简介
- 使用Selector(选择器), 可以使用一个线程处理多个客户端连接。
- Selector 能够检测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生(多个Channel以事件的方式可以注册到同一个Selector), 如果有事件发生, 便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理。这样就可以只用一个单线程去管理多个通道, 也就是管理多个连接和请求。
- 只有在连接有读写事件发生时, 才会进行续写, 就大大地减少了系统开销, 并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程, 不用去维护多个线程。
- 避免了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销
特性
- Netty的IO线程NioEventLoop聚合了Selector(选择器, 也被称为多路复用器), 可以同时并发处理成百上千个客户端连接。
- 当线程从某客户端Socket通道进行读写数据时, 若没有数据可用时, 该线程可以进行其他任务。
- 线程通常将非阻塞IO的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行IO操作, 所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。
- 由于读写操作都是非阻塞的(Buffer), 这就可以充分提升IO线程的运行效率, 避免由于频繁I/O阻塞导致的线程挂起。
- 一个I/O线程可以并发处理N个客户端连接和读写操作, 这从根本上解决了传统BIO一连接一线程模型, 架构的性能、弹性伸缩能力和可靠性都得到了极大的提升。
Selector类相关方法
-
public static Selector open(){}: 得到一个选择器对象
/** * Opens a selector. * * <p> The new selector is created by invoking the {@link * java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider#openSelector openSelector} method * of the system-wide default {@link java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider} * object. </p> * 新的选择器通过调用系统全局默认对象SelectorProvider的openSelector方法来创建新 * Selector对象 * * @return A new selector * * @throws IOException * If an I/O error occurs */ public static Selector open() throws IOException { return SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector(); }-
在这里使用了Provider(提供者)设计模式, 通过provider方法提供一个选择器提供者对象, 该对象再调用openSelector()方法生成了一个Selector。
/** * Returns the system-wide default selector provider for this invocation * of the Java virtual machine. * 为进行此次申请的Java虚拟机返回系统全局默认的选择器提供者 * * <p> The first invocation of this method locates the default provider * object as follows: </p> * 第一次请求该方法定位了默认的提供者对象如下: * <ol> * * <li><p> If the system property * <tt>java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider</tt> is defined then it * is taken to be the fully-qualified name of a concrete provider * class. * 如果系统所有物(选择提供者)被定义了, 那么它就会被认为是一个实体提供者类的完 * 全限定名 * The class is loaded and instantiated; if this process fails then an * unspecified error is thrown. </p></li> * 该类被加载并被初始化, 如果此过程失败了就会抛出 未定的错误 * * <li><p> If a provider class has been installed in a jar file that is * visible to the system class loader, and that jar file contains a * provider-configuration file named * <tt>java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider</tt> in the resource * directory <tt>META-INF/services</tt>, then the first class name * specified in that file is taken. * 如果提供者类已经被存入一个对系统类加载器可见的jar文件, 并且该jar文件包含了 * 一个在 META-INF/services 资源目录下的 名为 SelectorProvider的提供者配置 * 文件, 那么该文件中的第一个被列出的类名称被选择。 * * The class is loaded and instantiated; if this process fails then an * unspecified error is thrown. </p></li> * 该类会被加载并且初始化, 如果此过程失败了就会抛出 未定的错误。 * * <li><p> Finally, if no provider has been specified by any of the * above means then the system-default provider class is instantiated * and the result is returned. </p></li> * 最终, 如果没有提供者被任何以上方式定义, 那么系统默认提供者类就会被初始化, * 并返回该结果 * * </ol> * * <p> Subsequent invocations of this method return the provider that was * returned by the first invocation. </p> * 接下来的对该方法的请求返回第一次请求时被返回的提供者。 * * @return The system-wide default selector provider */ public static SelectorProvider provider() { // 这个lock是个对象, 不是锁哦, synchronized锁的只是Object synchronized (lock) { // 如果提供者不为空, 就返回提供者本身 if (provider != null) return provider; // 否则就调用获取控制器类的本地方法doPrivilege(给予权限) return AccessController.doPrivileged( // PrivilegedAction本身是一个接口, 实现该接口的类都要重写run方法 new PrivilegedAction<SelectorProvider>() { public SelectorProvider run() { // 如果是以属性的方式加载(方法底层比较复杂, 反射, 类加载器, 迭代器都有涉及) if (loadProviderFromProperty()) return provider; // 如果是以服务的方式加载(方法底层比较复杂, 同上) if (loadProviderAsService()) return provider; // 创建了一个新的提供者对象 provider = sun.nio.ch.DefaultSelectorProvider.create(); return provider; } }); } }
-
-
public int select(long timeout){}: 监控所有注册的通道, 当其中有IO操作可以进行时, 将对应的SelectionKey 加入到内部集合中并返回, 参数用来设置超时时间
- 这是SelectorImpl实现类中的反编译代码
public int select(long var1) throws IOException { // timeout < 0 就抛非法参数异常 if (var1 < 0L) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative timeout"); } else { // 如果timeout时间为0, 就执行lockAndDoSelect(-1L), 否则就执行lockAndDoSelect(原timeout时间) return this.lockAndDoSelect(var1 == 0L ? -1L : var1); } } // 不传参默认为0L(无延迟) public int select() throws IOException { return this.select(0L); } // 加锁并选择(无延迟) public int selectNow() throws IOException { return this.lockAndDoSelect(0L); } private int lockAndDoSelect(long var1) throws IOException { // 锁了当前对象 synchronized(this) { // 如果当前选择器没有打开, 就抛出选择器关闭异常 if (!this.isOpen()) { throw new ClosedSelectorException(); } else { int var10000; // 这其实是一个双重检查锁的单例模式 // 对当前选择器的publickeys加锁 synchronized(this.publicKeys) { // 对当前选择器的publicSelectedKeys加锁 synchronized(this.publicSelectedKeys) { var10000 = this.doSelect(var1); } } return var10000; } } } -
public Set
selectedKeys(){}: 从内部集合中得到所有的SelectionKey public Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys() { // 如果没有被打开并且工具类的bug级别为1.4, 就抛出异常 if (!this.isOpen() && !Util.atBugLevel("1.4")) { throw new ClosedSelectorException(); } else { // 否则就返回当前选择器的publicSelectedKeys return this.publicSelectedKeys; } }
