新代码在contribseq2seqpythonopsattention_decoder_fn.py
和之前代码相比 不再采用conv的方式来计算乘,直接使用乘法和linear
给出了两种attention的实现 传统的"bahdanau": additive (Bahdanau et al., ICLR'2015) Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate
以及"luong": multiplicative (Luong et al., EMNLP'2015) Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation
这里以 bahdanau为例
还是按照 Grammar as a Foreign Language的公式
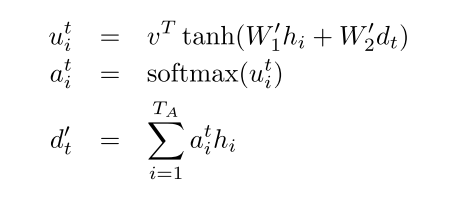
对应代码里面
将input encoder outputs 也就是输入的attention states作为 attention values
也就是在prepare_attention中
attention_values = attention_states
那么attention keys 对应 W_1h_i的部分,采用linear来实现
attention_keys = layers.linear(
attention_states, num_units, biases_initializer=None, scope=scope)
在创建score function的
_create_attention_score_fn 中完整定义了计算过程
这里去掉luong的实现部分 仅仅看bahdanau部分
with variable_scope.variable_scope(name, reuse=reuse):
if attention_option == "bahdanau":
#这里对应第一个公式最右面 query_w对应W_2, query是对应d_t
query_w = variable_scope.get_variable(
"attnW", [num_units, num_units], dtype=dtype)
#对应第一个公式最左侧的v
score_v = variable_scope.get_variable("attnV", [num_units], dtype=dtype)
def attention_score_fn(query, keys, values):
"""Put attention masks on attention_values using attention_keys and query.
Args:
query: A Tensor of shape [batch_size, num_units].
keys: A Tensor of shape [batch_size, attention_length, num_units].
values: A Tensor of shape [batch_size, attention_length, num_units].
Returns:
context_vector: A Tensor of shape [batch_size, num_units].
Raises:
ValueError: if attention_option is neither "luong" or "bahdanau".
"""
if attention_option == "bahdanau":
# transform query W_2*d_t
query = math_ops.matmul(query, query_w)
# reshape query: [batch_size, 1, num_units]
query = array_ops.reshape(query, [-1, 1, num_units])
# attn_fun 对应第一个公式的最左侧结果(=左侧) math_ops.reduce_sum(v * math_ops.tanh(keys + query), [2]) * + reduce_sum操作即是dot操作
scores = _attn_add_fun(score_v, keys, query)
# Compute alignment weights
# scores: [batch_size, length]
# alignments: [batch_size, length]
# TODO(thangluong): not normalize over padding positions.
#对应第二个公式计算softmax结果
alignments = nn_ops.softmax(scores)
# Now calculate the attention-weighted vector.
alignments = array_ops.expand_dims(alignments, 2)
#利用softmax得到的权重 计算attention向量的加权加和
context_vector = math_ops.reduce_sum(alignments * values, [1])
context_vector.set_shape([None, num_units])
#context_vector即对应 第三个公式 =的左侧
return context_vector
再看下计算出contenxt_vector之后的使用,这个方法正如论文中所说也和之前旧代码基本一致
也就是说将context和query进行concat之后通过linear映射依然得到num_units的长度 作为attention
def _create_attention_construct_fn(name, num_units, attention_score_fn, reuse):
"""Function to compute attention vectors.
Args:
name: to label variables.
num_units: hidden state dimension.
attention_score_fn: to compute similarity between key and target states.
reuse: whether to reuse variable scope.
Returns:
attention_construct_fn: to build attention states.
"""
with variable_scope.variable_scope(name, reuse=reuse) as scope:
def construct_fn(attention_query, attention_keys, attention_values):
context = attention_score_fn(attention_query, attention_keys,
attention_values)
concat_input = array_ops.concat([attention_query, context], 1)
attention = layers.linear(
concat_input, num_units, biases_initializer=None, scope=scope)
return attention
return construct_fn
最终的使用,cell_output就是attention,而next_input是cell_input和attention的concat
# construct attention
attention = attention_construct_fn(cell_output, attention_keys,
attention_values)
cell_output = attention
# argmax decoder
cell_output = output_fn(cell_output) # logits
next_input_id = math_ops.cast(
math_ops.argmax(cell_output, 1), dtype=dtype)
done = math_ops.equal(next_input_id, end_of_sequence_id)
cell_input = array_ops.gather(embeddings, next_input_id)
# combine cell_input and attention
next_input = array_ops.concat([cell_input, attention], 1)