背景
二胖上次写完参数校验(《二胖写参数校验的坎坷之路》)之后,领导一直不给他安排其他开发任务,就一直让他看看代码熟悉业务。二胖每天上班除了偶尔跟坐在隔壁的前端小姐姐聊聊天,就是看看这些
枯燥无味的业务代码,无聊的一匹。虽然二胖已是久经职场的老油条了,但是看到同事们的周报都写的满满的,而自己的周报,就一两行,熟悉了什么功能。心里还是慌得一匹,毕竟公司不养闲人啊。于是乎二胖终于鼓起勇气为了向领导表明自己的上进心,主动向领导要开发任务。领导一看这小伙子这么有上进心,于是就到任务看板里面挑了一个业务逻辑比较简单的任务分配给了二胖。二胖拿到这个任务屁颠屁颠的回到座位。任务比较简单,就是通过爬虫去爬取某些卖机票(某猪、某携、某团等)的网站的一些机票,然后保存到数据库。
同步入库
二胖拿到任务,三下五除二就把任务完成了。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
String mouZhuFlightPrice = getMouZhuFlightPrice();
String mouXieFlightPrice = getMouXieFlightPrice();
String mouTuanFlightPrice = getMouTuanFlightPrice();
saveDb(mouZhuFlightPrice);
saveDb(mouXieFlightPrice);
saveDb(mouTuanFlightPrice);
}
/**
* 模拟请求某猪网站 爬取机票信息
*
*
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static String getMouZhuFlightPrice() throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟请求某猪网站 爬取机票信息
Thread.sleep(10000);
return "获取到某猪网站的机票信息了";
}
/**
* 模拟请求某携网站 爬取机票信息
*
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static String getMouXieFlightPrice() throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟请求某携网站 爬取机票信息
Thread.sleep(5000);
return "获取到某携网站的机票信息了";
}
/**
* 模拟请求团网站 爬取机票信息
*
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static String getMouTuanFlightPrice() throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟请求某团网站 爬取机票信息
Thread.sleep(3000);
return "获取到某团网站的机票信息了";
}
/**
* 保存DB
*
* @param flightPriceList
*/
public static void saveDb(String flightPriceList) {
// 解析字符串 进行异步入库
}
这次二胖学乖了,任务完成了先去找下坐他对面的技术大拿(看他那发际线就知道了)同事“二狗”让二狗大拿帮忙指点一二,看看代码是否还能有优化的地方。毕竟领导对代码的性能、以及代码的优雅是有要求的。领导多次在部门的周会上提到让我们多看看“二狗”写的代码,学习下人家写代码的优雅、抽象、封装等等。二狗大概的瞄了下二胖写的代码,提出了个小小的建议“这个代码可以采用多线程来优化下哦,你看某猪这个网站耗时是拿到结果需要10s,其他的耗时都比它短,先有结果的我们可以先处理的,不需要等到大家都返回了再来处理的”。
轮循futureList获取结果
幸好二胖对多线程了解一点点,于是乎采用future的方式来实现。二胖使用一个List来保存每个任务返回的Future,然后去轮询这些Future,直到每个Future都已完成。由于需要先完成的任务需要先执行,且不希望出现因为排在前面的任务阻塞导致后面先完成的任务的结果没有及时获取的情况,所以在调用get方式时,需要将超时时间设置为0。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int taskSize = 3;
Future<String> mouZhuFlightPriceFuture = executor.submit(() -> getMouZhuFlightPrice());
Future<String> mouXieFlightPriceFuture = executor.submit(() -> getMouXieFlightPrice());
Future<String> mouTuanFlightPriceFuture = executor.submit(() -> getMouTuanFlightPrice());
List<Future<String>> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
futureList.add(mouZhuFlightPriceFuture);
futureList.add(mouXieFlightPriceFuture);
futureList.add(mouTuanFlightPriceFuture);
// 轮询,获取完成任务的返回结果
while (taskSize > 0) {
for (Future<String> future : futureList) {
String result = null;
try {
result = future.get(0, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
taskSize--;
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
taskSize--;
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
// 超时异常需要忽略,因为我们设置了等待时间为0,只要任务没有完成,就会报该异常
}
// 任务已经完成
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("result=" + result);
// 从future列表中删除已经完成的任务
futureList.remove(future);
taskSize--;
