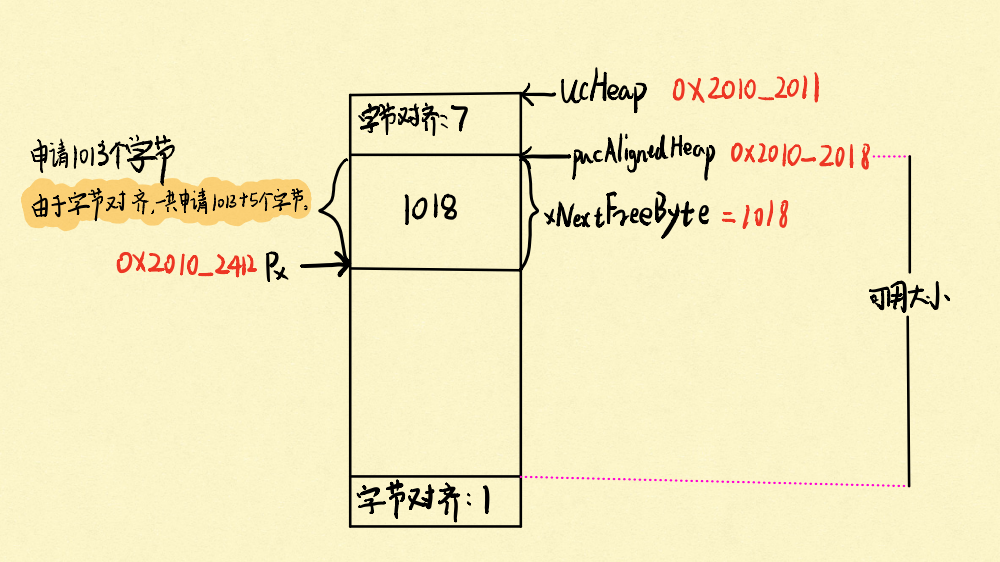
首先是字节对齐,根据不同硬件,字节对齐的长度不同。Cortex-M3是以8字节对齐的时候访问内存是更快的。heap1处理字节对齐是 &0x07,然后加上portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK 这个值,就可以做到字节对齐了。
如果是第一次分配的话,会先检查ucHeap是否处于字节对齐的位置,计算出对齐的位置后赋值给pucAlignedHeap,那么以后分配内存的时候都是以pucAlignedHeap的位置来开始分配。
分配内存时,会检查当前内存够不够分、有没有出现溢出的问题。xNextFreeByte是个全局变量,表示当前这个堆已经分配的大小,每次都会加上分配的内存大小,通过这个值,至少能得出当前用了多少RAM和还剩多少WRAM可用
heap1初始化图解:
2.heap2.c
heap2比heap复杂一下,重点在于分配和释放时,是以一种机制来操作的。
2.1申请内存
首先看prvHeapInit
static void prvHeapInit( void )
{
BlockLink_t *pxFirstFreeBlock;
uint8_t *pucAlignedHeap;
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) ( ( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) &ucHeap[ portBYTE_ALIGNMENT ] ) & ( ~( ( portPOINTER_SIZE_TYPE ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) ) );
/* xStart is used to hold a pointer to the first item in the list of free
blocks. The void cast is used to prevent compiler warnings. */
xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap;
xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0;
/* xEnd is used to mark the end of the list of free blocks. */
xEnd.xBlockSize = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE;
xEnd.pxNextFreeBlock = NULL;
/* To start with there is a single free block that is sized to take up the
entire heap space. */
pxFirstFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap;
pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE;
pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = &xEnd;
}
这一段是初始化,可以确定的是,使用了链表,并且有两个全局变量xStart,xEnd被初始化。
以及在堆中也有用来存放链表项的。在第一次调用pvPortMalloc时,就会调用prvHeapInit该函数,下面来分析pvPortMalloc
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize )
{