Selector示意图
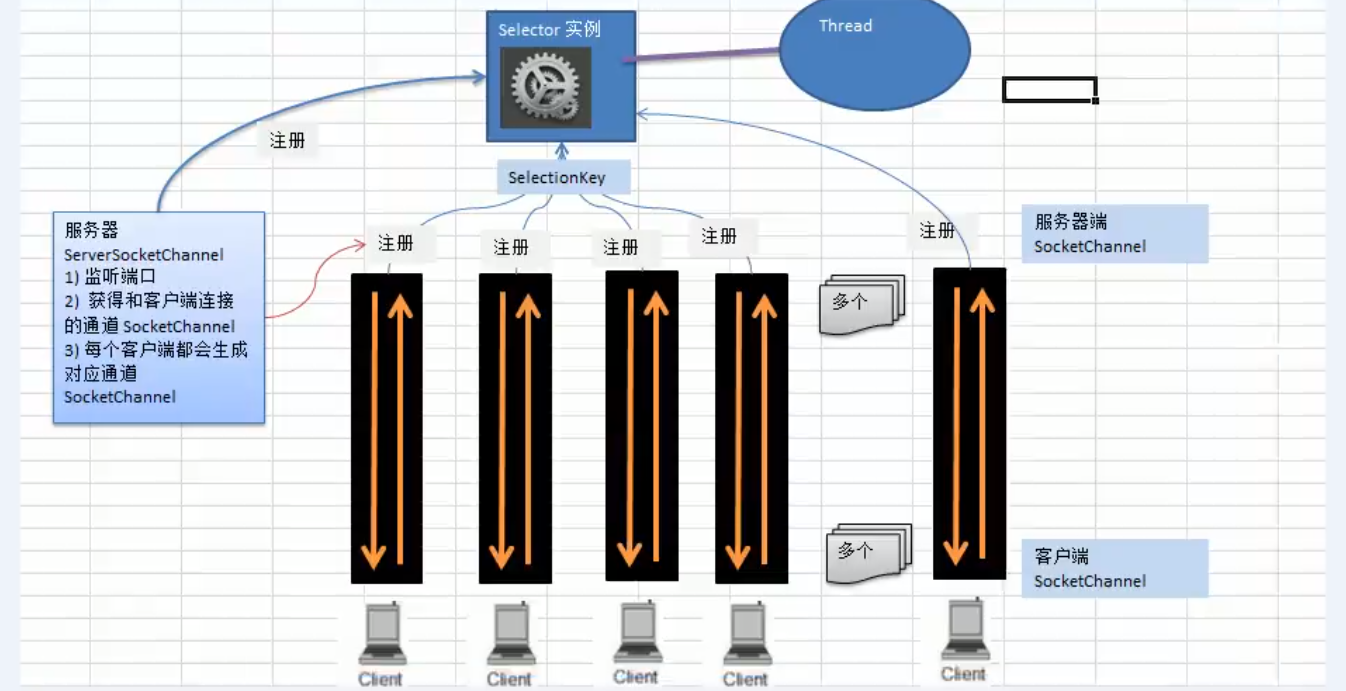
- 说明:
- 当客户端连接时, 会通过ServerSocketChannel得到SocketChannel
- 将socketChannel注册到Selector上, register(Selector selector, int ops), 一个selector上可以注册多个SocketChannel
- 注册后返回一个SelectionKey, 会与该Selector关联(集合)
- Selector 进行监听 select方法, 返回有事件发生的通道的个数
- 进一步得到各个 SelectionKey(发生的事件)
- 再通过Selectionkey 反向获取 SocketChannel, 方法channel()
- 可以通过得到的channel, 完成业务处理
服务端Demo
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建ServerSocketChannel -> ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 得到Selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 绑定一个端口:8888, 在服务器端监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888));
// 设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 把 serverSocketChannel注册到 selector, 连接事件为OP_ACCEPTOR
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 循环等待客户端连接
while (true){
// 无事件发生, 等待1秒
if(selector.select(1000) == 0){
System.out.println("Server waited for 1 second, no connection");
continue;
}
/*如果返回的>0, 就获取到相关的selectionKey集合
1. 如果返回的>0, 表示已经获取到关注的事件了
2. selector.selectedKeys()返回关注事件的集合
通过 selectionKeys反向获取通道
*/
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
// 遍历 Set<SelectionKey>, 使用迭代器遍历(iterator)
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()){
// 获取到selectionKey
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
// 根据key对应的通道发生的事件做相应的处理
if (key.isAcceptable()){ // 如果是OP_ACCEPT(有新的客户端连接)
// 为该客户端生成一个SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
// 将当前的 socketChannel 注册到 selector, 关注事件为OP_READ, 同时给socketChannel关联一个Buffer
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (key.isReadable()){ // 发生OP_READ
// 通过key反向获取到对应的channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 获取到该channel关联的buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("From Client: " + new String(buffer.array()));
}
// 手动从集合中移除当前的selectionKey, 防止重复操作
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
客户端Demo
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 提供服务器端ip 和 端口
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888);
// 连接服务器
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("Need time to connect, the client side won't block, we can do other works");
}
}
// 如果连接成功, 就发送数据
String str = "Hello, Hadoop, Storm, Spark, Flink";
// wraps a byte array into a buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
// 发送数据, 将buffer数据写入 channel
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();
}
}