gRPC
前言
之前这玩意一直没用到过,最近项目中用到了。好好研究下。
为什么使用gRPC
gRPC是Google公司基于Protobuf开发的跨语言的开源RPC框架。gRPC基于HTTP/2协议设计,可以基于一个HTTP/2链接提供多个服务,对于移动设备更加友好。
传输协议
gRPC: 可以使用TCP协议,也可以使用HTTP协议
HTTP:基于HTTP协议
传输效率
gRPC:使用自定义的TCP协议,或者使用HTTP协议,都可以减少报文的体积,提高传输的效率
HTTP:如果是基于HTTP1.1的协议,请求中会包含很多无用的内容,如果是基于HTTP2.0,那么简单的封装以下是可以作为一个RPC来使用的,这时标准RPC框架更多的是服务治理
性能消耗
gRPC:gRPC消息使用一种有效的二进制消息格式protobuf进行序列化。Protobuf在服务器和客户机上的序列化非常快。Protobuf序列化后的消息体积很小,
能够有效负载,在移动应用程序等有限带宽场景中显得很重要
HTTP:大部分是通过json来实现的,字节大小和序列化耗时都比Protobuf要更消耗性能
gRPC主要用于公司内部的服务调用,性能消耗低,传输效率高。HTTP主要用于对外的异构环境,浏览器接口调用,APP接口调用,第三方接口调用等。
gRPC入门
创建hello.proto文件,定义HelloService接口
syntax = "proto3";
package main;
message String {
string value = 1;
}
service HelloService {
rpc Hello (String) returns (String);
}
使用protoc-gen-go内置的gRPC插件生成gRPC代码:
protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. hello.proto
然后会生成hello.pb.go文件,服务端和客户端生成的代码都包含在内
运行服务端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_base"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Hello(
ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_base.String,
) (*gRPC_base.String, error) {
reply := &gRPC_base.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
func main() {
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
gRPC_base.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
首先是通过grpc.NewServer()构造一个gRPC服务对象,然后通过gRPC插件生成的RegisterHelloServiceServer函数注册我们实现的HelloServiceImpl服务。然后通过grpcServer.Serve(lis)在一个监听端口上提供gRPC服务。
定义客户端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_base"
"fmt"
"log"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:1234", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := gRPC_base.NewHelloServiceClient(conn)
reply, err := client.Hello(context.Background(), &gRPC_base.String{Value: "hello"})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(reply.GetValue())
}
其中grpc.Dial负责和gRPC服务建立链接,然后NewHelloServiceClient函数基于已经建立的链接构造HelloServiceClient对象。返回的client其实是
一个HelloServiceClient接口对象,通过接口定义的方法就可以调用服务端对应的gRPC服务提供的方法。
gRPC流
RPC是远程函数调用,因此每次调用的函数参数和返回值不能太大,否则将严重影响每次调用的响应时间。因此传统的RPC方法调用对于上传和下载较大数据量场景
并不适合。同时传统RPC模式也不适用于对时间不确定的订阅和发布模式。为此,gRPC框架针对服务器端和客户端分别提供了流特性。
在HelloService增加一个支持双向流的Channel方法
syntax = "proto3";
package main;
message String {
string value = 1;
}
service HelloService {
rpc Hello (String) returns (String);
rpc Channel (stream String) returns (stream String);
}
关键字stream指定启用流特性,参数部分是接收客户端参数的流,返回值是返回给客户端的流。
使用protoc-gen-go内置的gRPC插件生成gRPC代码:
protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. hello.proto
重新生成代码可以看到接口中新增加的Channel方法的定义:
type HelloServiceServer interface {
Hello(context.Context, *String) (*String, error)
Channel(HelloService_ChannelServer) error
}
type HelloServiceClient interface {
Hello(ctx context.Context, in *String, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (
*String, error,
)
Channel(ctx context.Context, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (
HelloService_ChannelClient, error,
)
}
实现流服务
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Channel(stream gRPC_stream.HelloService_ChannelServer) error {
for {
args, err := stream.Recv()
if err != nil {
// io.EOF表示客户端流关闭
if err == io.EOF {
return nil
}
return err
}
reply := &gRPC_stream.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
err = stream.Send(reply)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
实现服务端代码:
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_stream"
"io"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Hello(
ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_stream.String,
) (*gRPC_stream.String, error) {
reply := &gRPC_stream.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Channel(stream gRPC_stream.HelloService_ChannelServer) error {
for {
args, err := stream.Recv()
if err != nil {
// io.EOF表示客户端流关闭
if err == io.EOF {
return nil
}
return err
}
reply := &gRPC_stream.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
err = stream.Send(reply)
if err != nil {
return err
}
}
}
func main() {
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
gRPC_stream.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
客户端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_stream"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"time"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:1234", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := gRPC_stream.NewHelloServiceClient(conn)
stream, err := client.Channel(context.Background())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 发送
go func() {
for {
if err := stream.Send(&gRPC_stream.String{Value: "hi"}); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}()
// 接收
for {
reply, err := stream.Recv()
if err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
break
}
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(reply.GetValue())
}
}
证书认证
gRPC建立在HTTP/2协议之上,对TLS提供了很好的支持。我们使用公钥,私钥,实现一个基本的认证
首先看下代码目录结构
gRPC_cert
├── cert
│ ├── cert.conf
│ ├── server.crt
│ └── server.key
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── hello.pb.go
├── hello.proto
└── server
└── main.go
创建cert.conf
[ req ]
default_bits = 2048
prompt = no
default_md = sha256
req_extensions = req_ext
distinguished_name = dn
[ dn ]
C = UK
ST = London
L = London
O = liz Ltd.
