关联在实际业务需求中是随处可见的,比如:支付需要提交订单成功的订单号;修改个人资料需要登录成功响应报文信息。。。总之关联无处不在,今天来记一记Jmeter的关联功能。
Jmeter关联的方法比较常用的是正则表达式提取器,正则表达式提取器属于后置处理器,那么久抛出了一个比较大的知识点----正则表达式;
其实,正则表达式就是一种文本模式,相信都在windows我的电脑中搜索过文件嘛,那么肯定使用过“*”,其实都是类似。
记几个比较常用的:
^ ----->为匹配输入字符串的开始位置。
$ ----->为匹配输入字符串的结束位置。
. ------>匹配单字符。
+ ------>匹配一次或多次(大于等于1次)
?------>贪婪符,匹配到立即停止。
d------->匹配一个数字字符
------>匹配一个换行符
------->匹配一个回车符
。。。。。

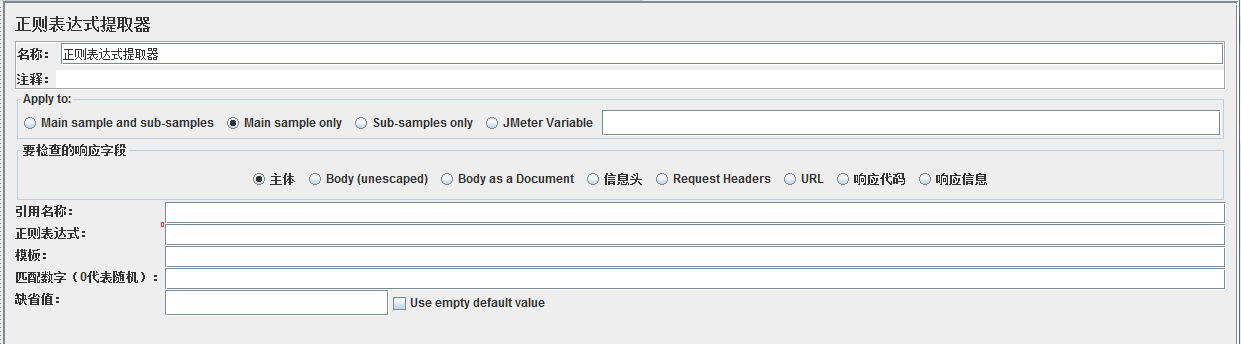
官方文档:
| Attribute | Description | Required |
|---|
| Name |
Descriptive name for this element that is shown in the tree. |
No |
| Apply to: |
This is for use with samplers that can generate sub-samples, e.g. HTTP Sampler with embedded resources, Mail Reader or samples generated by the Transaction Controller.
- Main sample only - only applies to the main sample
- Sub-samples only - only applies to the sub-samples
- Main sample and sub-samples - applies to both.
- JMeter Variable - assertion is to be applied to the contents of the named variable
Matching is applied to all qualifying samples in turn. For example if there is a main sample and 3 sub-samples, each of which contains a single match for the regex, (i.e. 4 matches in total). For match number = 3, Sub-samples only, the extractor will match the 3rd sub-sample. For match number = 3, Main sample and sub-samples, the extractor will match the 2nd sub-sample (1st match is main sample). For match number = 0 or negative, all qualifying samples will be processed. For match number > 0, matching will stop as soon as enough matches have been found. |
Yes |
| Field to check |
The following fields can be checked:
- Body - the body of the response, e.g. the content of a web-page (excluding headers)
- Body (unescaped) - the body of the response, with all Html escape codes replaced. Note that Html escapes are processed without regard to context, so some incorrect substitutions may be made.
| Note that this option highly impacts performances, so use it only when absolutely necessary and be aware of its impacts |
- Body as a Document - the extract text from various type of documents via Apache Tika (see View Results Tree Document view section).
| Note that the Body as a Document option can impact performances, so ensure it is OK for your test |
- Request Headers - may not be present for non-HTTP samples
- Response Headers - may not be present for non-HTTP samples
- URL
- Response Code - e.g. 200
- Response Message - e.g. OK
Headers can be useful for HTTP samples; it may not be present for other sample types. |
Yes |
| Reference Name |
The name of the JMeter variable in which to store the result. Also note that each group is stored as [refname]_g#, where [refname] is the string you entered as the reference name, and # is the group number, where group 0 is the entire match, group 1 is the match from the first set of parentheses, etc. |
Yes |
| Regular Expression |
The regular expression used to parse the response data. This must contain at least one set of parentheses "()" to capture a portion of the string, unless using the group $0$. Do not enclose the expression in / / - unless of course you want to match these characters as well. |
Yes |
| Template |
The template used to create a string from the matches found. This is an arbitrary string with special elements to refer to groups within the regular expression. The syntax to refer to a group is: '$1$' to refer to group 1, '$2$' to refer to group 2, etc. $0$ refers to whatever the entire expression matches. |
Yes |
| Match No. (0 for Random) |
Indicates which match to use. The regular expression may match multiple times.
- Use a value of zero to indicate JMeter should choose a match at random.
- A positive number N means to select the nth match.
- Negative numbers are used in conjunction with the ForEach Controller - see below.
|
Yes |
| Default Value |
If the regular expression does not match, then the reference variable will be set to the default value. This is particularly useful for debugging tests. If no default is provided, then it is difficult to tell whether the regular expression did not match, or the RE element was not processed or maybe the wrong variable is being used.
