2017-2018-1 20155321 《信息安全系统设计基础》课堂实践——实现mypwd
学习pwd命令
pwd命令:输出当前工作目录的绝对路径
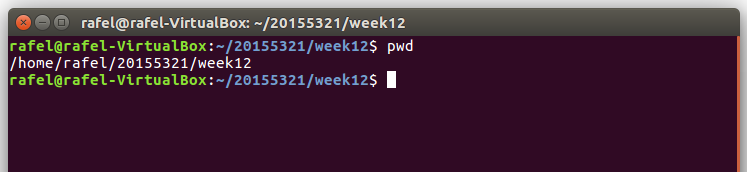
- 还可通过
man pwd具体查看pwd的详细用法

研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
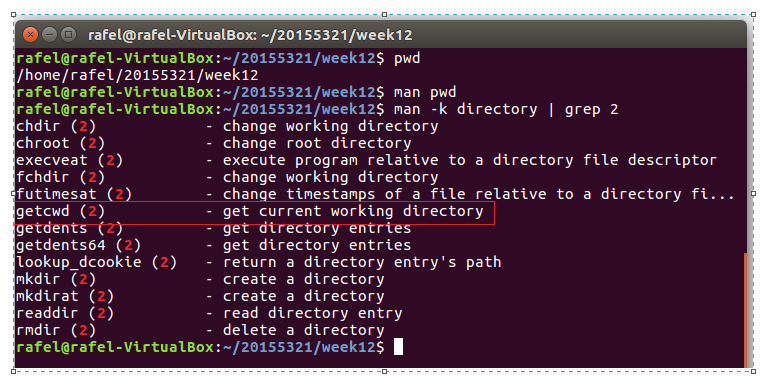
- 通过输入命令
man -k directory | grep 2寻找可以实现打印当前目录的系统调用函数,根据结果发现getcwd()函数可以实现此功能
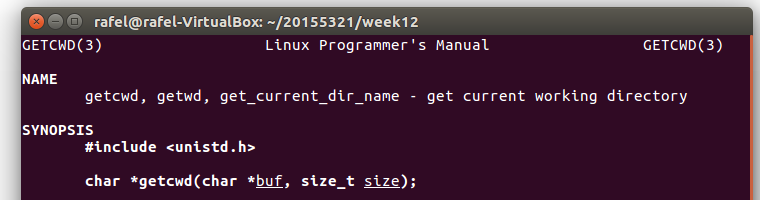
- 通过命令
man getcwd查看此函数的具体用法(包括其需要用到的头文件#include <unistd.h>和此函数相应的参数)
- 因此可得到相应的伪代码:
定义一个char数组用来保存当前目录的绝对路径;
调用内核函数```getcwd()```获取当前目录的绝对路径并保存至数组中;
if(返回的指针==NULL)
调用函数中存在错误,输出错误警告;
else
直接打印结果
实现mypwd
- 根据上述的伪代码可得到以下代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char buf[1024], *cwd =getcwd(buf, sizeof(buf));
if (cwd == NULL)
{
printf("error!
");
exit(1);
}
else
printf("%s
", cwd);
return 0;
}
测试mypwd
- 编译并运行可得到正确结果

实验反思
- 上述做法是直接调用了系统函数,没有涉及到文件系统的细节知识,在
Linux系统上,一个文件a可抽象为三个层次,如下图所示:
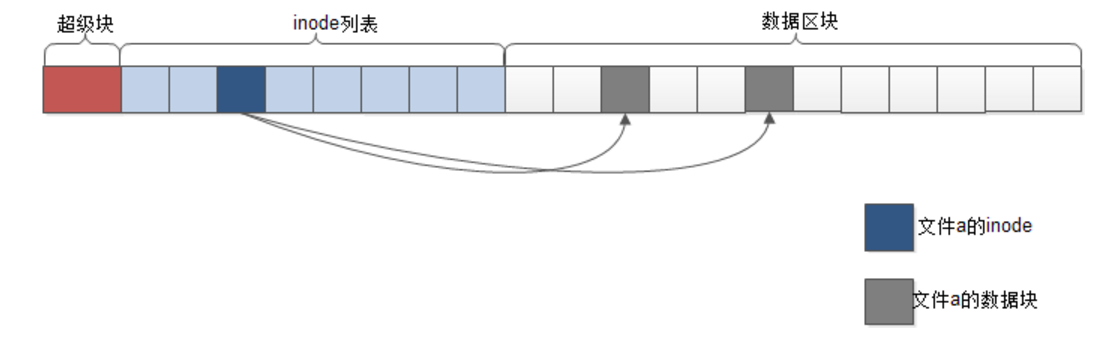
- 关于
i-node:i-node存储着根文件线管的属性信息以及指向该文件内容数据块的指针信息。一个i-node使用一个整数值(inode-number)来代表一个文件,该值对于一个文件系统而言是唯一的,即通过该值可以找到其对应的i-node。一般情况下,一个文件只有一个inode信息来描述它。 - 接下来就要获得
i-node,可用stat()函数进行实现,stat()函数的相关信息以及stat结构体如下所示:


- 打印
i-node信息的相关代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct stat file_stat;
if (stat(argv[1], &file_stat) != 0)
{
printf("error!
");
exit(0);
}
else
{
struct stat *fs = &file_stat;
printf("inode: %ld
", fs->st_ino);
printf("protection: %o
", fs->st_mode);
printf("number of hard links: %lu
", fs->st_nlink);
printf("user ID of owner: %d
", fs->st_uid);
printf("group ID of owner: %d
", fs->st_gid);
printf("file size in bytes: %ld
", fs->st_size);
printf("time of last access: %s", ctime(&fs->st_atime));
printf("time of last modification: %s", ctime(&fs->st_mtime));
printf("time of last change: %s", ctime(&fs->st_ctime));
}
return 0;
}
-
打印了
mypwd.c文件的i-node信息,如下所示:
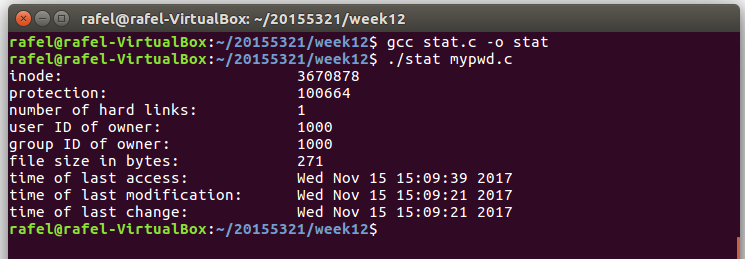
-
在
Linux系统中,目录A包含文件b,从文件系统的角度理解就是目录A的内容列表里有一个文件b的列表项,即b的inode-number和b``````filename -
用此方法实现
pwd命令的伪代码如下所示:
while(1)
{
通过文件名”.”获取当前目录的inode-number
通过文件名”..”获取当前目录的上一级目录的inode-number
if(当前目录的inode-number==上级目录的inode-number)
{
输出完整路径; //说明已是根目录
退出程序 ;
}
else
{
切换至父级目录获取并的inode-number
在父级目录中搜索对应的文件名并记录下来
}
}
- 实验代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//根据文件名获取文件inode-number
ino_t get_ino_byname(char *filename)
{
struct stat file_stat;
if (stat(filename, &file_stat) != 0)
{
printf("error!
");
exit(0);
}
return file_stat.st_ino;
}
//根据inode-number ,在当前目录中查找对应的文件名
char* find_name_byino(ino_t ino)
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
struct dirent *dptr = NULL;
char *filename = NULL;
if (NULL == (dp = opendir(".")))
{
printf("error!
");
exit(0);
}
else
{
while (NULL != (dptr = readdir(dp)))
{
if (dptr->d_ino == ino)
{
filename = strdup(dptr->d_name);
break;
}
}
closedir(dp);
}
return filename;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//记录目录名的栈
char *dir_stack[100];
unsigned current_depth = 0;
while(1){
//通过特殊的文件名“.”获取当前目录的inode-number
ino_t current_ino = get_ino_byname(".");
//通过特殊的文件名“..”获取当前目录的父级目录的inode-number
ino_t parent_ino = get_ino_byname("..");
if (current_ino == parent_ino)
break; //到达根目录
//否则切换至父级目录,根据步骤1获取的inode-number,在父级目录中搜索对应的文件名并记录下来
chdir("..");
dir_stack[current_depth++] = find_name_byino(current_ino);
}
//输出完整路径名
int i = current_depth-1;
for (i = current_depth-1; i>=0; i--) {
printf("/%s", dir_stack[i]);
}
printf("%s
", current_depth==0 ? "/" : "");
return 0;
}
- 实验结果如下,打印当前目录的绝对路径