OU = Information Technologies
emailAddress = email@email.com
CN = localhost
[ req_ext ]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[ alt_names ]
DNS.1 = localhost
生成private key
$ openssl genrsa -out cert/server.key 2048
$ openssl req -nodes -new -x509 -sha256 -days 1825 -config cert/cert.conf -extensions 'req_ext' -key cert/server.key -out cert/server.crt
启动gRPC服务端的时候传入证书的参数选项
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_cert"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Hello(
ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_cert.String,
) (*gRPC_cert.String, error) {
reply := &gRPC_cert.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
func main() {
creds, err := credentials.NewServerTLSFromFile("./gRPC/gRPC_cert/cert/server.crt", "./gRPC/gRPC_cert/cert/server.key")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer(grpc.Creds(creds))
gRPC_cert.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
credentials.NewServerTLSFromFile函数是从文件为服务器构造证书对象,然后通过grpc.Creds(creds)函数将证书包装为选项后作为参数传入grpc.NewServer函数。
客户端基于服务端的证书和服务端名字进行对服务端的认证校验
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_cert"
"fmt"
"log"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
// 带入证书的信息
creds, err := credentials.NewClientTLSFromFile(
"./gRPC/gRPC_cert/cert/server.crt", "localhost",
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:1234",
grpc.WithTransportCredentials(creds),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := gRPC_cert.NewHelloServiceClient(conn)
reply, err := client.Hello(context.Background(), &gRPC_cert.String{Value: "hello"})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(reply.GetValue())
}
demo地址https://github.com/boilingfrog/daily-test/tree/master/gRPC/gRPC_cert
这种需要讲服务端的证书进行下发,这样客户在交互的时候每次都需要带过来,但是这样是不安全的。在传输的过程中证书存在被
监听和替换的可能性。
可以引入根证书,通过对服务端和客户端来进行签名,来保证安全。
使用根证书
为了避免证书的传递过程中被篡改,可以通过一个安全可靠的根证书分别对服务器和客户端的证书进行签名。这样客户端或服务器在收到对方的证书后可以通过根
证书进行验证证书的有效性。
首先看下我的项目目录
gRPC_cert_ca
├── cert
│ ├── ca.key
│ ├── ca.pem
│ ├── cert.conf
│ ├── client
│ │ ├── client.csr
│ │ ├── client.key
│ │ └── client.pem
│ ├── server
│ │ ├── server.csr
│ │ ├── server.key
│ │ └── server.pem
│ ├── server.crt
│ └── server.key
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── hello.pb.go
├── hello.proto
└── server
└── main.go
生成根证书
公钥
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048
秘钥
openssl req -new -x509 -days 7200 -key ca.key -out ca.pem
生成秘钥的时候需要填写信息
Country Name (2 letter code) []:
State or Province Name (full name) []:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) []:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (eg, fully qualified host name) []:localhost
Email Address []:
Common Name这个我们需要注意下,这个是主机名,测试的我就放了localhost
server端
生成 Key
openssl ecparam -genkey -name secp384r1 -out server.key
生成CSR
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
需要填写信息
Country Name (2 letter code) []:
State or Province Name (full name) []:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) []:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (eg, fully qualified host name) []:localhost
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
使用ca进行证书的签发
openssl x509 -req -sha256 -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650 -in server.csr -out server.pem
注意下自己的ca公钥秘钥的路径问题
client
生成key
openssl ecparam -genkey -name secp384r1 -out client.key
生成csr
openssl req -new -key client.key -out client.csr
使用ca进行证书的签发
openssl x509 -req -sha256 -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650 -in client.csr -out client.pem
到此完成证书的生成
server端的代码
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Hello(
ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_cert_ca.String,
) (*gRPC_cert_ca.String, error) {
reply := &gRPC_cert_ca.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
func main() {
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("./gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca/cert/server/server.pem", "./gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca/cert/server/server.key")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("tls.LoadX509KeyPair err: %v", err)
}
certPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ca, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca/cert/ca.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ioutil.ReadFile err: %v", err)
}
if ok := certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(ca); !ok {
log.Fatalf("certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM err")
}
c := credentials.NewTLS(&tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
ClientCAs: certPool,
})
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer(grpc.Creds(c))
gRPC_cert_ca.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
服务器端使用credentials.NewTLS函数生成证书,通过ClientCAs选择CA根证书,并通过ClientAuth选项启用对客户端进行验证。
