下图展示的是Bean从创建,装载到容器,到最终被销毁的整个生命周期过程。
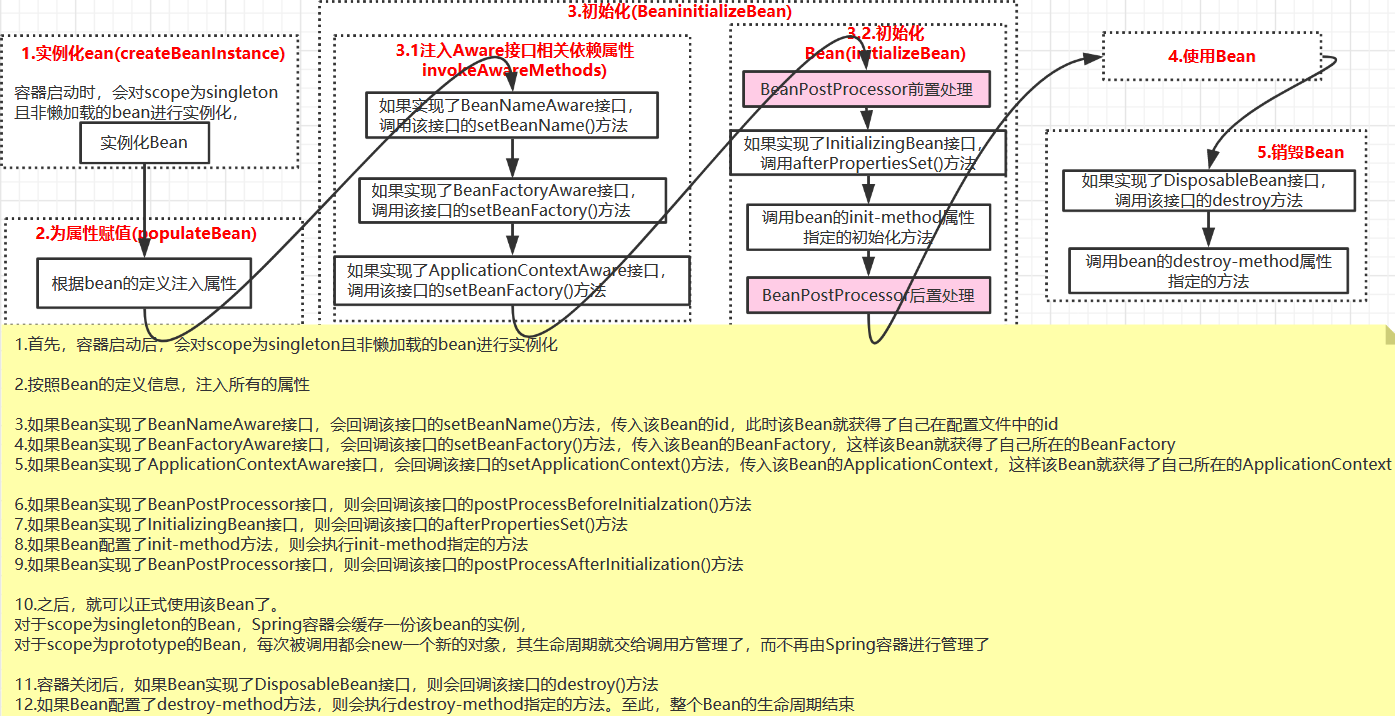
1.实例化Bean(createBeanInstance)
创建Bean实例。根据指定bean使用相应的策略来创建Bean,如:工厂方法(instantiateUsingFactoryMethod)、构造方法注入(autowireConstructor)、简单初始化(instantiateBean)。
Bean的实例化过程中并未进行属性的注入,仅仅是简单的实例化。实例化的Bean被包装成了BeanWrapper对象,BeanWrapper提供了设置对象属性的接口,从而避免了使用反射机制来设置属性。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中的doCreateBean方法
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) { // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); //确保Bean的class必须是public if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName()); } //1.使用工厂方法创建Bean。(有factoryMethodName属性,说明配置文件中配置了factory-method) if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) { return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); } // Shortcut when re-creating the same bean... boolean resolved = false; boolean autowireNecessary = false; if (args == null) { synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) { //一个类有多个构造方法,每个构造函数都有不同的参数,所以调用前需要先根据参数锁定构造方法或对应的工厂方法 if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) { resolved = true; autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved; } } } //如果已经解析过,则直接使用解析好的构造方法,不需要再次锁定 if (resolved) { if (autowireNecessary) { //2.使用构造器自动注入 return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null); } else { //3.使用默认构造方法 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); } } // Need to determine the constructor... //需要根据参数解析构造方法 Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName); if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR || mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) { //构造方法自动注入 return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args); } // No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor. //使用默认构造方法 return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); }
2.设置Bean属性(populateBean)
实例化后的对象被包装在BeanWrapper对象中,并且此时对象仍然是一个原生的状态,并没有进行依赖注入。 紧接着,Spring根据BeanDefinition中的信息进行依赖注入,并且通过BeanWrapper提供的设置属性的接口完成依赖注入。

如果Bean有依赖,则在为属性赋值时会先通过getBean去获取依赖的Bean。这在Spring源码系列3 - IOC容器的启动过程中分析Bean的循环引用问题时讲述过,这里不再赘述。
/** * Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values * from the bean definition. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param mbd the bean definition for the bean * @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance */ protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) { PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); if (bw == null) { if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance"); } else { // Skip property population phase for null instance. return; } } // Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the // state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example, // to support styles of field injection. if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { return; } } } } int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode(); if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); // Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable. if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) { autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } // Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable. if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } pvs = newPvs; } boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors(); boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE); if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) { PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); if (hasInstAwareBpps) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); if (pvs == null) { return; } } } } if (needsDepCheck) { checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs); } } applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); }
3.初始化Bean
实际上在Spring源码系列3 - IOC容器的启动过程中,我们就已经总结过Bean的创建过程。Bean的创建过程主要经过下面几个过程。
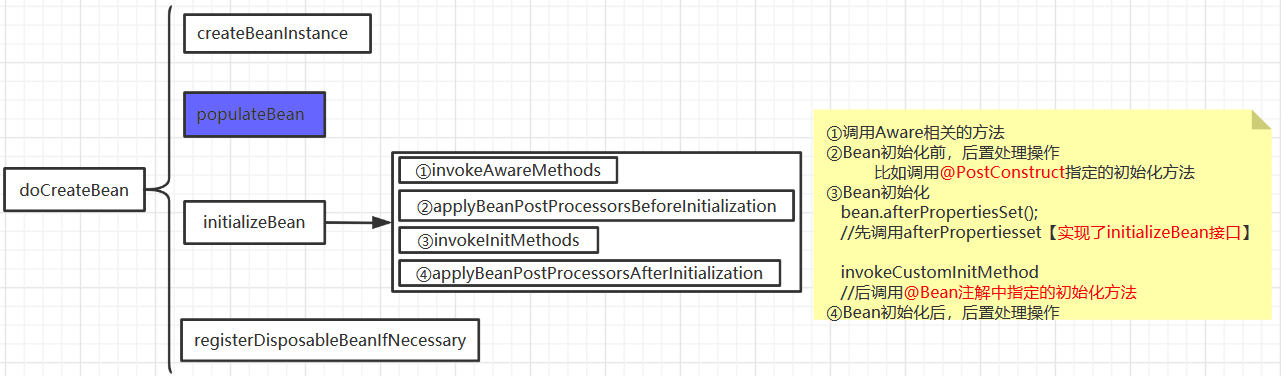
其中的第②步,是在Bean初始化之前做一些后置操作,比如@PostConstruct指定的初始化方法就是在此执行,处理该过程的组件是InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。而第④步,与第②步对应。是在Bean初始化之后做一些后置操作。
