类加载器
Java字节码文件通过类加载器,加载到Java运行时环境(jvm虚拟机),得到字节码对象,对字节码进行修改即为反射


1)BootStrap:引导类加载器:加载都是最基础的文件
2)ExtClassLoader:扩展类加载器:加载都是基础的文件
3)AppClassLoader:应用类加载器:三方jar包和自己编写java文件
获得字节码对象的三种方式:
字节码对象.getClassLoader();
//获得Demo字节码文件的类加载器 Class clazz = Demo.class;//获得Demo的字节码对象 ClassLoader classLoader = clazz.getClassLoader();//获得类加载器 //getResource的参数路径相对classes(src) //获得classes(src)下的任何的资源 String path = classLoader.getResource("com/itheima/classloader/jdbc.properties").getPath(); //classLoader.getResourceAsStream(""); System.out.println(path);
注解
jdk5提供的注解
@Override:告知编译器此方法是覆盖父类的
@Deprecated:标注过时
@SuppressWarnings:压制警告
发现的问题:
不同的注解只能在不同的位置使用(方法上、字段上、类上)
编写一个注解
关键字:@interface
注解的属性:
语法:返回值 名称();
注意:如果属性的名字是value,并且注解的属性只有一个 那么在使用注解时可以省略value

注解属性类型只能是以下几种
1.基本类型
2.String
3.枚举类型
4.注解类型
5.Class类型
6.以上类型的一维数组类型
使用注解
在类/方法/字段 上面是@XXX
解析使用了注解的类
介入一个概念:元注解:代表修饰注解的注解,作用:限制定义的注解的特性
@Retention
SOURCE: 注解在源码级别可见
CLASS:注解在字节码文件级别可见
RUNTIME:注解在整个运行阶段都可见
@Target
代表注解修饰的范围:类上使用,方法上使用,字段上使用
FIELD:字段上可用此注解
METHOD:方法上可以用此注解
TYPE:类/接口上可以使用此注解

注意:要想解析使用了注解的类 , 那么该注解的Retention必须设置成Runtime
定义注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnno { //注解的属性 String name(); int age() default 28; //String value(); //String[] value(); }
使用注解
@MyAnno(name = "zhangsan") public class MyAnnoTest { @SuppressWarnings("all") @MyAnno(name = "zhangsan") //@MyAnno({ "aaa","bbb","ccc"}) public void show(String str){ System.out.println("show running..."); } }
解析注解
public class MyAnnoParser { public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { //解析show方法上面的@MyAnno //直接的目的是 获得show方法上的@MyAnno中的参数 //获得show方法的字节码对象 Class clazz = MyAnnoTest.class; Method method = clazz.getMethod("show", String.class); //获得show方法上的@MyAnno MyAnno annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnno.class); //获得@MyAnno上的属性值 System.out.println(annotation.name());//zhangsan System.out.println(annotation.age());//28 //根据业务需求写逻辑代码 } }
(这里为了能调用写成main方法)关于注解解析的实质:从注解中解析出属性值&获得字节码对象(并且通过.getAnnotation()方法再获取到使用了注解的方法和属性)
编写单元测试注解@MyTest
