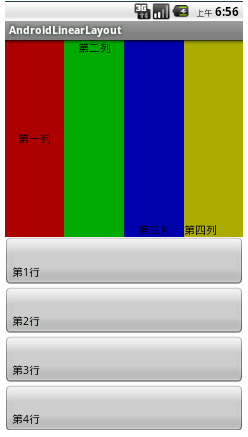
一、LinearLayout:线性布局
用来控制其子View以水平或垂直方式展开显示
重要属性
orientation(方向)
layout_weight(权重)
layout_weight(权重)的值
=0(默认值):指定多大空间就占据多大的空间
>0:将父视图中的可用空间进行分割, 值越大权重就越大, 占据的比例就会越大
Layout_weight的使用场景
将布局的宽度或高度平均分成几个等份
垂直方向上占用中间所有空间 或 水平方向上占用中间所有空间
android:gravity 与 android:layout_gravity的区别
android:gravity是指定本元素的子元素相对它的对齐方式。
android:layout_gravity是指定本元素相对它的父元素的对齐方式
案例参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangs1986/archive/2013/01/17/2864237.html
代码
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" 6 tools:context=".LinearLayoutActivity" > 7 8 <LinearLayout 9 android:layout_width="match_parent" 10 android:layout_height="match_parent" 11 android:layout_weight="1" 12 android:orientation="horizontal" > 13 14 <Button 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 android:layout_height="match_parent" 17 android:layout_weight="1" 18 android:background="#aa0000" 19 android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical" 20 android:text="第一列" 21 android:textSize="15sp" > 22 </Button> 23 24 <Button 25 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 26 android:layout_height="match_parent" 27 android:layout_weight="1" 28 android:background="#00aa00" 29 android:gravity="center_horizontal" 30 android:text="第二列" 31 android:textSize="15sp" > 32 </Button> 33 34 <Button 35 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 36 android:layout_height="match_parent" 37 android:layout_weight="1" 38 android:background="#0000aa" 39 android:gravity="center|bottom" 40 android:text="第三列" 41 android:textSize="15sp" > 42 </Button> 43 44 <Button 45 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 46 android:layout_height="match_parent" 47 android:layout_weight="1" 48 android:background="#aaaa00" 49 android:gravity="bottom" 50 android:text="第四列" 51 android:textSize="15sp" > 52 </Button> 53 </LinearLayout> 54 55 <LinearLayout 56 android:layout_width="match_parent" 57 android:layout_height="match_parent" 58 android:layout_weight="1" 59 android:orientation="vertical" > 60 61 <Button 62 android:layout_width="match_parent" 63 android:layout_height="match_parent" 64 android:layout_weight="1" 65 android:gravity="bottom" 66 android:text="第1行" 67 android:textSize="15sp" > 68 </Button> 69 70 <Button 71 android:layout_width="match_parent" 72 android:layout_height="match_parent" 73 android:layout_weight="1" 74 android:gravity="bottom" 75 android:text="第2行" 76 android:textSize="15sp" > 77 </Button> 78 79 <Button 80 android:layout_width="match_parent" 81 android:layout_height="match_parent" 82 android:layout_weight="1" 83 android:gravity="bottom" 84 android:text="第3行" 85 android:textSize="15sp" > 86 </Button> 87 88 <Button 89 android:layout_width="match_parent" 90 android:layout_height="match_parent" 91 android:layout_weight="1" 92 android:gravity="bottom" 93 android:text="第4行" 94 android:textSize="15sp" > 95 </Button> 96 </LinearLayout> 97 98 </LinearLayout>
二、RelativeLayout:相对布局
相对布局: 用来控制其子View以相对定位的方式进行布局显示
相对布局是最灵活, 最强大,也是学习难度最大的布局
相对布局相关属性比较多:
兄弟视图之间: 同方向对齐, 反方向对齐
与父视图之间: 同方向对齐, 居中
相对兄弟视图定位
同方向对齐属性
android:layout_alignBaseline 该控件的Baseline与给定ID控件的Baseline对齐
android:layout_alignLeft 该控件的左边与给定ID控件的左边对齐
android:layout_alignTop 该控件的顶部与给定ID控件的顶部对齐
android:layout_alignRight 该控件的右边与给定ID控件的右边对齐
android:layout_alignBottom 该控件的底部与给定ID控件的底部对齐
反方向对其属性
android:layout_toLeftOf 将该控件置于给定ID控件的左边
android:layout_toRightOf 将该控件置于给定ID控件的右边
android:layout_above 将该控件置于给定ID控件的上面
android:layout_below 将该控件置于给定ID控件的下面
相对父视图定位
与父视图同方向对齐
android:layout_alignParentLeft 该控件的左边与父控件的左边对齐
android:layout_alignParentTop 该控件的顶部与父控件的顶部对齐
android:layout_alignParentRight 该控件的右边与父控件的右边对齐
