《Effective C#》之减少装箱和拆箱_天极网 http://dev.yesky.com/msdn/359/3486359.shtml
《Effective C#》之减少装箱和拆箱
例如,对于如下简单的装箱和拆箱操作语句。
object obj = i;//Boxing
if( obj is int )
int j = (int) obj;//Unboxing
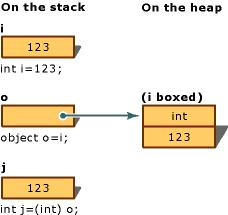
明白了这两名词的意思,现在说说为什么要减少装箱和拆箱操作。
原因有两个,主要是关于效率:一个就是对于堆的操作效率比较低;另一个就是对于堆上分配的内存资源,需要GC来回收,从而降低程序效率。
考虑到这两点因素,那么需要在程序中减少装箱和拆箱操作。
如何减少呢,涉及到这两个操作比较多的是,格式化输出操作,例如:String.Format,Console.WriteLine之类的语句。
例如:
| Console.WriteLine( "Number list:{0}, {1}, {2}",1,2,3 ); |
对于“1,2,3”来说,相当于前面的“123”一样,需要经过装箱和拆箱两个操作。那么如何避免呢,其实只要向WriteLine传递引用类型数据即可,也就是按照如下的方式。
| Console.WriteLine( "Number list:{0}, {1}, {2}", 1.ToString(),2.ToString(),3.ToString() ); |
由于“1.ToString()”的结果是String类型,属于引用类型,因此不牵扯装箱和拆箱操作。
其次,牵扯到装箱和拆箱操作比较多的就是在集合中,例如:ArrayList或者HashTable之类。
把值类型数据放到集合中,可能会出现潜在错误。例如:
| public struct Person { private string _Name; public string Name { get{ return _Name; } set{ _Name = value; } } public Person( string PersonName ) { _Name = PersonName; } public override string ToString() { return _Name; } } // Using the person in a collection ArrayList arrPersons = new ArrayList(); Person p = new Person( "OldName" ); arrPersons.Add( p ); // Try to change the name p = ( Person ) arrPersons[0] ; p.Name = "NewName"; Debug.WriteLine( ( (Person ) arrPersons[0] ).Name );//It's "OldName" |
这个问题其实在前面的文章中已经讲过了。有人可能会说,是否可以按照如下的方式去修改呢。
| ( (Person ) arrPersons[0] ).Name = "NewName";//Can't be compiled |
很不幸,如上操作不能通过编译。为什么呢,对于“( (Person ) arrPersons[0] )”来说,是系统用一个临时变量来接收拆箱后的值类型数据,那么由于值类型是分配在栈上,那么操作是对实体操作,可是系统不允许对一个临时值类型数据进行修改操作。
| // Using the person in a collection ArrayList arrPersons = new ArrayList(); Person p = new Person( "OldName" ); arrPersons.Add( p ); // Try to change the name p = ( Person ) arrPersons[0] ; p.Name = "NewName"; arrPersons.RemoveAt( 0 );//Remove old data first arrPersons.Insert( 0, p );//Add new data Debug.WriteLine( ( (Person ) arrPersons[0] ).Name );//It's "NewName" |
其实,这样操作会产生过多装箱和拆箱操作。那么更好的方法,可以通过接口来完成,从而减少装箱和拆箱操作。对于这个例子的接口实现应该如下。