However, if you have several test elements that set the same variable, you may wish to leave the variable unchanged if the expression does not match. In this case, remove the default value once debugging is complete.
|
No, but recommended |
| Use empty default value |
If the checkbox is checked and Default Value is empty, then JMeter will set the variable to empty string instead of not setting it. Thus when you will for example use ${var} (if Reference Name is var) in your Test Plan, if the extracted value is not found then ${var} will be equal to empty string instead of containing ${var} which may be useful if extracted value is optional. |
No |
|
|
|
正则表达式会写,用这个很eazy。
现如今,restful风格(http+json)的接口很是流行,响应信息为json格式的,那么就还能简单一点,不用正则表达式那么复杂。
而json的数据类型有对象、数组、字符串、数字(整型、浮点)、布尔、null;使用jsonpath语法来进行提取判断。
Jmeter也有专门提取json的提取器,当然是第三方插件咯。。。Json Path Extractor
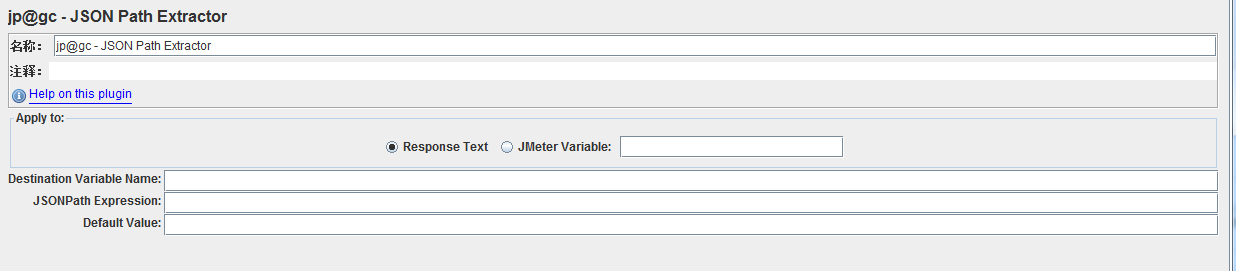
json是key-value类型的,当然也会碰到数组,关于这些也来记一记。
(参考:http://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath/)
Demo(一段json报文):
{ "store": {
"book": [
{ "category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "Herman Melville",
"title": "Moby Dick",
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3",
"price": 8.99
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
| XPath |
JSONPath |
结果 |
/store/book/author |
$.store.book[*].author |
书点所有书的作者
|
//author |
$..author |
所有的作者
|
/store/* |
$.store.* |
store的所有元素。所有的bookst和bicycle
|
/store//price |
$.store..price |
store里面所有东西的price
|
//book[3] |
$..book[2] |
第三个书
|
//book[last()] |
$..book[(@.length-1)] |
最后一本书 |
//book[position()<3] |
$..book[0,1]
$..book[:2]
|
前面的两本书。 |
//book[isbn] |
$..book[?(@.isbn)] |
过滤出所有的包含isbn的书。 |
//book[price<10] |
$..book[?(@.price<10)] |
过滤出价格低于10的书。 |
//* |
$..* |
所有元素。
|
可以看出其中的缺省符,通配符还是很常用的。经常会懵的就是碰到数组;还有就是jsonpath是从0开始数节点。
那么有jsonpath,也就有xpath^_^
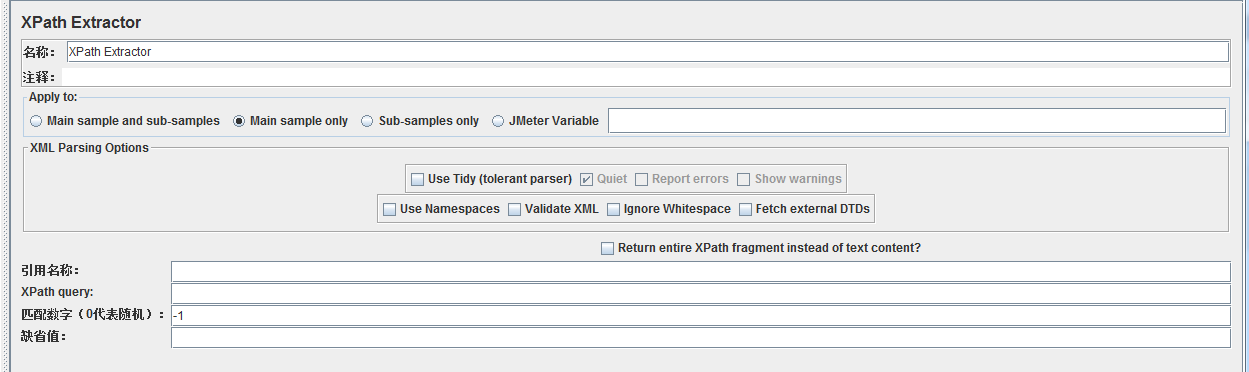
同样,它对于xml类型的报文信息提取比较简洁,数节点即可^_^。上方表格第一列便是xpath的相关语法。只是需要谨记的一点就是jsonpath数节点是从0开始数,而xpath数节点是从1开始数。
| XPath |
JSONPath |
Description |
| / |
$ |
表示根元素 |
| . |
@ |
当前元素 |
| / |
. or [] |
子元素 |
| .. |
n/a |
父元素 |
| // |
.. |
递归下降,JSONPath是从E4X借鉴的。 |
| * |
* |
通配符,表示所有的元素 |
| @ |
n/a |
属性访问字符 |
| [] |
[] |
子元素操作符
|
| | |
[,] |
连接操作符在XPath 结果合并其它结点集合。JSONP允许name或者数组索引。
|
| n/a |
[start:end:step] |
数组分割操作从ES4借鉴。
|
| [] |
?() |
应用过滤表示式
|
| n/a |
() |
脚本表达式,使用在脚本引擎下面。
|
| () |
n/a |
Xpath分组 |