android:layout_alignParentBottom 该控件的底部与父控件的底部对齐
相对父视图居中属性
android:layout_centerInParent 垂直水平居中
android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中
android:layout_centerHorizontal 水平居中
案例:

代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <EditText android:id="@+id/ed_relative_msg" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:hint="Message"> <requestFocus /> </EditText> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_relative_ok" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/ed_relative_msg" android:layout_alignRight="@id/ed_relative_msg" android:text="Ok"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_relative_cancle" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignTop="@id/btn_relative_ok" android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn_relative_ok" android:layout_marginRight="10dp" android:text="Cancle"/> </RelativeLayout>
三、FrameLayout:帧布局
帧布局中的每一个子View都代表一个画面,默认以屏幕左上角作为( 0,0 )坐标
按定义的先后顺序依次逐屏显示 , 后面出现的会覆盖前面的画面
通过子View的android:layout_gravity?属性来指定子视图的位置
| 属性名称 | 对应方法 | 描述 |
| android:foreground | setForeground(Drawable) | 设置绘制在所有子控件之上的内容 |
| android:foregroundGravity | setForegroundGravity(int) | 设置绘制在所有子控件之上内容的gravity属性 |
在FreamLayout中,子控件是通过栈来绘制的,所以后添加的子控件会被控制在上层。
案例:参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/moonsilvering/archive/2011/12/30/2308091.html

代码:
1: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2: <resources> 3: <string name="app_name">FrameExample</string> 4: <string name="big">大的</string> 5: <string name="middle">中的</string> 6: <string name="small">小的</string> 7: </resources> 3)在项目res/values目录下新建一个colors.xml,在其中输入如下代码。 1: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2: <resources> 3: <color name="red">#FF0000</color> 4: <color name="green">#00FF00</color> 5: <color name="blue">#0000FF</color> 6: <color name="white">#FFFFFF</color> 7: </resources> 4)打开项目res/layout目录下的main.xml文件,将其中已有的代码替换为如下代码。 1: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2: <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3: android:id="@+id/FrameLayout01" 4: android:layout_width="fill_parent" 5: android:layout_height="fill_parent" 6: android:background="@color/white" > 7: 8: <TextView 9: android:id="@+id/TextView01" 10: android:layout_width="wrap_content" 11: android:layout_height="wrap_content" 12: android:text="@string/big" 13: android:textColor="@color/green" 14: android:textSize="60dp" > 15: </TextView> 16: 17: <TextView 18: android:id="@+id/TextView02" 19: android:layout_width="wrap_content" 20: android:layout_height="wrap_content" 21: android:text="@string/middle" 22: android:textColor="@color/red" 23: android:textSize="40dp" > 24: </TextView> 25: 26: <TextView 27: android:id="@+id/TextView03" 28: android:layout_width="wrap_content" 29: android:layout_height="wrap_content" 30: android:text="@string/small" 31: android:textColor="@color/blue" 32: android:textSize="20dp" > 33: </TextView> 34: 35: </FrameLayout>
一下为常用的一些基本属性
常用基本属性四、属性的划分
针对任何View的属性
常用的最基本属性
内边距属性 padding
外边距属性 margin
只针对RelativeLayout的属性
反方向对齐属性 to/above/below
同方向对齐属性 align
相对父视图的属性 alignparent/center
只针对LinearLayout的属性
权重属性 weight
方向属性 oritation
id 为控件指定相应的ID
@+id/idname 添加一个ID
layout_width 指定当前视图的宽度
layout_height 指定当前视图的宽度
text 指定控件当中显示的文字
textSize 指定控件当中字体的大小
background 指定该控件所使用的背景(图片|颜色)
layout_gravity 控件本身相对于父视图的位置
grivity 指定控件中的内容的基本位置
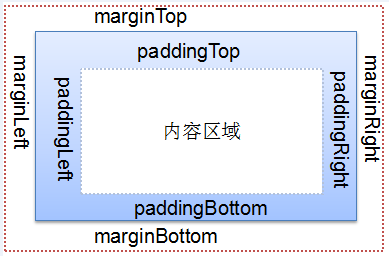
内边距与外边距(公共属性)
内边距:
android:padding
android:paddingLeft
android:paddingTop
android:paddingRight
android:paddingBottom
外边距
android:layout_margin
android:layout_marginLeft
android:layout_marginTop
android:layout_marginRight
android:layout_marginBottom