| public interface IPersonName { string Name{ get;set;} } public struct Person:IPersonName { private string _Name; public string Name { get{ return _Name; } set{ _Name = value; } } public Person( string PersonName ) { _Name = PersonName; } public override string ToString() { return _Name; } } // Using the person in a collection ArrayList arrPersons = new ArrayList(); Person p = new Person( "OldName" ); arrPersons.Add( p ); // Change the name ( (IPersonName)arrPersons[0] ).Name = "NewName"; Debug.WriteLine( ( (Person ) arrPersons[0] ).Name );//It's "NewName" |
很多人就问,为什么值类型不能修改,即
| ( (Person ) arrPersons[0] ).Name = "NewName";//Can't be compiled |
而如上的接口类型就能修改呢,即
| ( (IPersonName)arrPersons[0] ).Name = "NewName"; |
这是由于产生的临时变量的类型不同,前者已经在前面进行说明了,后者由于产生的临时变量的类型为IPersonName,属于引用类型,那么相当于临时变量就是原对象的引用,那么对于对于它的修改会直接修改到原对象,因此是可以的。可以说这里的不同本身在于产生临时对象的类型不同,从而造成本质的区别。
通过接口来改写,这样就减少了装箱和拆箱操作,同时也保证了修改的正确性。不过要注意的是,这里接口对于的是引用类型,如果接口访问的或者返回的是值类型,那么用接口虽说能实现了,但是对于装箱和拆箱操作来说,并没有减少。
对于装箱和拆箱操作来说,基本上就讲完了,只要记住频繁装箱和拆箱操作会降低程序效率,因此在编写的时候要尽量避免。
https://tig.qpic.cn/doc/2018腾讯移动游戏技术评审标准与实践案例.pdf
Struct和Class的基本情况大致已经清楚,我们的真正目的是想知道如何架构我们的数据操作模块,才能充分地利用值类型和引用类型的,让效率最高(即装箱或拆线少,堆内存少)。
字符串拼接
数据结论
Struct在栈中不产生GC,class在堆中,会产生GC。对Struct的结点修改时,修改完以后记得重新赋值。因为Struct赋值是copy而不是引用,修改完以后,以前的不生效。
意义
堆栈的空间有限,对于大量的逻辑的对象,创建类要比创建结构好一些。结构表示轻量对象,并且结构的成本较低,适合处理大量短暂的对象。在表现抽象和多级别的对象层次时,类是最好的选择。大多数情况下该类型只是一些数据时,结构是最佳的选择。
C# | Boxing And Unboxing - GeeksforGeeks https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-sharp-boxing-unboxing/
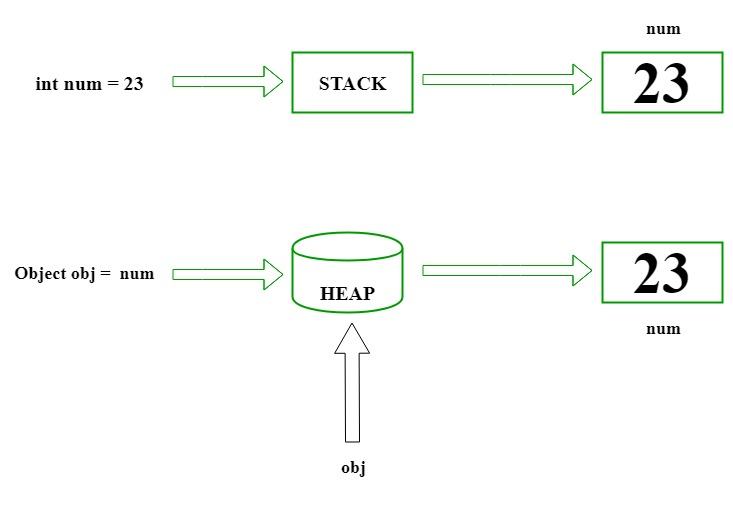
// C# implementation to demonstrate // the Boxing using System; class GFG { // Main Method static public void Main() { // assigned int value // 2020 to num int num = 2020; // boxing object obj = num; // value of num to be change num = 100; System.Console.WriteLine ("Value - type value of num is : {0}", num); System.Console.WriteLine ("Object - type value of obj is : {0}", obj); }
Value - type value of num is : 100 Object - type value of obj is : 2020
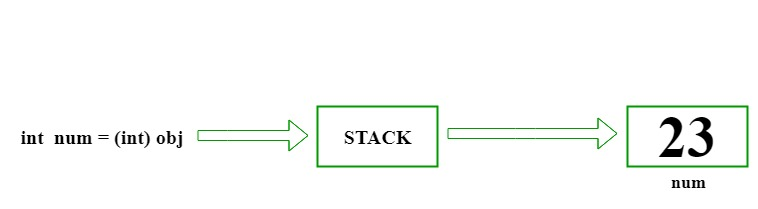
// C# implementation to demonstrate // the Unboxing using System; class GFG { // Main Method static public void Main() { // assigned int value // 23 to num int num = 23; // boxing object obj = num; // unboxing int i = (int)obj; // Display result Console.WriteLine("Value of ob object is : " + obj); Console.WriteLine("Value of i is : " + i); } } -
Value of ob object is : 23 Value of i is : 23