Computer Systems A Programmer's Perspective Second Edition
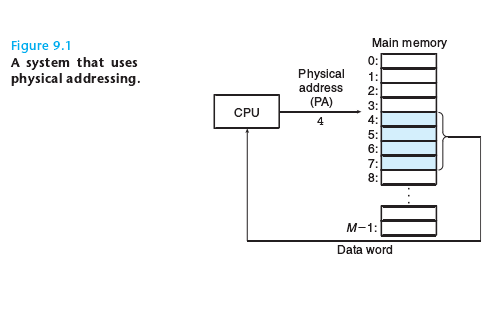
The main memory of a computer system is organized as an array of
M
contiguous
byte-sized cells. Each byte has a unique physical address (PA). The first byte has
an address of 0, the next byte an address of 1, the next byte an address of 2,
and so on. Given this simple organization, the most natural way for a CPU to
access memory would be to use physical addresses. We call this approach physical
addressing. Figure 9.1 shows an example of physical addressing in the context of
a load instruction that reads the word starting at physical address 4.
When the CPU executes the load instruction, it generates an effective physical
address and passes it to main memory over the memory bus. The main memory
fetches the 4-byte word starting at physical address 4 and returns it to the CPU,
which stores it in a register.
Early PCs used physical addressing, and systems such as digital signal pro-
cessors, embedded microcontrollers, and Cray supercomputers continue to do so.
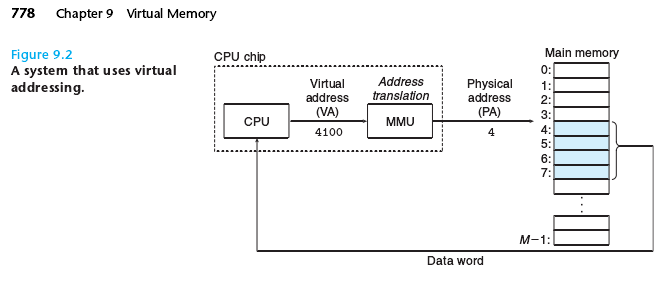
However, modern processors use a form of addressing known as virtual address-
ing, as shown in Figure 9.2.
With virtual addressing, the CPU accesses main memory by generating a vir-
tual address (VA), which is converted to the appropriate physical address before
being sent to the memory. The task of converting a virtual address to a physical
one is known as address translation. Like exception handling, address translation
requires close cooperation between the CPU hardware and the operating sys-
tem. Dedicated hardware on the CPU chip called the memory management unit
(MMU) translates virtual addresses on the fly, using a look-up table stored in main
memory whose contents are managed by the operating system.
主存
存储器管理单元