BlockLink_t *pxBlock, *pxPreviousBlock, *pxNewBlockLink;
static BaseType_t xHeapHasBeenInitialised = pdFALSE;
void *pvReturn = NULL;
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* If this is the first call to malloc then the heap will require
initialisation to setup the list of free blocks. */
if( xHeapHasBeenInitialised == pdFALSE )
{
prvHeapInit();
xHeapHasBeenInitialised = pdTRUE;
}
/* The wanted size is increased so it can contain a BlockLink_t
structure in addition to the requested amount of bytes. */
if( xWantedSize > 0 )
{
xWantedSize += heapSTRUCT_SIZE;
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number of bytes. */
if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 )
{
/* Byte alignment required. */
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) );
}
}
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize < configADJUSTED_HEAP_SIZE ) )
{
/* Blocks are stored in byte order - traverse the list from the start
(smallest) block until one of adequate size is found. */
pxPreviousBlock = &xStart;
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock;
while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) )
{
pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock;
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
}
/* If we found the end marker then a block of adequate size was not found. */
if( pxBlock != &xEnd )
{
/* Return the memory space - jumping over the BlockLink_t structure
at its start. */
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + heapSTRUCT_SIZE );
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out of the
list of free blocks. */
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into two. */
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE )
{
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new block
following the number of bytes requested. The void cast is
used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the compiler. */
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize );
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the single
block. */
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize;
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize;
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( pxNewBlockLink ) );
}
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize;
}
}
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize );
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 )
{
if( pvReturn == NULL )
{
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void );
vApplicationMallocFailedHook();
}
}
#endif
return pvReturn;
}
这可比heap1复杂多了。
首先初次调用会调用prvHeapInit,初始化一个用于维护可用内存的链表。具体如下:

start是这段可用内存的头结点,end是尾结点,维护可用内存这句话很重要,一定要记住。
接下来我们要申请一段8字节的内存即pvPortMalloc(8),看看发生了什么:

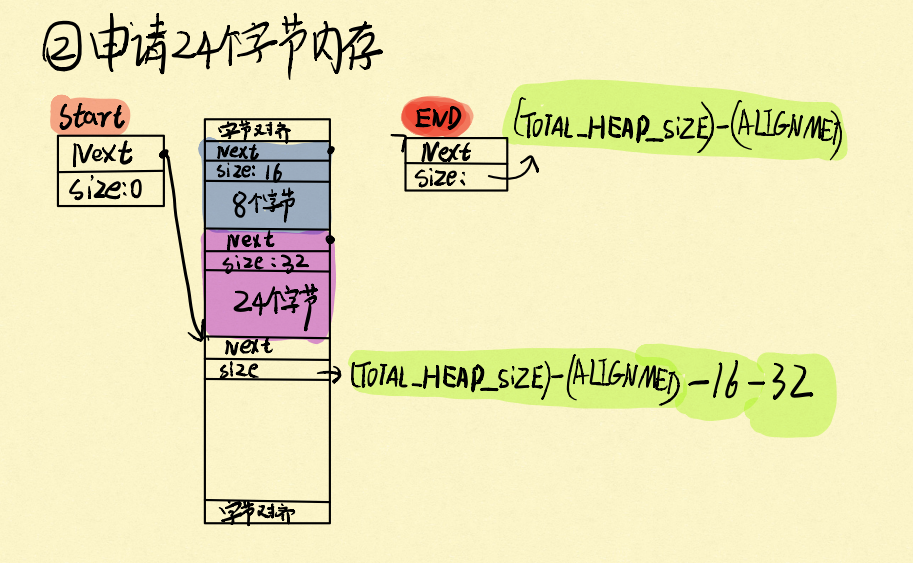
很明显,在堆里面,给你申请了16字节,前8个字节就是保存关于这段内存的描述,pxNextFreeBlock和xBlockSize,xBlockSize指整块内存的大小(包括保存信息的8字节大小的结构体),pxNextFreeBlock在释放内存的时候会用到。申请完了可用内存大小要减相对应的大小。
再申请一段24字节的内存:
2.2释放内存
具体函数:
void vPortFree( void *pv )
{
uint8_t *puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv;
BlockLink_t *pxLink;
if( pv != NULL )
{
/* The memory being freed will have an BlockLink_t structure immediately
before it. */
puc -= heapSTRUCT_SIZE;
/* This unexpected casting is to keep some compilers from issuing
byte alignment warnings. */
pxLink = ( void * ) puc;
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* Add this block to the list of free blocks. */
