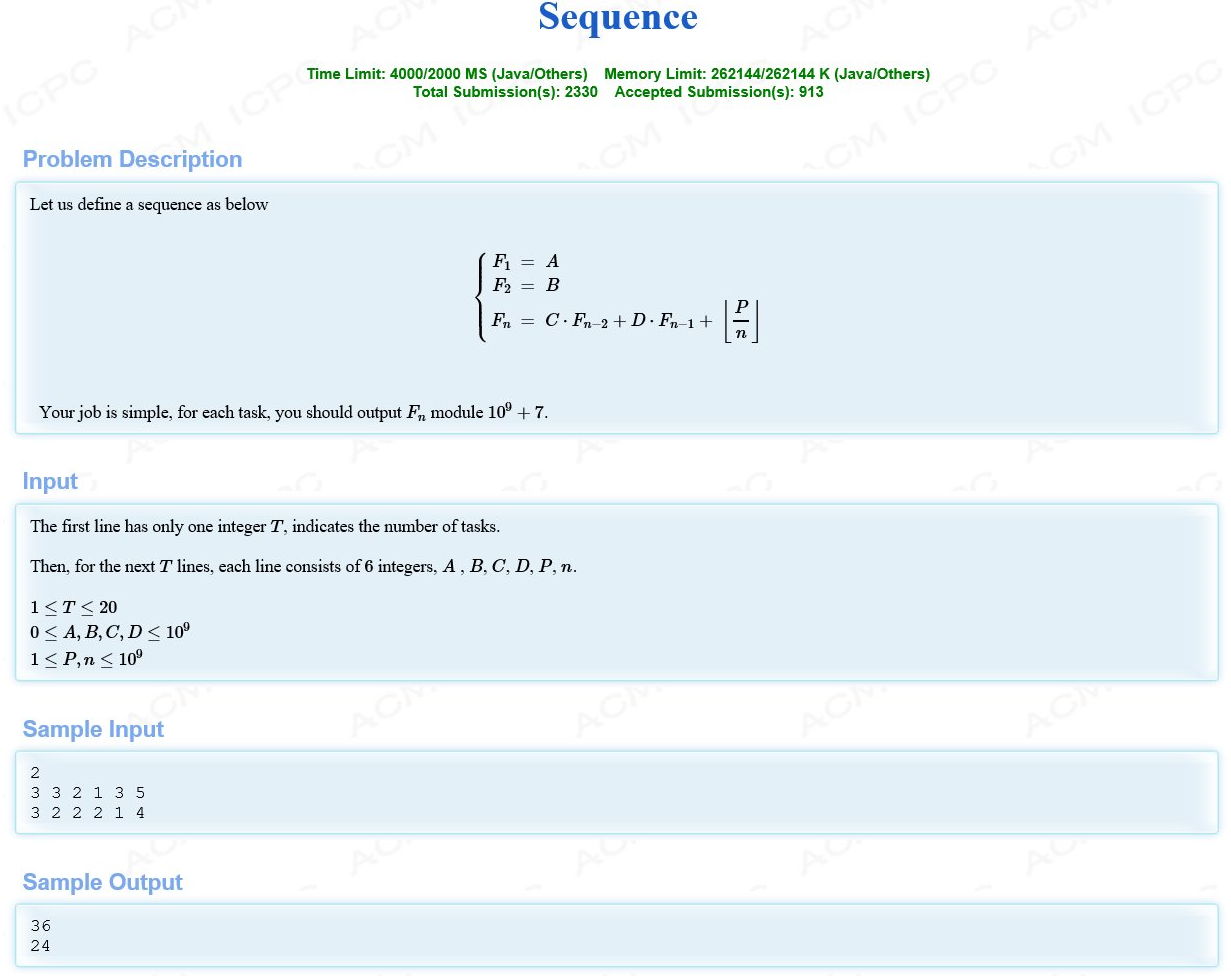
题意:就是一个矩阵快速幂的题目,难点在于p/n向下取整
解法一:
构造递推式:
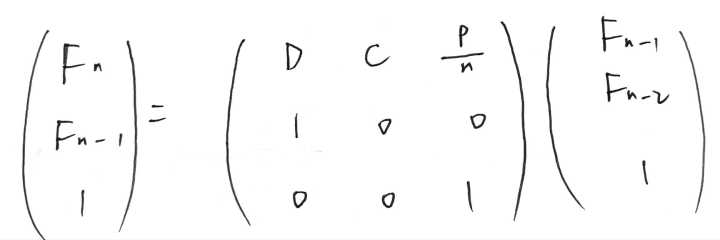
这种构造方式很好想,可以发现递推矩阵T与一般矩阵不同之处在于p/n的值一直在变
所以我们不能直接用矩阵快速幂把递推矩阵乘上n-2次
所以此时用到分段的思想:
在某一个区间内,p/i的值是相同的
经过计算这个区间是(i,p/(p/i))
所以我们对每一段用矩阵快速幂即可
从F3一直计算到Fn,一共计算n-2次
值的注意的是n>p时的情况,先计算到Fp,后面p/n都等于0,直接矩阵快速幂到Fn
以及当p==1时,需要特判(因为p-2为负数)
还有要注意矩阵左乘右乘,根据递推式应该是一直右乘,学高代的都知道结果会有很大区别
最后结果为Fn=(ans[0][0]*F2%mod+ans[0][1]*F1%mod+ans[0][2])%mod;
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long using namespace std; const int mod=1e9+7; struct mat { LL a[3][3]; }; mat matmul(mat x,mat y) { mat res; memset(res.a,0,sizeof res.a); int i,j,k; for(i=0;i<3;i++) { for(j=0;j<3;j++) { for(k=0;k<3;k++) { res.a[i][j]+=x.a[i][k]*y.a[k][j]%mod; res.a[i][j]%=mod; } } } return res; } mat matpow(mat x,LL n) { mat res; memset(res.a,0,sizeof res.a); for(int i=0;i<3;i++)res.a[i][i]=1; while(n>0) { if(n&1)res=matmul(res,x); x=matmul(x,x); n>>=1; } return res; } void solve() { LL a,b,c,d,p,n; scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&a,&b,&c,&d,&p,&n); mat t,ans; memset(t.a,0,sizeof t.a); memset(ans.a,0,sizeof ans.a); for(int i=0;i<3;i++)ans.a[i][i]=1; t.a[0][0]=d; t.a[0][1]=c; t.a[1][0]=1; t.a[2][2]=1; if(n==1)printf("%I64d ",a); else if(n==2)printf("%I64d ",b); else { LL i,j; if(p>=n) { for(i=3;i<=n;i=j+1) { j=p/(p/i); t.a[0][2]=p/i; mat pos=matpow(t,min(j-i+1,n-i+1)); ans=matmul(pos,ans); } } else { for(i=3;i<=p;i=j+1) { j=p/(p/i); t.a[0][2]=p/i; mat pos=matpow(t,j-i+1); ans=matmul(pos,ans); } t.a[0][2]=0; mat pos; if(p==1)pos=matpow(t,n-2); else pos=matpow(t,n-p); ans=matmul(pos,ans); } LL res=(ans.a[0][0]*b%mod+ans.a[0][1]*a%mod+ans.a[0][2])%mod; printf("%I64d ",res); } } int main() { int T; cin>>T; while(T--) { solve(); } return 0; }
解法二:
构造递推式https://blog.csdn.net/riba2534/article/details/81672080

这种方法递推矩阵是没有变的
还是要分段去乘
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long using namespace std; const int mod=1e9+7; struct mat { LL a[3][3]; }; mat matmul(mat a,mat b) { mat c; memset(c.a,0,sizeof c.a); int i,j,k; for(i=0;i<3;i++) { for(j=0;j<3;j++) { for(k=0;k<3;k++) { c.a[i][j]=(c.a[i][j]+a.a[i][k]*b.a[k][j]%mod)%mod; } } } return c; } mat matpow(mat a,LL b) { mat ans; memset(ans.a,0,sizeof ans.a); for(int i=0;i<3;i++)ans.a[i][i]=1; while(b>0) { if(b&1)ans=matmul(ans,a); a=matmul(a,a); b>>=1; } return ans; } void solve() { LL a,b,c,d,p,n; scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&c,&d,&p,&n); if(n==1)printf("%lld ",a); else { mat t,sta; memset(t.a,0,sizeof t.a); memset(sta.a,0,sizeof sta.a); t.a[0][0]=d; t.a[1][0]=c; t.a[0][1]=1; t.a[2][2]=1; t.a[2][0]=1; sta.a[0][0]=b; sta.a[0][1]=a; if(p>=n) { LL i,j; for(i=3;i<=n;i=j+1) { j=p/(p/i); sta.a[0][2]=p/i; mat pos=matpow(t,min(j-i+1,n-i+1)); sta=matmul(sta,pos); } } else { LL i,j; for(i=3;i<=p;i=j+1) { j=p/(p/i); sta.a[0][2]=p/i; mat pos=matpow(t,j-i+1); sta=matmul(sta,pos); } sta.a[0][2]=0; mat pos; if(p<3)pos=matpow(t,n-2); else pos=matpow(t,n-p); sta=matmul(sta,pos); } printf("%lld ",sta.a[0][0]); } } int main() { int T; cin>>T; while(T--) { solve(); } return 0; }