客户端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("./gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca/cert/client/client.pem", "./gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca/cert/client/client.key")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("tls.LoadX509KeyPair err: %v", err)
}
certPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ca, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca/cert/ca.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ioutil.ReadFile err: %v", err)
}
if ok := certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(ca); !ok {
log.Fatalf("certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM err")
}
c := credentials.NewTLS(&tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
ServerName: "localhost",
RootCAs: certPool,
})
conn, err := grpc.Dial(":1234",
grpc.WithTransportCredentials(c),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := gRPC_cert_ca.NewHelloServiceClient(conn)
reply, err := client.Hello(context.Background(), &gRPC_cert_ca.String{Value: "hello"})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(reply.GetValue())
}
在credentials.NewTLS函数调用中,客户端通过引入一个CA根证书和服务器的名字来实现对服务器进行验证。客户端在链接服务器时会首先请求服务器的证书,
然后使用CA根证书对收到的服务器端证书进行验证。
ca认证的demohttps://github.com/boilingfrog/daily-test/tree/master/gRPC/gRPC_cert_ca
gRPC实现token认证
对于每个gRPC请求我们还会用到token的认证
要实现对每个gRPC方法进行认证,需要实现grpc.PerRPCCredentials接口:
type PerRPCCredentials interface {
// GetRequestMetadata gets the current request metadata, refreshing
// tokens if required. This should be called by the transport layer on
// each request, and the data should be populated in headers or other
// context. If a status code is returned, it will be used as the status
// for the RPC. uri is the URI of the entry point for the request.
// When supported by the underlying implementation, ctx can be used for
// timeout and cancellation.
// TODO(zhaoq): Define the set of the qualified keys instead of leaving
// it as an arbitrary string.
GetRequestMetadata(ctx context.Context, uri ...string) (
map[string]string, error,
)
// RequireTransportSecurity indicates whether the credentials requires
// transport security.
RequireTransportSecurity() bool
}
在GetRequestMetadata方法中返回认证需要的必要信息。RequireTransportSecurity方法表示是否要求底层使用安全链接。在真实的环境中建议必须要求
底层启用安全的链接,否则认证信息有泄露和被篡改的风险。
看下代码结构
gRPC_token
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── hello.pb.go
├── hello.proto
└── server
└── main.go
服务端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_token"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc/codes"
"google.golang.org/grpc/metadata"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type Authentication struct {
User string
Password string
}
type grpcServer struct {
auth *Authentication
}
func (p *grpcServer) Hello(
ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_token.String,
) (*gRPC_token.String, error) {
// 初始化信息,测试用的
p.Init()
// 检验
if err := p.auth.Auth(ctx); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
reply := &gRPC_token.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
// 测试使用
func (p *grpcServer) Init() {
p.auth = &Authentication{
User: "liz",
Password: "123456",
}
}
// 认证
func (a *Authentication) Auth(ctx context.Context) error {
md, ok := metadata.FromIncomingContext(ctx)
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("missing credentials")
}
var appid string
var appkey string
if val, ok := md["user"]; ok {
appid = val[0]
}
if val, ok := md["password"]; ok {
appkey = val[0]
}
if appid != a.User || appkey != a.Password {
return grpc.Errorf(codes.Unauthenticated, "invalid token")
}
return nil
}
func main() {
grpcServer1 := grpc.NewServer()
gRPC_token.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer1, new(grpcServer))
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer1.Serve(lis)
}
主要通过Authentication.Auth()实现了对token信息的校验,通过metadata.FromIncomingContext(ctx)获取请求中的认证信息,然后进行匹配校验。
客户端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_token"
"fmt"
"log"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type Authentication struct {
User string
Password string
}
// 返回认证需要的必要信息
func (a *Authentication) GetRequestMetadata(context.Context, ...string) (
map[string]string, error,
) {
return map[string]string{"user": a.User, "password": a.Password}, nil
}
// 表示是否要求底层使用安全链接,测试的代码就是使用了false
func (a *Authentication) RequireTransportSecurity() bool {
return false
}
func main() {
// 初始化账户,密码
auth := Authentication{
User: "liz",
Password: "123456",
}
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:1234", grpc.WithInsecure(),
grpc.WithPerRPCCredentials(&auth),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := gRPC_token.NewHelloServiceClient(conn)
reply, err := client.Hello(context.Background(), &gRPC_token.String{Value: "hello"})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(reply.GetValue())
}
