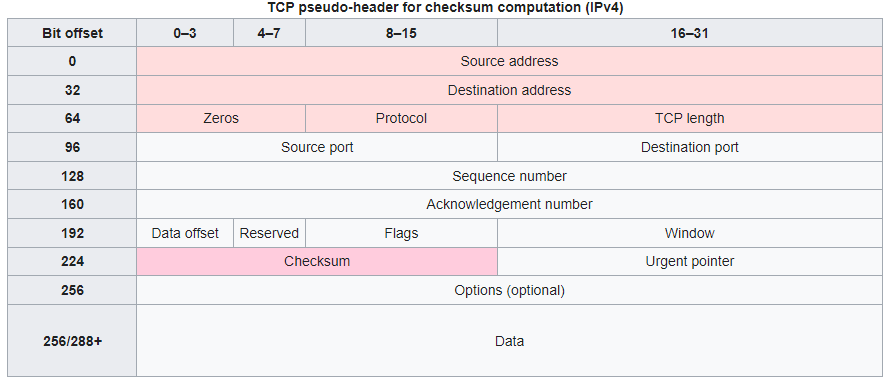

TCP checksum for IPv4[edit]
When TCP runs over IPv4, the method used to compute the checksum is defined in RFC 793:
The checksum field is the 16 bit one's complement of the one's complement sum of all 16-bit words in the header and text. If a segment contains an odd number of header and text octets to be checksummed, the last octet is padded on the right with zeros to form a 16-bit word for checksum purposes. The pad is not transmitted as part of the segment. While computing the checksum, the checksum field itself is replaced with zeros.
In other words, after appropriate padding, all 16-bit words are added using one's complement arithmetic. The sum is then bitwise complemented and inserted as the checksum field. A pseudo-header that mimics the IPv4 packet header used in the checksum computation is shown in the table below.
| Bit offset | 0–3 | 4–7 | 8–15 | 16–31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Source address | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | Destination address | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 64 | Zeros | Protocol | TCP length | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 96 | Source port | Destination port | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 128 | Sequence number | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 160 | Acknowledgement number | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 192 | Data offset | Reserved | Flags | Window | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 224 | Checksum | Urgent pointer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 256 | Options (optional) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 256/288+ | Data |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The source and destination addresses are those of the IPv4 header. The protocol value is 6 for TCP (cf. List of IP protocol numbers). The TCP length field is the length of the TCP header and data (measured in octets).
TCP checksum for IPv6[edit]
When TCP runs over IPv6, the method used to compute the checksum is changed, as per RFC 2460:
- Any transport or other upper-layer protocol that includes the addresses from the IP header in its checksum computation must be modified for use over IPv6, to include the 128-bit IPv6 addresses instead of 32-bit IPv4 addresses.
A pseudo-header that mimics the IPv6 header for computation of the checksum is shown below.
| Bit offset | 0–7 | 8–15 | 16–23 | 24–31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Source address | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 128 | Destination address | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 160 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 192 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 256 | TCP length | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 288 | Zeros | Next header = Protocol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 320 | Source port | Destination port | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 352 | Sequence number | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 384 | Acknowledgement number | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 416 | Data offset | Reserved | Flags | Window | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 448 | Checksum | Urgent pointer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 480 | Options (optional) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 480/512+ | Data |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Source address: the one in the IPv6 header
- Destination address: the final destination; if the IPv6 packet doesn't contain a Routing header, TCP uses the destination address in the IPv6 header, otherwise, at the originating node, it uses the address in the last element of the Routing header, and, at the receiving node, it uses the destination address in the IPv6 header.
- TCP length: the length of the TCP header and data
- Next Header: the protocol value for TCP
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_Control_Protocol