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) );
xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize;
traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize );
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
}
}
在释放的时候,很简单:它会把释放的这块内存的节点,从小到大地插入到维护可用内存的链表上,比如我们释放掉24字节的内存:
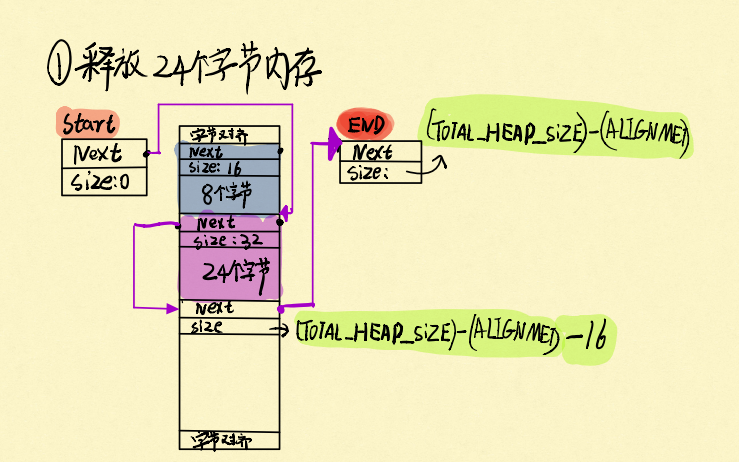
那块被我们释放的内存已经插入到可用内存的链表上了,
我们再释放掉8字节的内存,注意,这个8字节是整个链表中最小的节点,前面说过,释放的时候会从小到大的往可用内存链表里面插入:
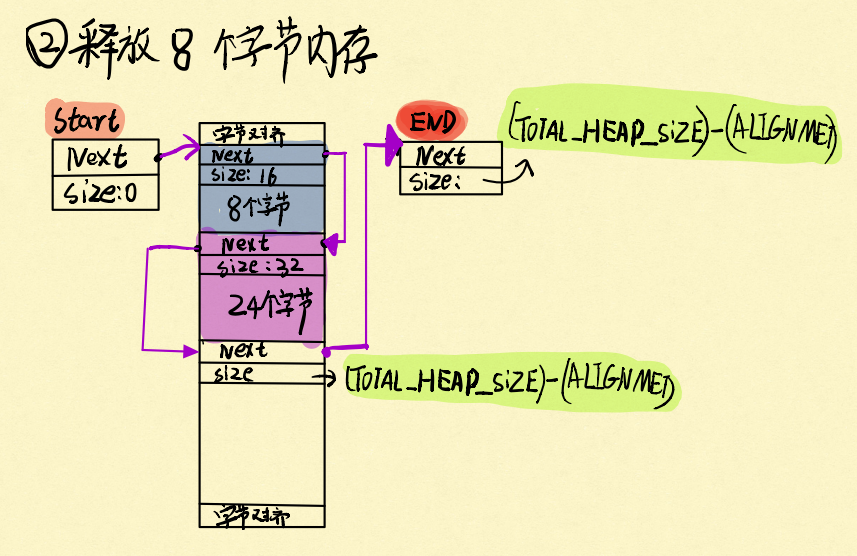
2.3 重新启用被释放过的内存
为什么要从小到大的插入?原因是当申请内存的时候,会根据heap2的算法,先从释放掉的内存里面找,找出足够大小的内存。比如,我们刚刚释放了一个8字节的内存,此时我们再想申请8内存大小的内存,heap2算法就会遍历出这块内存,并拿它出来给作为存储的地址。
如果在释放内存链表里面,有一块比较大的内存,比如,我们想要一块16字节的内存,根据heap2的算法,遍历出一块24字节的内存,那么heap2算法会把一块内存一分为二:一块16字节和一块8字节,16字节自然是返回出去给别人去用,另外一块则又以小到大的方式插入到可用内存链表里面。
heap2有一个缺点:内存碎片泄露。假设一个程序里面需要一直申请和释放,那么就会产生很多内存碎片,时间长了,内存就会越来越不够用,这是一种很危险的行为。
3.heap3.c
4.heap4.c
heap2和heap4分配内存的方式很相似。
我们想看初始化函数:
static void prvHeapInit( void )
{
BlockLink_t *pxFirstFreeBlock;
uint8_t *pucAlignedHeap;
size_t uxAddress;
size_t xTotalHeapSize = configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE;
/* Ensure the heap starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */
uxAddress = ( size_t ) ucHeap;
if( ( uxAddress & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 )
{
uxAddress += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 );
uxAddress &= ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK );
xTotalHeapSize -= uxAddress - ( size_t ) ucHeap;
}
pucAlignedHeap = ( uint8_t * ) uxAddress;
/* xStart is used to hold a pointer to the first item in the list of free
blocks. The void cast is used to prevent compiler warnings. */
xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap;
xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0;
/* pxEnd is used to mark the end of the list of free blocks and is inserted
at the end of the heap space. */
uxAddress = ( ( size_t ) pucAlignedHeap ) + xTotalHeapSize;
uxAddress -= xHeapStructSize;
uxAddress &= ~( ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK );
pxEnd = ( void * ) uxAddress;
pxEnd->xBlockSize = 0;
pxEnd->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL;
/* To start with there is a single free block that is sized to take up the
entire heap space, minus the space taken by pxEnd. */
pxFirstFreeBlock = ( void * ) pucAlignedHeap;
pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize = uxAddress - ( size_t ) pxFirstFreeBlock;
pxFirstFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd;
/* Only one block exists - and it covers the entire usable heap space. */
xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize;
xFreeBytesRemaining = pxFirstFreeBlock->xBlockSize;
/* Work out the position of the top bit in a size_t variable. */
xBlockAllocatedBit = ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 );
}
首先,和heap2相同的是,它也是维护一条可用内存的单链表,有一个头结点和尾结点,但是不同的是,heap4的尾结点end存储在堆里面,而heap2是存储在静态变量区。可用变量大小也比heap2少8个字节。具体如图:
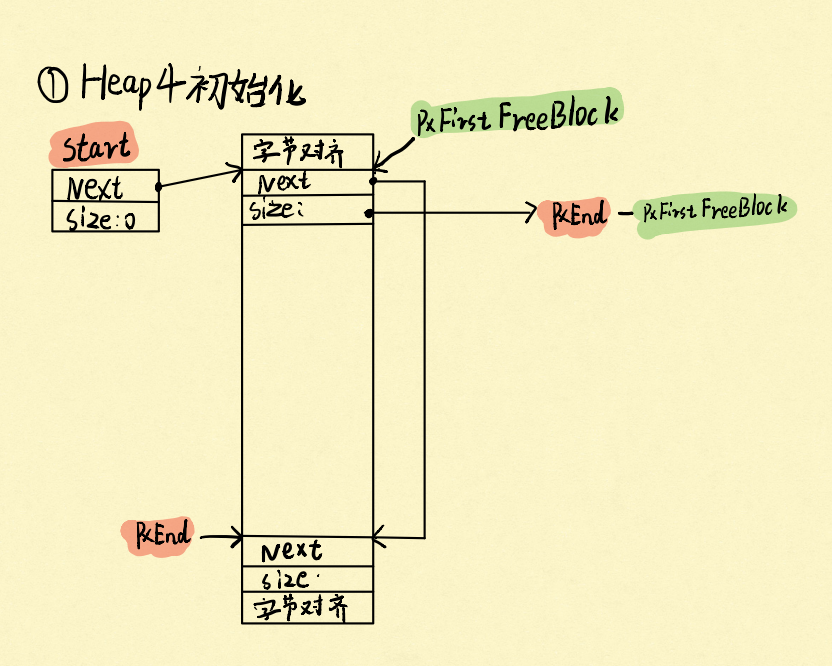
4.1 申请内存
接下来我们看配分内存函数:
void *pvPortMalloc( size_t xWantedSize )
{
BlockLink_t *pxBlock, *pxPreviousBlock, *pxNewBlockLink;
void *pvReturn = NULL;
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* If this is the first call to malloc then the heap will require
initialisation to setup the list of free blocks. */
if( pxEnd == NULL )
{
prvHeapInit();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* Check the requested block size is not so large that the top bit is