通过grpc.WithPerRPCCredentials函数将Authentication对象转为grpc.Dial参数。测试的代码,使用grpc.WithInsecure()忽略证书认证。
代码的demohttps://github.com/boilingfrog/daily-test/tree/master/gRPC/gRPC_token
和Web服务共存
gRPC构建在HTTP/2协议之上,因此我们可以将gRPC服务和普通的Web服务架设在同一个端口之上。
代码在之前的ca认证的demo基础之上,加入web服务
我的目录结构
gRPC_web
├── cert
│ ├── ca.key
│ ├── ca.pem
│ ├── client
│ │ ├── client.csr
│ │ ├── client.key
│ │ └── client.pem
│ └── server
│ ├── server.csr
│ ├── server.key
│ └── server.pem
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── hello.pb.go
├── hello.proto
└── server
└── main.go
服务端代码
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_web"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Hello(
ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_web.String,
) (*gRPC_web.String, error) {
reply := &gRPC_web.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
func main() {
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/server/server.pem", "./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/server/server.key")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("tls.LoadX509KeyPair err: %v", err)
}
certPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ca, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/ca.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ioutil.ReadFile err: %v", err)
}
if ok := certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(ca); !ok {
log.Fatalf("certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM err")
}
c := credentials.NewTLS(&tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
ClientAuth: tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert,
ClientCAs: certPool,
})
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer(grpc.Creds(c))
gRPC_web.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
w.Write([]byte("hello"))
})
http.ListenAndServeTLS(":1234", "./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/server/server.pem", "./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/server/server.key",
http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.ProtoMajor != 2 {
mux.ServeHTTP(w, r)
return
}
if strings.Contains(
r.Header.Get("Content-Type"), "application/grpc",
) {
grpcServer.ServeHTTP(w, r)
return
}
mux.ServeHTTP(w, r)
return
}),
)
}
因为gRPC服务已经实现了ServeHTTP方法,可以直接作为Web路由处理对象。如果将gRPC和Web服务放在一起,会导致gRPC和Web路径的冲突,在处理时我们需要区分两类服务。
客户端实现
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_web"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
cert, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair("./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/client/client.pem", "./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/client/client.key")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("tls.LoadX509KeyPair err: %v", err)
}
certPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ca, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./gRPC/gRPC_web/cert/ca.pem")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("ioutil.ReadFile err: %v", err)
}
if ok := certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(ca); !ok {
log.Fatalf("certPool.AppendCertsFromPEM err")
}
c := credentials.NewTLS(&tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert},
ServerName: "localhost",
RootCAs: certPool,
})
conn, err := grpc.Dial(":1234",
grpc.WithTransportCredentials(c),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
client := gRPC_web.NewHelloServiceClient(conn)
reply, err := client.Hello(context.Background(), &gRPC_web.String{Value: "hello"})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(reply.GetValue())
}
当然除了grpc可以调用之外,我们同样可以请求web服务进行调用
demo地址https://github.com/boilingfrog/daily-test/tree/master/gRPC/gRPC_web
验证器
Protobuf中可以加入对字段的校验
一个简单的认证
看下我的代码结构
gRPC_validator
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── hello.pb.go
├── hello.proto
├── hello.validator.pb.go
└── server
└── main.go
syntax = "proto3";
package gRPC_validator;
import "github.com/mwitkow/go-proto-validators/validator.proto";
service HelloService {
rpc Hello (RequestInfo) returns (String);
}
message RequestInfo {
string name = 1 [
(validator.field) = {regex: "^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{4,16}$"}
];
int64 age = 2 [
(validator.field) = {int_gt: 0, int_lt: 100}
];
}
message String {
string value = 1;
}
然后生成go代码,不过我们需要下载一个新的插件
$ go get github.com/mwitkow/go-proto-validators/protoc-gen-govalidators
使用新的插件生成代码
$ protoc --proto_path=. --proto_path=${GOPATH}/src --govalidators_out=. --go_out=plugins=grpc:. hello.proto
注意:
我们要弄明白protoc中proto_path参数的含义
- proto_path: 指定了在哪个目录中搜索import中导入的和要编译为.go的proto文件,可以定义多个
所以添加proto_path就可以了,指定两个地址,一个是import的地址,一个是要编译为.go的proto文件的地址
$ protoc --proto_path=. --proto_path=${GOPATH}/src --govalidators_out=. --go_out=plugins=grpc:. hello.proto
需要注意下,要不会出现import找不到的错误
然后我们会发现生成一个独立的名为hello.validator.pb.go的文件:
// Code generated by protoc-gen-gogo. DO NOT EDIT.