// 此处必须break,否则会抛出并发修改异常。(也可以通过将futureList声明为CopyOnWriteArrayList类型解决)
break; // 进行下一次while循环
}
}
}
}
上述代码有两个小细节需要注意下:
-
如采用
ArrayList的话futureList删除之后需要break进行下一次while循环,否则会产生我们意想不到的ConcurrentModificationException异常。具体原因可看下《ArrayList的删除姿势你都掌握了吗》这个文章,里面有详细的介绍。 -
在捕获了
InterruptedException和ExecutionException异常后记得taskSize--否则就会发生死循环。如果生产发生了死循环你懂的,cpu被你打满,程序假死等。你离被开除也不远了。 -
上面轮询
future列表非常的复杂,而且还有很多异常需要处理,还有很多细节需要考虑,还有被开除的风险。所以这种方案也被pass了。
自定义BlockingQueue实现
- 上述方案被
pass之后,二胖就在思考可以借用哪种数据来实现下先进先出的功能,貌似队列可以实现下这个功能。所以二胖又写了一版采用队列来实现的功能。
final static ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(6, 6,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Future<String> mouZhuFlightPriceFuture = executor.submit(() -> getMouZhuFlightPrice());
Future<String> mouXieFlightPriceFuture = executor.submit(() -> getMouXieFlightPrice());
Future<String> mouTuanFlightPriceFuture = executor.submit(() -> getMouTuanFlightPrice());
// 创建阻塞队列
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3);
executor.execute(() -> run(mouZhuFlightPriceFuture, blockingQueue));
executor.execute(() -> run(mouXieFlightPriceFuture, blockingQueue));
executor.execute(() -> run(mouTuanFlightPriceFuture, blockingQueue));
// 异步保存所有机票价格
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
String result = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(result);
saveDb(result);
}
}
private static void run(Future<String> flightPriceFuture, BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
try {
blockingQueue.put(flightPriceFuture.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 这次比上个版本好多了,代码也简洁多了。不过按理说这种需求应该是大家经常遇到的,应该不需要自己来实现把,
JAVA这么贴心的语言应该会有api可以直接拿来用吧。
CompletionService实现
- 二胖现在毕竟也是对代码的简洁性有追求的人了。于是乎二胖去翻翻自己躺在书柜里吃灰的并发相关的书籍,看看是否有解决方案。

终于皇天不负有心人在二胖快要放弃的时候突然发现了新大陆。
《Java并发编程实战》一书6.3.5节CompletionService:Executor和BlockingQueue,有这样一段话:
如果向Executor提交了一组计算任务,并且希望在计算完成后获得结果,那么可以保留与每个任务关联的Future,然后反复使用get方法,同时将参数timeout指定为0,从而通过轮询来判断任务是否完成。这种方法虽然可行,但却有些繁琐。幸运的是,还有一种更好的方法:完成服务CompletionService。
final static ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(6, 6,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletionService completionService = new ExecutorCompletionService(executor);
completionService.submit(() -> getMouZhuFlightPrice());
completionService.submit(() -> getMouXieFlightPrice());
completionService.submit(() -> getMouTuanFlightPrice());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
String result = (String)completionService.take().get();
System.out.println(result);
saveDb(result);
}
}
当我们使用了CompletionService不用遍历future列表,也不需要去自定义队列了,代码变得简洁了。下面我们就来分析下CompletionService实现的原理吧。
CompletionService 介绍
- 我们可以先看下
JDK源码中CompletionService的javadoc说明吧
/**
* A service that decouples the production of new asynchronous tasks
* from the consumption of the results of completed tasks. Producers
* {@code submit} tasks for execution. Consumers {@code take}
* completed tasks and process their results in the order they
* complete.