下面,我们就来从源码入手分析一下Bean的初始化,也就是initializeBean方法。
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { //① 调用Aware相关方法 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { //② Bean初始化前调用后置处理方法。【@PostConstruct指定方法在此调用】 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { //③ 调用初始化方法(afterPropertiesSet方法,init方法) invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { //④ Bean初始化之后调用后置处理方法 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
initializeBean-->invokeInitMethods
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { //如果实现了InitializingBean接口 boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'"); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { try { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() throws Exception { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { throw pae.getException(); } } else { //1.调用afterPropertiesSet方法【若实现了InitializingBean接口,afterPropertiesSet方法在此调用】 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } } if (mbd != null) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (initMethodName != null && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { //2.调用自定义的init方法【@Bean中指定的初始化方法在此调用】 invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
如果该Bean实现了InitializingBean接口,则会调用afterPropertiesSet方法。最后执行@Bean中指定的初始化方法。
4.使用Bean
也就是getBean的过程,从容器中获取Bean。
5.销毁Bean
注册DisposableBean和destroy-method
Spring中不但提供了对于初始化方法的扩展入口,同样也提供了销毁方法的扩展入口。对于销毁方法的扩展,除了我们熟知的配置属性destroy-method方法外,用户还可以注册后置处理器(DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor)来统一处理bean的销毁方法。前面分析了初始化Bean的过程,最后有一个registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary步骤,其正是用于在Bean初始化完成后注册销毁方法的。
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null); if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) { if (mbd.isSingleton()) { // Register a DisposableBean implementation that performs all destruction // work for the given bean: DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors, // DisposableBean interface, custom destroy method. //单例模式下注册需要销毁的Bean,此方法中会处理实现DisposableBean接口的Bean。 //并且对所有的bean使用DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors处理 registerDisposableBean(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); } else { // A bean with a custom scope... //非单例Bean的处理(scope值为非singleton) Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope()); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'"); } scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); } } }
销毁Bean
destroy-->close-->doClose-->destroyBeans()
-->DefaultListableBeanFactory#destroySingletons-->
-->DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#destroySingleton-->destroyBean
-->DisposableBeanAdapter#destroy()
@Override public void destroy() { if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) { for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) { //1.JSR250:调用@PreDestroy指定的销毁方法 processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName); } } if (this.invokeDisposableBean) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'"); } try { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() throws Exception { ((DisposableBean) bean).destroy(); return null; } }, acc); } else { //2.如果Bean实现了DisposableBean接口,则调用Bean自身的destory方法 ((DisposableBean) bean).destroy(); } } catch (Throwable ex) { String msg = "Invocation of destroy method failed on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'"; if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.warn(msg, ex); } else { logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex); } } } if (this.destroyMethod != null) { //3.调用@Bean注解中destroyMethod属性执行的销毁方法 invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod); } else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) { Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod(); if (methodToCall != null) { invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall); } } }
由上面代码可得知,Bean销毁的几种方式的先后调用顺序如下图。

最后,在Spring源码系列5 - Bean的初始化/销毁的几种方式总结中对Bean的初始化和销毁的几种方式再次进行了总结。
面试题:
1.Bean的生命周期?
2.Bean的作用域?