// source: hello.proto
package gRPC_validator
import (
fmt "fmt"
proto "github.com/golang/protobuf/proto"
_ "github.com/mwitkow/go-proto-validators"
github_com_mwitkow_go_proto_validators "github.com/mwitkow/go-proto-validators"
math "math"
regexp "regexp"
)
// Reference imports to suppress errors if they are not otherwise used.
var _ = proto.Marshal
var _ = fmt.Errorf
var _ = math.Inf
var _regex_RequestInfo_Name = regexp.MustCompile(`^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{4,16}$`)
func (this *RequestInfo) Validate() error {
if !_regex_RequestInfo_Name.MatchString(this.Name) {
return github_com_mwitkow_go_proto_validators.FieldError("Name", fmt.Errorf(`value '%v' must be a string conforming to regex "^[a-zA-Z0-9_-]{4,16}$"`, this.Name))
}
if !(this.Age > 0) {
return github_com_mwitkow_go_proto_validators.FieldError("Age", fmt.Errorf(`value '%v' must be greater than '0'`, this.Age))
}
if !(this.Age < 100) {
return github_com_mwitkow_go_proto_validators.FieldError("Age", fmt.Errorf(`value '%v' must be less than '100'`, this.Age))
}
return nil
}
func (this *String) Validate() error {
return nil
}
调用这个函数,实现对字段的校验
demo地址:https://github.com/boilingfrog/daily-test/tree/master/gRPC/gRPC_validator
REST接口
开元社区中grpc-gateway项目就实现了将gRPC服务转为REST服务的能力。
grpc-gateway的工作原理如下图
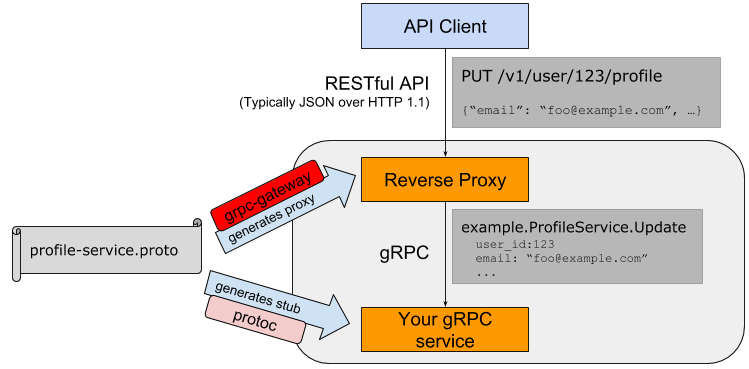
通过在Protobuf文件中添加路由相关的元信息,通过自定义的代码插件生成路由相关的处理代码,最终将REST请求转给更后端的gRPC服务处理。
放上我的代码目录
gRPC_restful
├── client
│ └── main.go
├── hello.pb.go
├── hello.pb.gw.go
├── hello.proto
├── httpServer
│ └── main.go
└── server
└── main.go
Protobuf代码
syntax = "proto3";
package gRPC_restful;
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}
service RestService {
rpc GetMes(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {
option (google.api.http) = {
get: "/mes/{value}"
};
}
rpc PostMes(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/mes"
body: "*"
};
}
}
上面的GetMes和PostMes提供了rpc接口,然后下面定义了相应的restful接口
我们需要安装下protoc-gen-grpc-gateway插件
go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
然后生成代码
protoc --proto_path=. --proto_path=$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis --grpc-gateway_out=. --go_out=plugins=grpc:. hello.proto
proto_path的patch需要注意下
grpc的server
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_restful"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) GetMes(ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_restful.StringMessage) (*gRPC_restful.StringMessage, error) {
reply := &gRPC_restful.StringMessage{Value: args.Value}
return reply, nil
}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) PostMes(ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_restful.StringMessage) (*gRPC_restful.StringMessage, error) {
reply := &gRPC_restful.StringMessage{Value: args.Value + "post"}
return reply, nil
}
func main() {
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
gRPC_restful.RegisterRestServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