set. The top bit of the block size member of the BlockLink_t structure
is used to determine who owns the block - the application or the
kernel, so it must be free. */
if( ( xWantedSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) == 0 )
{
/* The wanted size is increased so it can contain a BlockLink_t
structure in addition to the requested amount of bytes. */
if( xWantedSize > 0 )
{
xWantedSize += xHeapStructSize;
/* Ensure that blocks are always aligned to the required number
of bytes. */
if( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0x00 )
{
/* Byte alignment required. */
xWantedSize += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) );
configASSERT( ( xWantedSize & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
if( ( xWantedSize > 0 ) && ( xWantedSize <= xFreeBytesRemaining ) )
{
/* Traverse the list from the start (lowest address) block until
one of adequate size is found. */
pxPreviousBlock = &xStart;
pxBlock = xStart.pxNextFreeBlock;
while( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize < xWantedSize ) && ( pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock != NULL ) )
{
pxPreviousBlock = pxBlock;
pxBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
}
/* If the end marker was reached then a block of adequate size
was not found. */
if( pxBlock != pxEnd )
{
/* Return the memory space pointed to - jumping over the
BlockLink_t structure at its start. */
pvReturn = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock ) + xHeapStructSize );
/* This block is being returned for use so must be taken out
of the list of free blocks. */
pxPreviousBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock;
/* If the block is larger than required it can be split into
