自然语言处理中的Attention机制
1. 前言
最开始Attention只是人们的直觉,后来被第一次应用到机器翻译中的词对其任务中。Attention机制利用每个元素被赋予的重要性评分来对序列数据进行编码。目前Attention机制有很多的变体,并且应用到了不同的任务中如:情感分类、文本摘要、QA、依存分析等。总的来说,Attention机制可以得到一个上下文编码,这个编码是序列向量的加权求和,权重是归一化的attention分数。与查询向量匹配度高的向量被赋予更高的权重,所以Attention机制本质也是一种寻址机制。本文尝试总结Attention机制的原理及其各种变体,希望对读者有所帮助。
2. Attention机制的第一个应用
传统的机器翻译任务[1]是基于Encoder-Decoder结构的,其中Encoder和Decoder都是RNN。然而,使用这样的结构做机器翻译任务是有缺陷的。第一个缺陷是RNN网络具有遗忘性,对于稍微长一点的句子编码和解码效果不佳;第二个缺陷是,解码器在解码过程中没有显示的单词对其操作,导致其翻译时注意力被分散在整个序列中。为了解决机器翻译中的这两个问题,(Bahdanau, Cho, and Bengio 2014)[2] 最早引进了Attention机制。
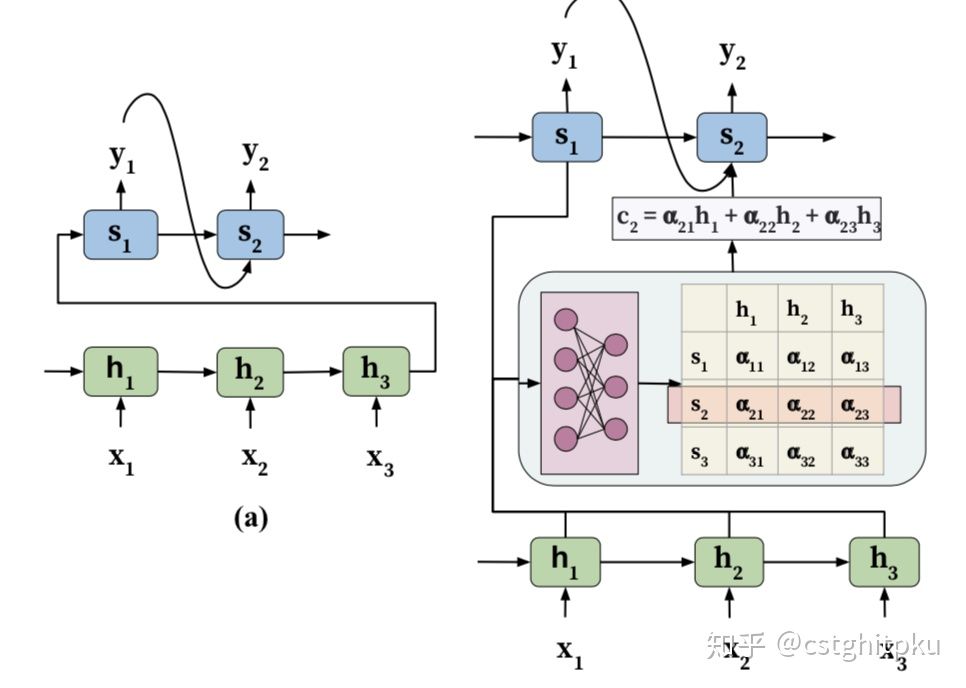
如上图(b),在解码阶段对每个词的解码时不仅会考虑上一个隐变量,还会考虑一个关注于此单词的上下文编码(c_i)。这个(c)的计算过程是使用上个单词的隐遍量(s_{i-1})与编码时所有时间点的隐变量({h_1, h_2,...,h_n})计算重要性评分({e_1, e_2, ..., e_n}),这个评分归一化之后的向量({alpha_1, alpha_2, ..., alpha_n})作为权重,与({h_1, h_2,...,h_n})计算加权和得到。至于(e)的计算,图中使用的是加性方式下面会介绍。
3. Attention的通用定义
上面介绍的是机器翻译任务。为了形式化Attention机制,这里定义向量序列:
(V={v_i} in R^{n*d_v}),于是关注于(u)的上下文编码(c)的计算可以写为:
其中,(uin R^{d_u})是与任务相关的查询向量。(a(u,v))是一个可以学习的对其函数,其输出是一个用来衡量向量(u,v)的匹配质量的数值。(Luong, Pham, and
Manning 2015)[3]给出几种常用的attention score的计算方式:
乘法
加性
MLP
4. Attention的变体
Attention的变体主要份两个方向:
- 计算attention score的函数(a(u,v))的设计
- 加权求和时的方式
4.1 计算attention score时的变体
除了第3节中介绍的几种计算attention score的方式,还有如下几种变体:
多维的Attention
其实就是将attention机制独立重复k次,这样就可以得到k组attention(即attention scores不再是一个向量,而是一个二维矩阵了)、k组c了。这样的好处是每一组attention的关注点可能有所不同。如果需要将k组c合并成一个,则将其concat起来然后与矩阵进行笛卡尔积就行了。Transformer里面的multi-head就是这么操作的。这样的模型有一个缺点,多个头可能关注点可能相同或者相似。为了解决这个问题,(Du et al. 2018; Lin et al. 2017)[4][5]提出使用下面的正则化项:
其中A是Attention矩阵。
Feed-forward Attention
(Raffel, C. and Ellis, D.P., 2015)[6]提出了一种简单的、无需查询变量的attention机制。
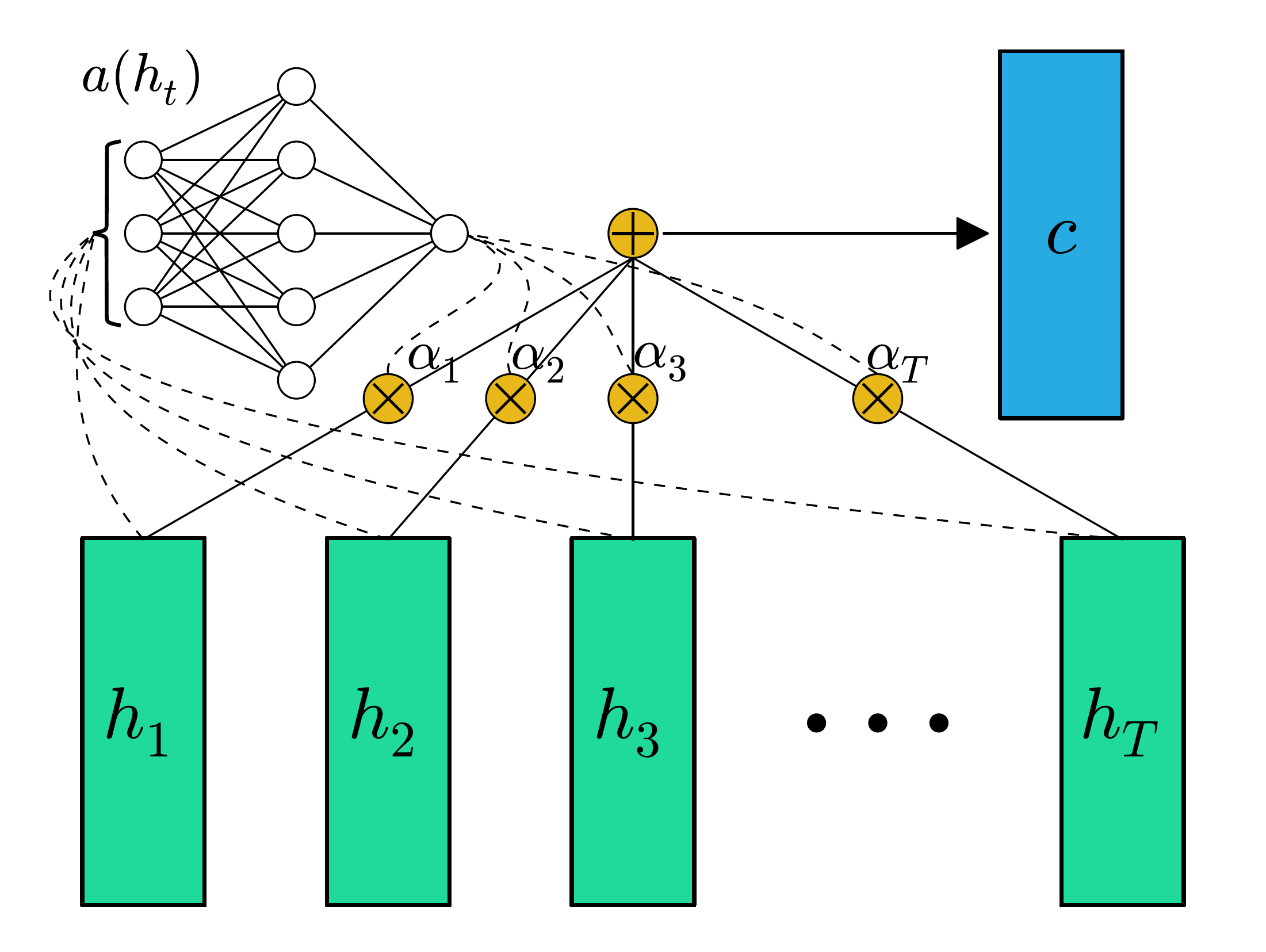
这种方式直接通过(h_i)获得这个向量的attention score,加权求和得到的向量是句子的表示(c)。这个表示去除了不重要的单词信息同时强化突出重要信息。
计算attention score的函数(a(h_i))是一个可以学习的函数,不过此函数仅仅依赖(h_i).
(a(h_i))可以是一个MLP:
或者是利用向量点积(其实就是一个神经元的感知机):
其中(w in R^{1*dim}, b in R) 是一个可以学习的向量。
层级的Attention
(Yang et al. 2016)[7]使用自底向上的方式获得文本的向量表示,进而用于分类任务。首先句子中每个单词进行attention计算获得这个句子的向量编码,然后对所有句子进行attention计算获得文本的向量编码。
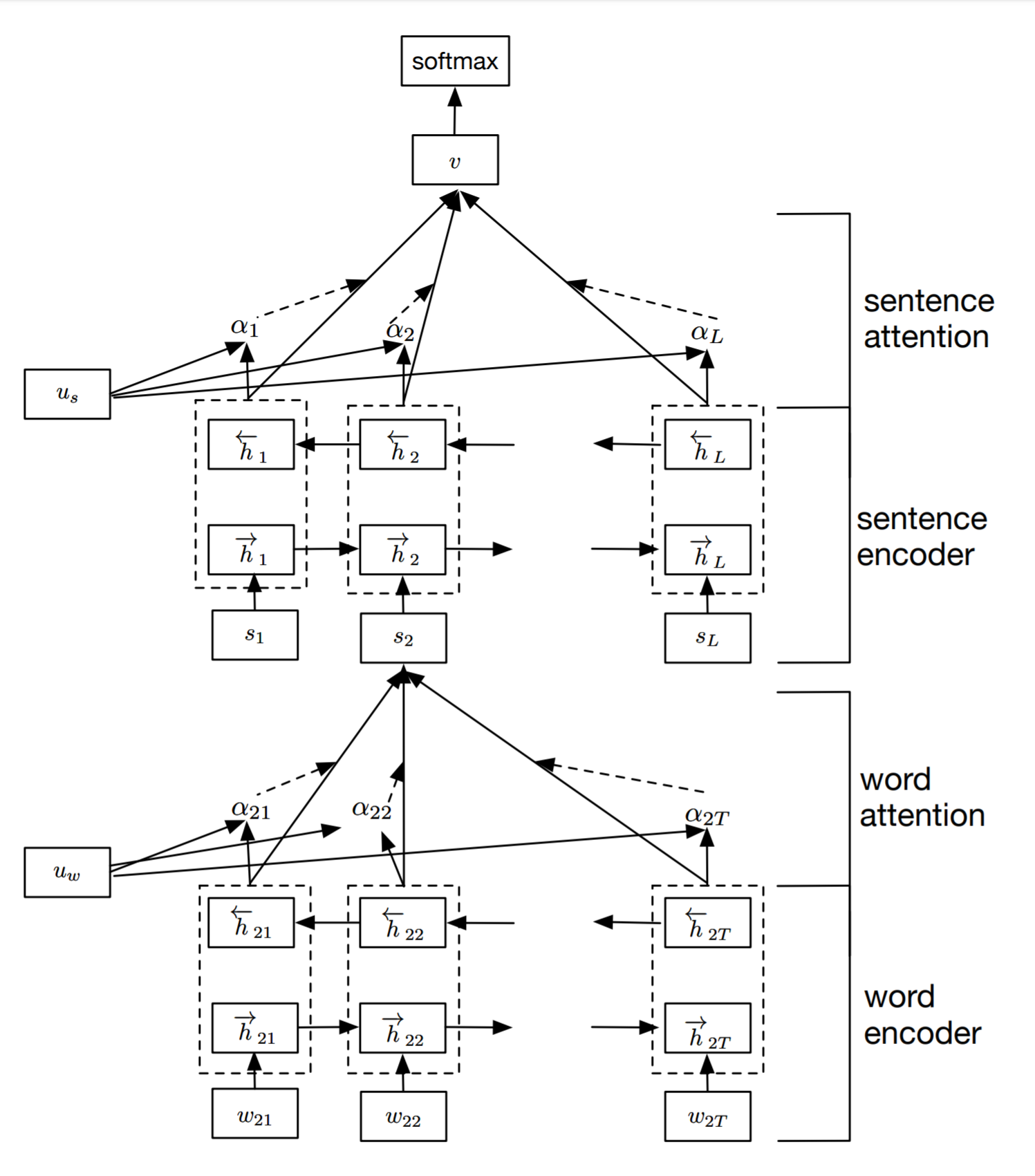
具体地:
其中(h_i^{(t)})为第(i)个句子的第(t)个单词, (v_i)为第(i)个句子的编码。我们把(u_w、u_s)叫做单词级和句子级的匹配向量。这里attention score的计算方式其实是feed-forward attention方式。
自注意力机制
上面的Attention机制都需要一个查询向量,而得到的向量(c)也是关于这个查询向量的上下文向量。Transformer(Vaswani et al. 2017)[8]提出了一种不需要查询向量的Attention机制,即自注意力机制。自注意力机制允许在没有任何额外信息的情况下通过输入句子本身获得句子的上下文向量。
首先,需要重新形式化attention为一下过程(Key,Value and Query):
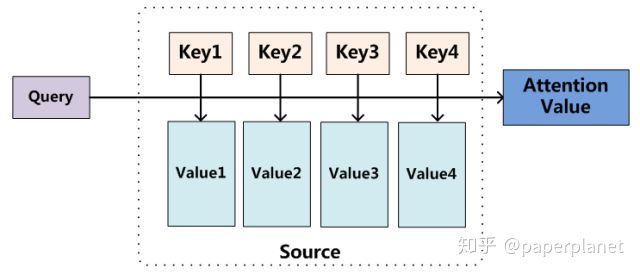
查询向量(q)与所有的(k)计算attention score,归一化后得到attention作为(value)的权重得到最后的Attention Value即为关于查询向量(q)的上下文向量。其实通用的Attention可以看作是上述形式化的k=q=v时的特例。
如何得到(q、k、v)呢?
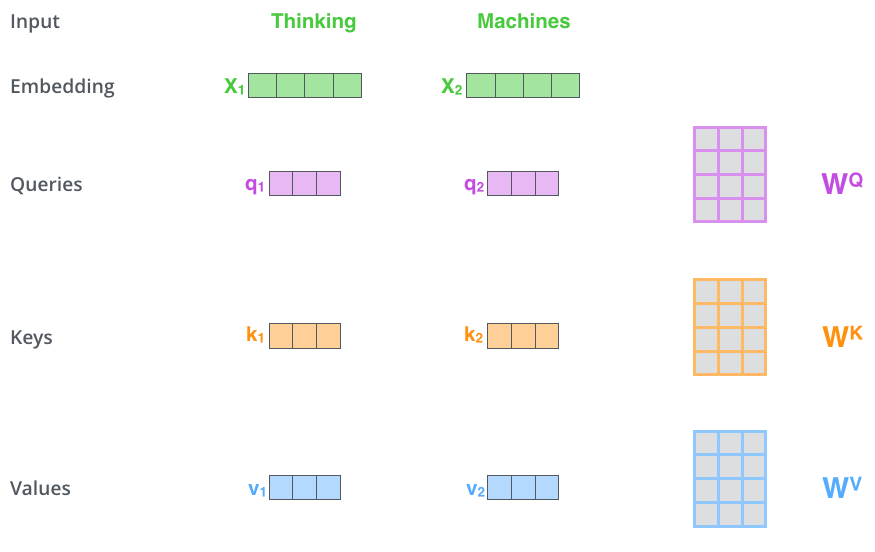
(q、k、v)向量由输入(x)本身分别与可以优化的矩阵(W^Q、W^K、W^V)进行笛卡尔集得到。attention的计算过程和其他的计算过程是类似的,Transformer中计算attention score的方式是维度归一化后的余弦相似度((q^Tk/sqrt {dim}))。
基于记忆的Attention
在介绍自注意力的那一小结中介绍了Q-K-V的Attention结构,其实这就是所谓的Memory-based attention.
4.2 加权时的变体
Soft attention、global attention、动态 attention
以上三种就是attention 通用定义中的注意力机制。在得到attention score之后对value进行加权而不是选择其中权重最大的,所以被称为soft attention。同时,这种机制考虑了所有的value,所以被称为global attention。而被成为动态attention,是因为每次查询都会重新计算attention。
Hard attention
Hard attention的思想是在寻址时不再考虑所有value的加权求和,而是只考虑用最重要的value来表示上下文向量。这个value可以是通过取最大attention权重的value,也可以是通过对attention score表示的多项式分布采样得到的value。Hard attention并不常见,因为有max pooling或者采样操作,所以整个模型不再可微,需要通过方差约归或者强化学习等技术来帮助训练。
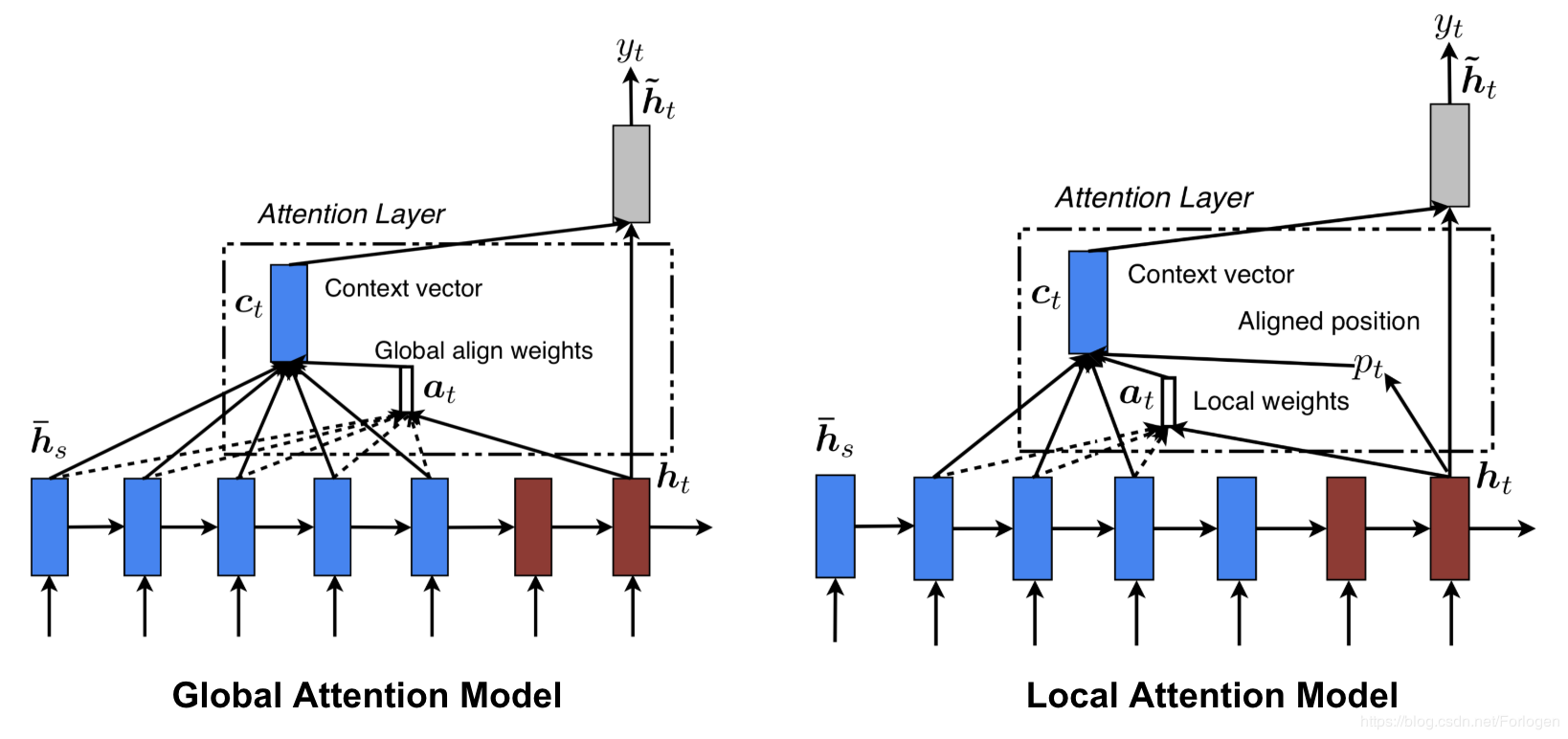
local attention
(Luong et al. 2015)[9]提出了局部注意力和全局注意力机制。由于全局注意力需要考虑所有的value的加权和,计算量大。所以考虑只在一个窗口内进行加权求和,即局部注意力。
注:本文主要参考(Hu 2018)[10]的综述完成。
References:
Kalchbrenner, N. and Blunsom, P., 2013, October. Recurrent continuous translation models. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (pp. 1700-1709). ↩︎
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K. and Bengio, Y., 2014. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473. ↩︎
Luong, M.T., Pham, H. and Manning, C.D., 2015. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.04025. ↩︎
Du, J.; Han, J.; Way, A.; and Wan, D. 2018. Multi-level structured self-attentions for distantly supervised relation extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.00699. ↩︎
Lin, Z.; Feng, M.; Santos, C. N. d.; Yu, M.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, B.; and Bengio, Y. 2017. A structured self-attentive sentence embedding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.03130. ↩︎
Raffel, C. and Ellis, D.P., 2015. Feed-forward networks with attention can solve some long-term memory problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.08756. ↩︎
Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Dyer, C.; He, X.; Smola, A.; and Hovy, E. 2016. Hierarchical attention networks for document classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 1480–1489. ↩︎
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł. and Polosukhin, I., 2017. Attention is all you need. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 5998-6008). ↩︎
Luong, M.T., Pham, H. and Manning, C.D., 2015. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.04025. ↩︎
Hu, D., 2019, September. An introductory survey on attention mechanisms in NLP problems. In Proceedings of SAI Intelligent Systems Conference (pp. 432-448). Springer, Cham. ↩︎