http的server
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_restful"
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/runtime"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
err := gRPC_restful.RegisterRestServiceHandlerFromEndpoint(
ctx, mux, "localhost:1234",
[]grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()},
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
demo地址:https://github.com/boilingfrog/daily-test/tree/master/gRPC/gRPC_restful
grpcurl工具
gRPC同样也提供了一个名为reflection的反射包,用于为gRPC服务提供查询。配合grpcurl一款使用go写,就能查询gRPC列表或调用gRPC方法。
启动反射服务
package main
import (
"context"
"daily-test/gRPC/gRPC_grpcurl"
"log"
"net"
"google.golang.org/grpc/reflection"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
)
type HelloServiceImpl struct{}
func (p *HelloServiceImpl) Hello(ctx context.Context, args *gRPC_grpcurl.String) (*gRPC_grpcurl.String, error) {
reply := &gRPC_grpcurl.String{Value: "hello:" + args.GetValue()}
return reply, nil
}
func main() {
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer()
gRPC_grpcurl.RegisterHelloServiceServer(grpcServer, new(HelloServiceImpl))
// Register reflection service on gRPC server.
reflection.Register(grpcServer)
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
grpcServer.Serve(lis)
}
服务端的加入
reflection.Register(grpcServer)
将grpc.Server注册到反射服务中,下游就能进行反射的查看。
查看服务列表
首先手动安装grpcurl工具
$ go get github.com/fullstorydev/grpcurl
$ go install github.com/fullstorydev/grpcurl/cmd/grpcurl
命令常用到的参数
- -plaintext 忽略tls证书的验证过程
- -cert 配置公钥信息
- -key 配置私钥信息
- list 获取端口上的grpc服务的列表
- describe 查看服务的描述信息
查看服务列表
$ grpcurl -plaintext localhost:1234 list
gRPC_grpcurl.HelloService
grpc.reflection.v1alpha.ServerReflection
查看某个服务的方法列表
$ grpcurl -plaintext localhost:1234 list gRPC_grpcurl.HelloService
gRPC_grpcurl.HelloService.Hello
查看某个服务的描述信息
$ grpcurl -plaintext localhost:1234 describe gRPC_grpcurl.HelloService
gRPC_grpcurl.HelloService is a service:
service HelloService {
rpc Hello ( .gRPC_grpcurl.String ) returns ( .gRPC_grpcurl.String );
}
获取类型信息
$ grpcurl -plaintext localhost:1234 describe gRPC_grpcurl.String
gRPC_grpcurl.String is a message:
message String {
string value = 1;
}
测试请求
调用方法,可以使用grpcurl代替客户端进行访问请求
$ grpcurl -plaintext -d '{"value": "gopher"}' localhost:1234 gRPC_grpcurl.HelloService.Hello
{
"value": "hello:gopher"
}
-d后面跟的是请求的json数据
如果-d参数是@则表示从标准输入读取json输入参数,这一般用于比较输入复杂的json数据,也可以用于测试流方法。
参考
【https://www.cnblogs.com/yilezhu/p/10645804.html】https://www.cnblogs.com/yilezhu/p/10645804.html
【gRPC 官方文档中文版】https://doc.oschina.net/grpc?t=60133
【HTTP和RPC的优缺点】https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1353110
【gRPC入门】https://chai2010.gitbooks.io/advanced-go-programming-book/content/ch4-rpc/ch4-04-grpc.html
【Using TLS/SSL certificates for gRPC client and server communications in Golang - Updated】http://www.inanzzz.com/index.php/post/jo4y/using-tls-ssl-certificates-for-grpc-client-and-server-communications-in-golang-updated