two. */
if( ( pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize ) > heapMINIMUM_BLOCK_SIZE )
{
/* This block is to be split into two. Create a new
block following the number of bytes requested. The void
cast is used to prevent byte alignment warnings from the
compiler. */
pxNewBlockLink = ( void * ) ( ( ( uint8_t * ) pxBlock ) + xWantedSize );
configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pxNewBlockLink ) & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 );
/* Calculate the sizes of two blocks split from the
single block. */
pxNewBlockLink->xBlockSize = pxBlock->xBlockSize - xWantedSize;
pxBlock->xBlockSize = xWantedSize;
/* Insert the new block into the list of free blocks. */
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( pxNewBlockLink );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
xFreeBytesRemaining -= pxBlock->xBlockSize;
if( xFreeBytesRemaining < xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining )
{
xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xFreeBytesRemaining;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* The block is being returned - it is allocated and owned
by the application and has no "next" block. */
pxBlock->xBlockSize |= xBlockAllocatedBit;
pxBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
traceMALLOC( pvReturn, xWantedSize );
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
#if( configUSE_MALLOC_FAILED_HOOK == 1 )
{
if( pvReturn == NULL )
{
extern void vApplicationMallocFailedHook( void );
vApplicationMallocFailedHook();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif
configASSERT( ( ( ( size_t ) pvReturn ) & ( size_t ) portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) == 0 );
return pvReturn;
}
heap4和heap2分配的时候是一样的,先从空闲列表上,找到能装得下的空闲块,如图:
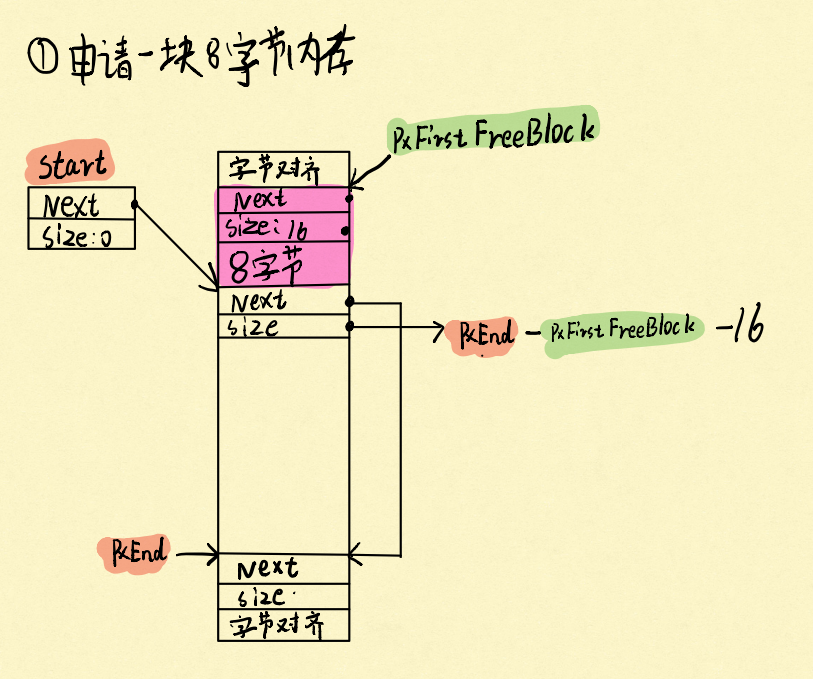
4.2 释放内存
接下来要重点说说释放内存:
void vPortFree( void *pv )
{
uint8_t *puc = ( uint8_t * ) pv;
BlockLink_t *pxLink;
if( pv != NULL )
{
/* The memory being freed will have an BlockLink_t structure immediately
before it. */
puc -= xHeapStructSize;
/* This casting is to keep the compiler from issuing warnings. */
pxLink = ( void * ) puc;
/* Check the block is actually allocated. */
configASSERT( ( pxLink->xBlockSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) != 0 );
configASSERT( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL );
if( ( pxLink->xBlockSize & xBlockAllocatedBit ) != 0 )
{
if( pxLink->pxNextFreeBlock == NULL )
{
/* The block is being returned to the heap - it is no longer
allocated. */
pxLink->xBlockSize &= ~xBlockAllocatedBit;
vTaskSuspendAll();
{
/* Add this block to the list of free blocks. */
xFreeBytesRemaining += pxLink->xBlockSize;
traceFREE( pv, pxLink->xBlockSize );
prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList( ( ( BlockLink_t * ) pxLink ) );
}
( void ) xTaskResumeAll();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
}
heap4和heap2最大的不同:就是heap4会将相邻的两个内存合并成一块内存,这样就可以解决内存泄漏的问题。比如我们申请了四块8字节的内存:
那么申请的结果就如图:
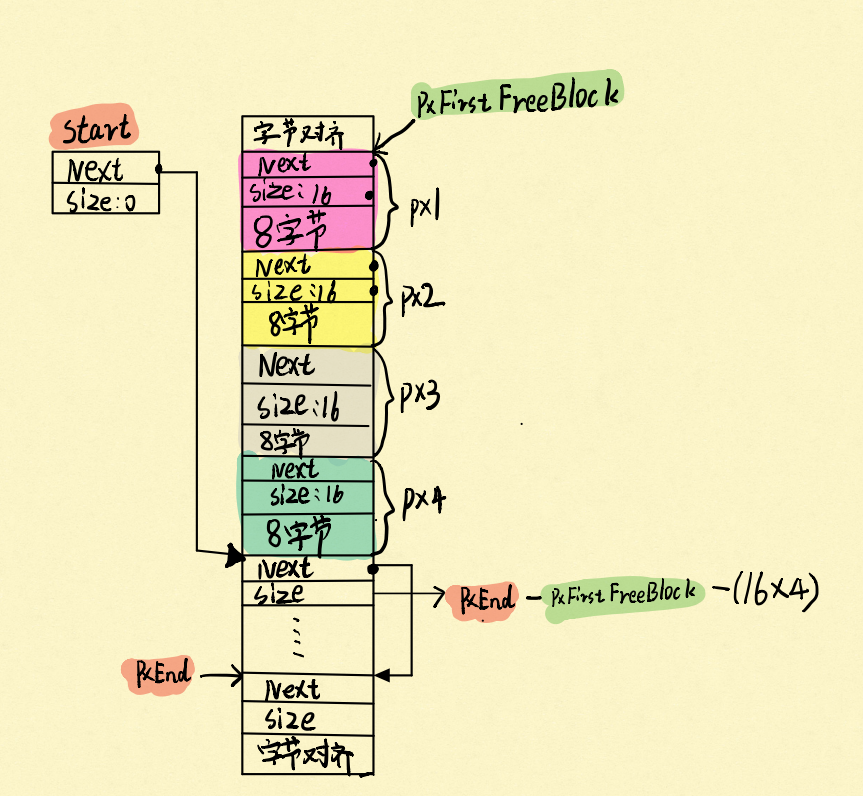
接下来按照顺序,先释放px1,再释放px2,会发生什么事:
先释放px1:
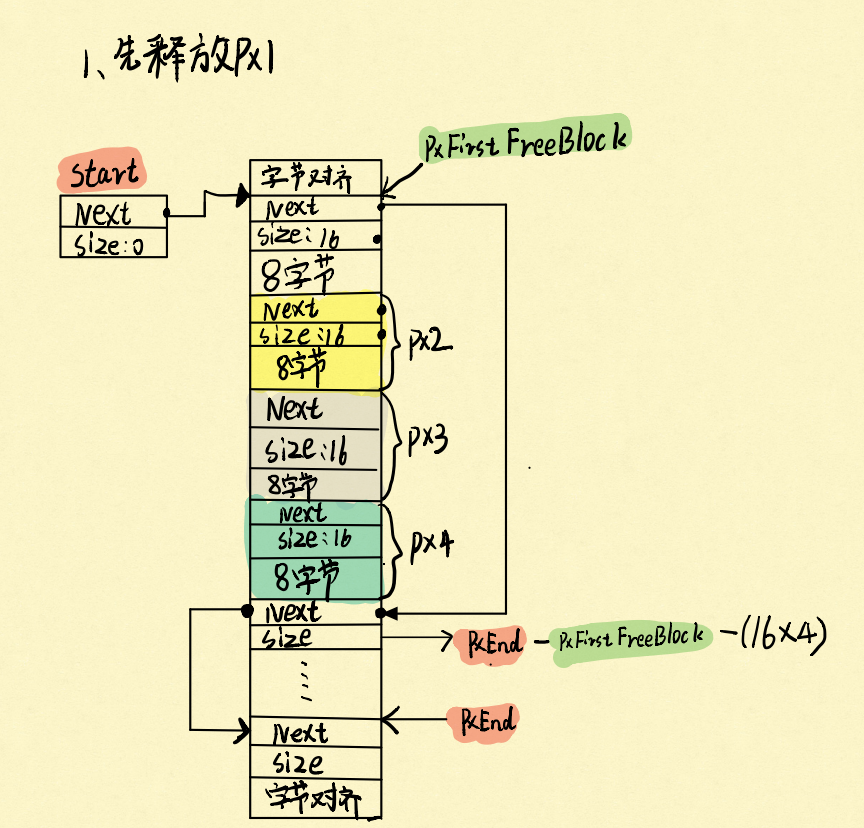
再释放px2:
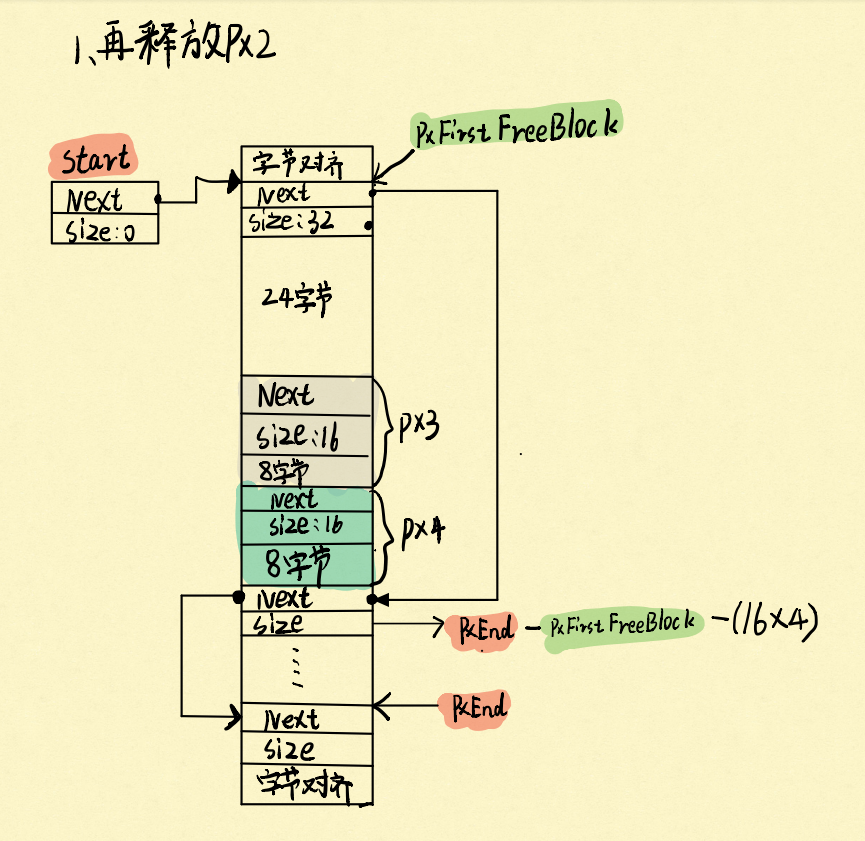
可以看到,根据heap4的合并算法,把释放的相邻两块内存合并成一块内存了。但也是有局限的,如果释放的内存相邻不是空闲内存,那么就不会合并,举个例子:
这次我们先释放px1,再释放px3,看看会发生什么:
先释放px1:
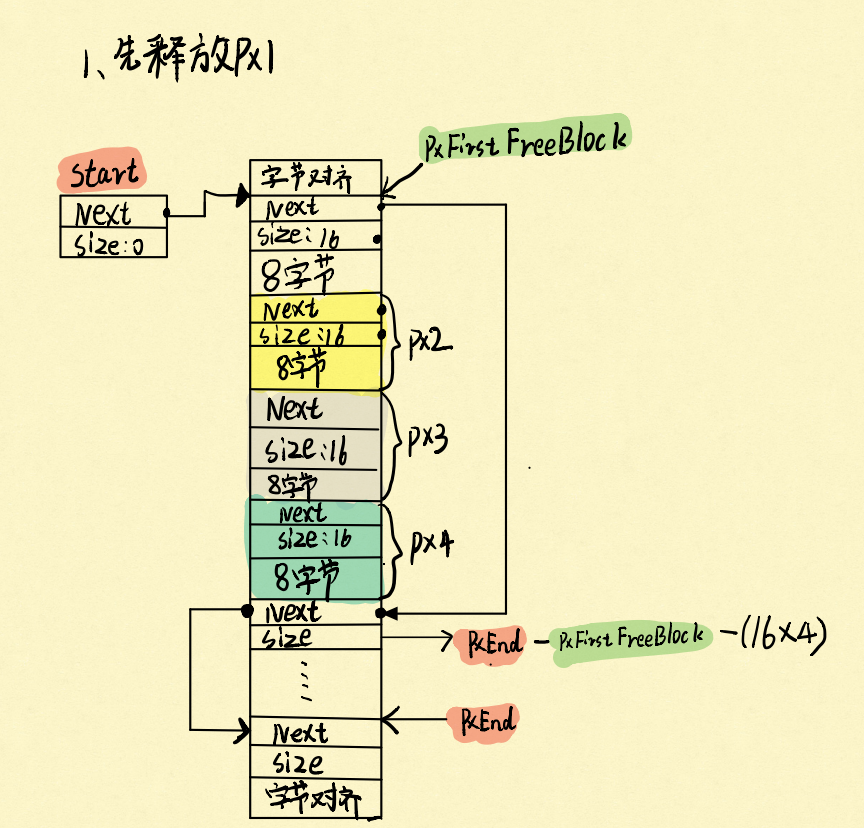
再释放px3:
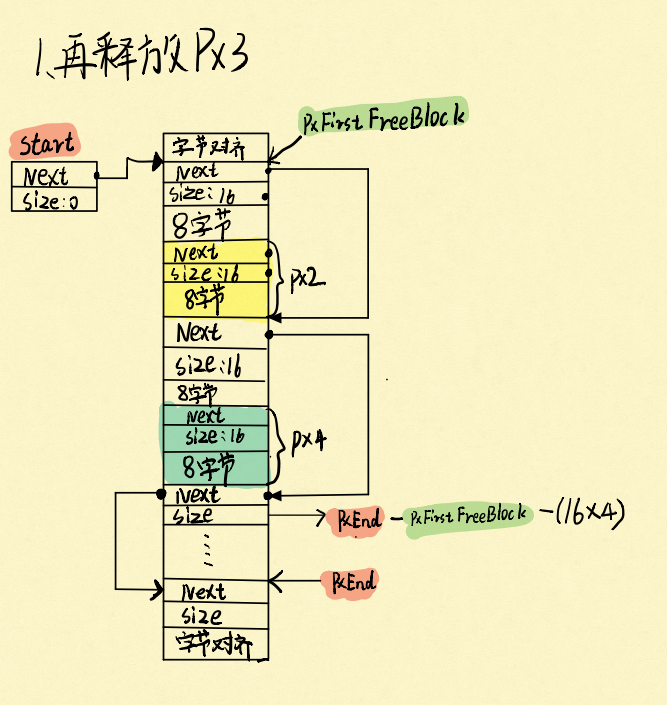
PS:空闲块也是和heap2一样,按从小到大排序插入空闲链表中的。