大概意思是CompletionService实现了生产者提交任务和消费者获取结果的解耦,生产者和消费者都不用关心任务的完成顺序,由CompletionService来保证,消费者一定是按照任务完成的先后顺序来获取执行结果。
成员变量
既然需要按照任务的完成顺序获取结果,那内部应该也是通过队列来实现的吧。打开源码我们可以看到,里面有三个成员变量
public class ExecutorCompletionService<V> implements CompletionService<V> {
// 执行task的线程池,创建CompletionService必须指定;
private final Executor executor;
//主要用于创建待执行task;
private final AbstractExecutorService aes;
//存储已完成状态的task,默认是基于链表结构的阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue。
private final BlockingQueue<Future<V>> completionQueue;
任务提交
ExecutorCompletionService任务的提交和执行都是委托给Executor来完成。当提交某个任务时,该任务首先将被包装为一个QueueingFuture
public Future<V> submit(Callable<V> task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<V> f = newTaskFor(task);
executor.execute(new QueueingFuture(f));
return f;
}
任务完成后何时进入队列
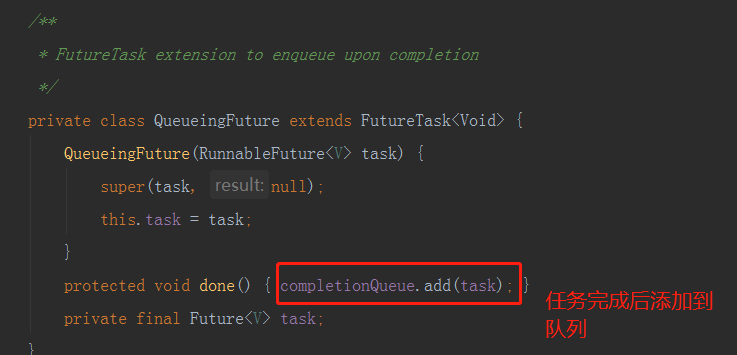 从源码可以看出,
从源码可以看出,QueueingFuture是FutureTask的子类,实现了done方法,在task执行完成之后将当前task添加到completionQueue,将返回结果加入到阻塞队列中,加入的顺序就是任务完成的先后顺序。done方法的具体调用在FutureTask的finishCompletion方法。
获取已完成任务
public Future<V> take() throws InterruptedException {
return completionQueue.take();
}
public Future<V> poll() {
return completionQueue.poll();
}
public Future<V> poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return completionQueue.poll(timeout, unit);
}
take和poll都是调用BlockingQueue提供的方法。
take()获取任务阻塞,直到可以拿到任务为止。poll()获取任务不阻塞,如果没有获取到任务直接返回null。poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)带超时时间等待的获取任务方法(一般推荐使用这种)
总结
CompletionService把线程池Executor和阻塞队列BlockingQueue融合在一起,能够让批异步任务的管理更简单,将生产者提交任务和消费者获取结果的解耦。CompletionService能够让异步任务的执行结果有序化,先执行完的先进入阻塞队列,利用这个特性,我们可以轻松实现后续处理的有序性,避免无谓的等待。
结束
- 由于自己才疏学浅,难免会有纰漏,假如你发现了错误的地方,还望留言给我指出来,我会对其加以修正。
- 如果你觉得文章还不错,你的转发、分享、赞赏、点赞、留言就是对我最大的鼓励。
- 感谢您的阅读,十分欢迎并感谢您的关注。
参考
《java并发编程实战》
https://www.jianshu.com/p/19093422dd57
https://blog.csdn.net/cbjcry/article/details/84222853
https://www.jianshu.com/p/493ae1b107e4