public class TestDemo { //程序员开发中测试用的 @Test public void test1(){ System.out.println("test1 running..."); } @MyTest public void test2(){ System.out.println("test2 running..."); } @MyTest public void test3(){ System.out.println("test3 running..."); } }
定义@MyTest
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyTest { //不需要属性 }
解析注解
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MyTestParster { public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException { //获得TestDemo Class clazz = TestDemo.class; //获得所有的方法 Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); if(methods!=null){ //获得注解使用了@MyTest的方法 for(Method method:methods){ //判断该方法是否使用了@MyTest注解 boolean annotationPresent = method.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest.class); if(annotationPresent){ //该方法使用MyTest注解了 method.invoke(clazz.newInstance(), null); } } } } }
(当然这个解析方法这里只能直接执行,没法修改IDE使其从使用的地方调用过来)
动态代理
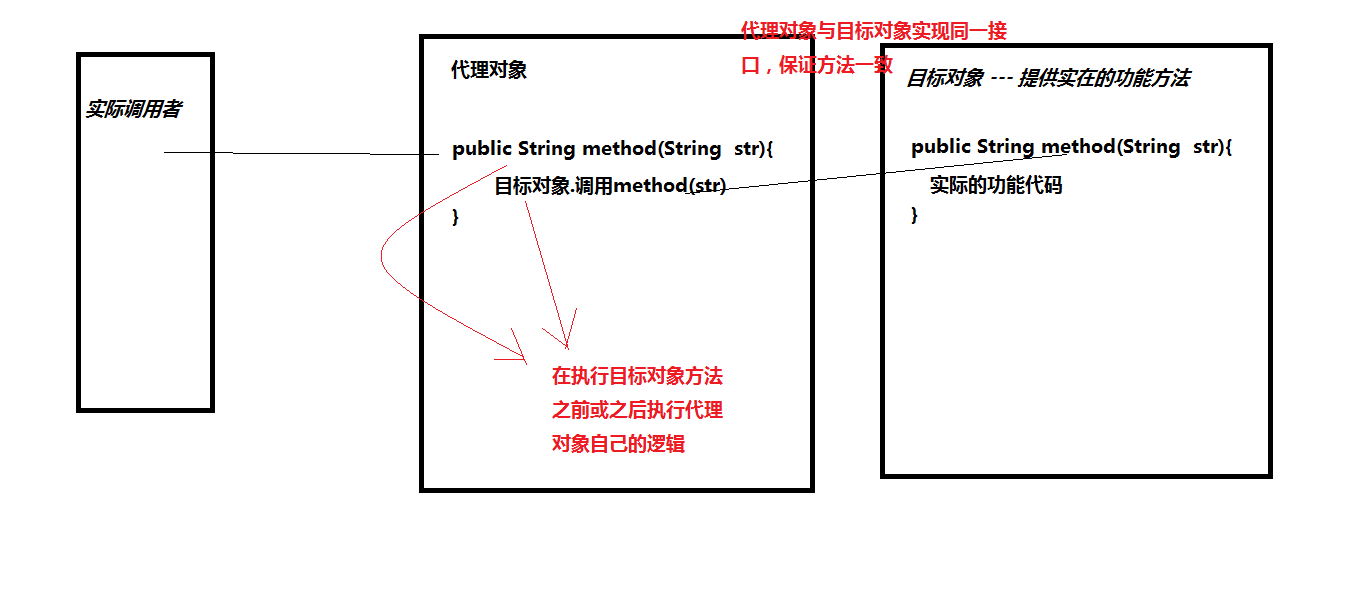
1.什么是代理(中介)
目标对象/被代理对象 ------ 房主:真正的租房的方法
代理对象 ------- 黑中介:有租房子的方法(调用房主的租房的方法)
执行代理对象方法的对象 ---- 租房的人
流程:我们要租房----->中介(租房的方法)------>房主(租房的方法)
抽象:调用对象----->代理对象------>目标对象
2.动态代理
动态代理:不用手动编写一个代理对象,不需要一一编写与目标对象相同的方法,这个过程,在运行时 的内存中动态生成代理对象。------字节码对象级别的代理对象
实现同一接口
public interface TargetInterface { public void method1(); public String method2(); public int method3(int x); }
目标对象
public class Target implements TargetInterface{ @Override public void method1() { System.out.println("method1 running..."); } @Override public String method2() { System.out.println("method2 running..."); return "method2"; } @Override public int method3(int x) { return x; } }
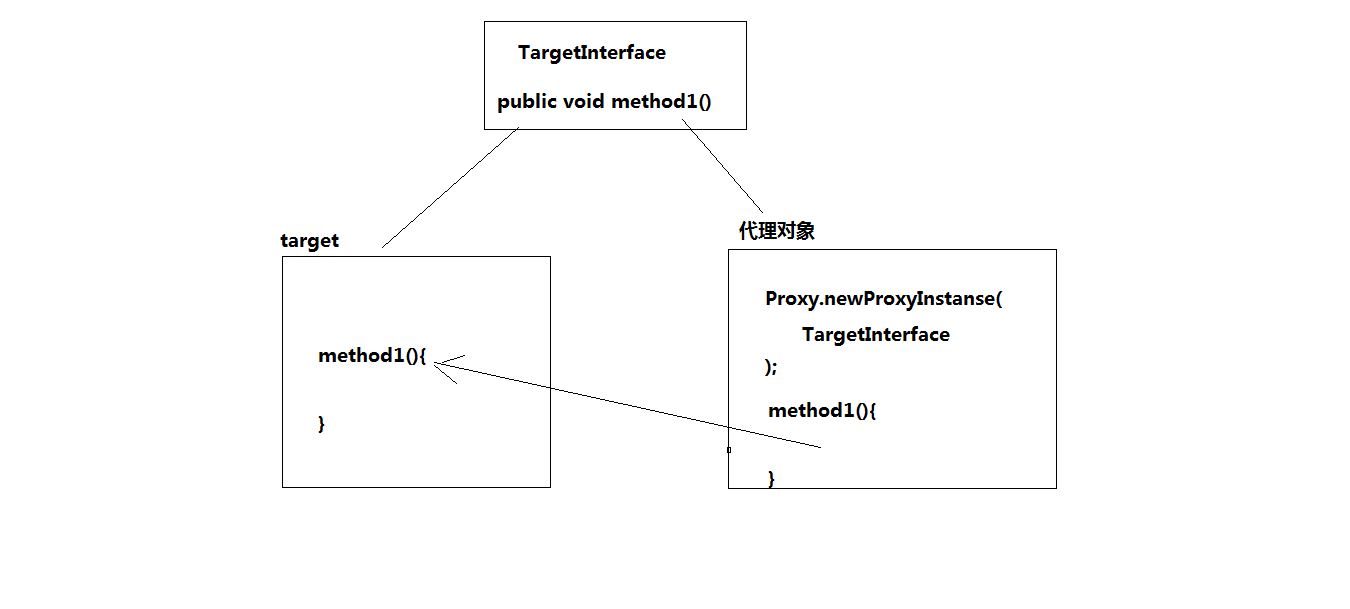
调用
public class ProxyTest { @Test public void test1(){ //获得动态的代理对象----在运行时 在内存中动态的为Target创建一个虚拟的代理对象 //objProxy是代理对象 根据参数确定到底是谁的代理对象 TargetInterface objProxy = (TargetInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance( Target.class.getClassLoader(), //与目标对象相同的类加载器 new Class[]{TargetInterface.class}, new InvocationHandler() { //invoke 代表的是执行代理对象的方法 @Override //method:代表目标对象的方法字节码对象 //args:代表目标对象的响应的方法的参数 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("目标方法前的逻辑"); //执行目标对象的方法 Object invoke = method.invoke(new Target(), args); System.out.println("目标方法后的逻辑"); return invoke; } } ); objProxy.method1(); String method2 = objProxy.method2(); System.out.println(method2); } }
