第1节:日期和时间
1.Linux的两种时钟:
系统时钟:由Linux内核通过CPU的工作频率进行的
硬件时钟:主板
2.相关命令
date 显示和设置系统时间
hwclock,clock 显示硬件时钟
-s,--hctosys 以硬件时钟为准,校准系统时钟
-w,--systohc 以系统时钟为准,校准硬件时钟
3.时区
/etc/localtime
4.显示日历
cal 显示当月日历
cal -y 显示当年日历
4.timedatectl
[root@centos7 ~]# timedatectl
Local time: Mon 2019-04-29 02:34:31 CST
Universal time: Sun 2019-04-28 18:34:31 UTC
RTC time: Sun 2019-04-28 18:34:30
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: no
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
(Linux(RHEL7及CentOS7)的时间设置篇(timedatectl,date,hwclock):https://blog.csdn.net/solaraceboy/article/details/78831319(转载自:MRIVANDU)
第2节:实验:时间同步
第2节:实验:时间同步
ntpdate ip
ntpdate -u 可以越过防火墙与主机同步
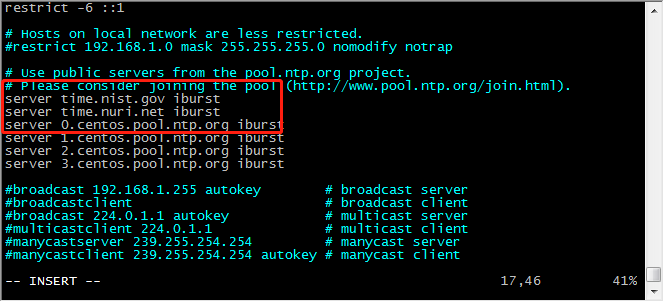
修改配置文件ntp.conf,永久联网后自动同步时间
nano /etc/ntp.conf
添加:server ip iburst
图001
启动ntpd服务命令
CentOS7
systemctl start ntpd
CentOS6
service ntpd start
ntpdate同步更新时间:https://www.cnblogs.com/luchuangao/p/7795293.html(转载自:luchuangao)