调用2
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; public class ProxyTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { final Target target = new Target(); //动态创建代理对象 TargetInterface proxy = (TargetInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance( target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override //被执行几次?------- 看代理对象调用方法几次 //代理对象调用接口相应方法 都是调用invoke /* * proxy:是代理对象 * method:代表的是目标方法的字节码对象 * args:代表是调用目标方法时参数 */ public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //反射知识点 Object invoke = method.invoke(target, args);//目标对象的相应方法 //retrun返回的值给代理对象 return invoke; } } ); proxy.method1();//调用invoke---Method:目标对象的method1方法 args:null 返回值null String method2 = proxy.method2();//调用invoke---Method:目标对象的method2方法 args:null 返回值method2 int method3 = proxy.method3(100);////调用invoke-----Method:目标对象的method3方法 args:Object[]{100} 返回值100 System.out.println(method2); System.out.println(method3); } }
注意:JDK的Proxy方式实现的动态代理 目标对象必须有接口 没有接口不能实现jdk版动态代理
应用:
开启事务,结束事务,中间写业务
Spring AOP
另:使用动态代理完成全局编码(另一种是通过装饰者模式方法增强)
public class EncodingFilter implements Filter{ @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { final HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request; //使用动态代理完成全局编码 HttpServletRequest enhanceRequset = (HttpServletRequest) Proxy.newProxyInstance( req.getClass().getClassLoader(), req.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //对getParameter方法进行增强 String name = method.getName();//获得目标对象的方法名称 if("getParameter".equals(name)){ String invoke = (String) method.invoke(req, args);//乱码 //转码 invoke = new String(invoke.getBytes("iso8859-1"),"UTF-8"); return invoke; } return method.invoke(req, args); } } );
chain.doFilter(enhanceRequset, response); } @Override public void destroy() { } @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { } }