任何算法(程序)都可以由顺序结构、 选择结构和循环结构这三种基本结构组合来实现。
1、顺序结构
顺序结构中,按语句的自然顺序依次执行。
2、选择结构
(1)多分支决策:if-else。这是简单分之结构,
1 import math 2 def main(): 3 print("求二次方程的实根 ")#换行,反斜杠和n 4 a,b,c=eval(input("输入二次函数的系数(a,b,c):"))#用逗号隔开,同时输入三个数 5 delt=b**2-4*a*c 6 if delt>0: 7 delt=math.sqrt(b**2-4*a*c) 8 root1=(-b+delt)/(2*a) 9 root2=(-b-delt)/(2*a) 10 print("二次函数的实根为:",root1,root2) 11 # print("二次函数的实根为root1=%f,root2=%f:"%root1,%root2) 编译不通,留看 12 elif delt==0: 13 delt=math.sqrt(delt) 14 root1=(-b+delt)/(2*a) 15 print("相同的实根",root1) 16 else: 17 print('没有实根') 18 19 main()
if-elif-elif-else 多个互斥的判断语句
(2)
1 from math import * 2 def main(): 3 print("二次方程求根方法") 4 a,b,c=eval(input("输入系数:")) 5 delta=b**2-4*a*c 6 if delta<0: 7 print("方程没有实根") 8 else: 9 if delta==0: 10 root=-b/2*a 11 print("相同的实根",root) 12 else delta>0: 13 delta=sqrt(delta) 14 root1=(-b+delta)/(2*a) 15 root2=(-b-delta)/(2*a) 16 print("实根为:",root1,root2) 17 18 main()
这是from math import *这种形式,调用函数不用前面加库名;再有体会if-if-if、if-else嵌套if-else 形式和if-elif-elif-else形式区别
3、异常处理机制
如果处理错误或特殊情况的分支语句过多,那么处理正常情况的主程序就会变得不清晰
(1)
1 def main(): 2 try: 3 number1,number2=eval(input("enter two number,separated by a comma ")) 4 result=number1/number2 5 6 except ZeroDivisionError: 7 print("Division by zero!") 8 except SyntaxError: 9 print("A comma may be missing in the input") 10 except : 11 print("Something wrong in the input") 12 else: 13 print("No excepting,the result is",result) 14 finally: 15 print("executing the final clause") 16 main()

从这段代码中可以看出,try-except的执行顺序,先执行try中的内容,如果没有错误,执行else和finally中内容;如果出错,执行except内容,最后执行finally内容。
(2)将try-except 加入二次方程根代码
1 import math 2 def main(): 3 print('this program finds the real solutions to a quadratic') 4 try: 5 a,b,c=eval(input("please enter the coefficients(a,b,c) ")) 6 discroot=math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c) 7 root1=(-b+discroot)/(2*a) 8 root2=(-b-discroot)/(2*a) 9 print("the solutions are:",root1,root2) 10 except: 11 print("some thing went trong") 12 13 main()
(3)标准异常
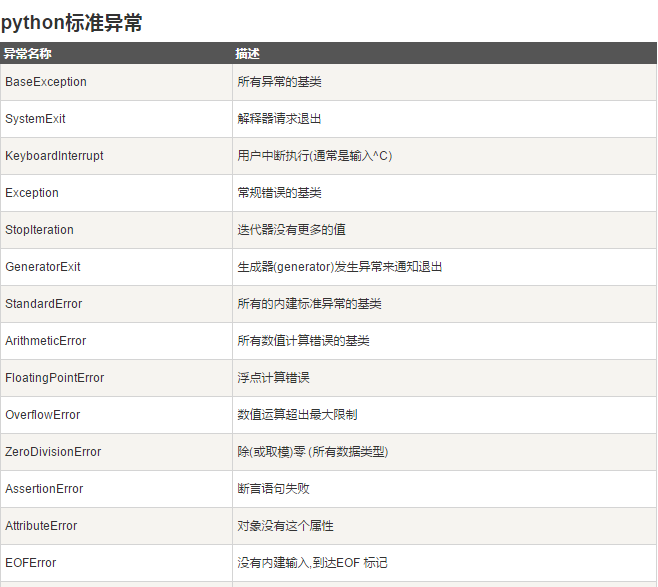

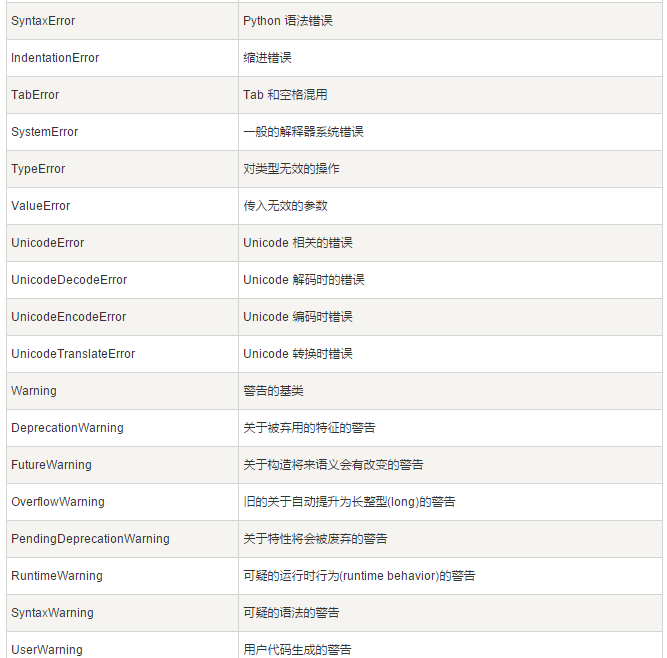
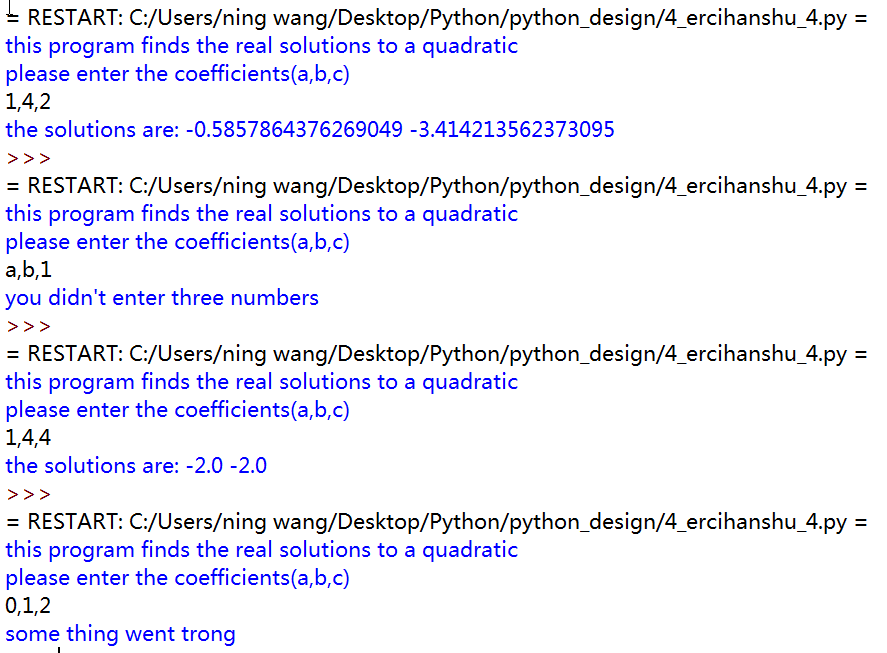
1 import math 2 def main(): 3 print('this program finds the real solutions to a quadratic') 4 try: 5 a,b,c=eval(input("please enter the coefficients(a,b,c) ")) 6 discroot=math.sqrt(b*b-4*a*c) 7 root1=(-b+discroot)/(2*a) 8 root2=(-b-discroot)/(2*a) 9 print("the solutions are:",root1,root2) 10 except ValueError as exc0bj: 11 if str(exc0bj)=="math domain error": 12 print("No real roots") 13 else: 14 print("you didn't give me the right number of codfficients") 15 except NameError: 16 print("you didn't enter three numbers") 17 except TypeError: 18 print("you input was not the correct form") 19 except: 20 print("some thing went trong") 21 22 main()
4、分支结构——数值比较
(1)四个数值比较
<1>通盘比较 :每个数与其他数全部比较
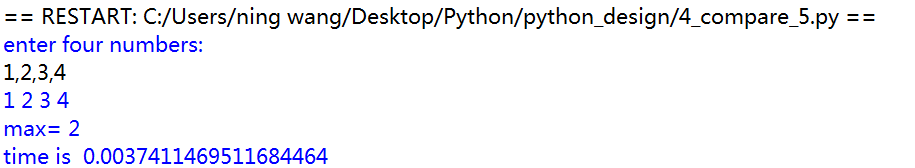
1 import math 2 import time 3 4 def main(): 5 try: 6 a,b,c,d=eval(input("enter four numbers: ")) 7 time.clock() 8 if a>=b and a>=c and a>=d: 9 print("max=",a) 10 elif b>=a and b>=c and b>=d: 11 print("max=",b) 12 elif c>=a and c>=b and c>=d: 13 print("max=",c) 14 else: 15 print('max=',d) 16 except: 17 print("wrong") 18 print("time is ",time.clock()) 19 main()
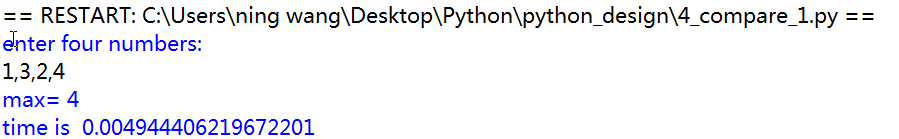
此种方法,在数据多时,耗时,耗内存,存在重复比较的情况。
<2>策略2:决策树
决策树方法可以避免冗余比较,先判断x1>x2,如果成立再判断x1>x3,否则判断x2>x3,虽然效率高,但设计三个以上的方案,复杂性会爆炸性地增长
1 import math 2 import time 3 4 def main(): 5 try: 6 a,b,c,d=eval(input("enter four numbers: ")) 7 time.clock() 8 if a>=b: 9 if a>=c: 10 if a>=d: 11 print("max=",a) 12 else: 13 print("max=",d) 14 else: 15 if c>=d: 16 print("max=",c) 17 else: 18 print("max=",d) 19 else: 20 if b>=c: 21 if b>=d: 22 print("max=",b) 23 else: 24 print("max=",d) 25 else: 26 if c>=d: 27 print("max=",c) 28 else: 29 print("max=",d) 30 except: 31 print("wrong") 32 print("time is ",time.clock()) 33 main()

<3>顺序处理
逐个扫描每个值,保留最大者以max变量保存当前最大值,完成最后一个扫描时,max就是最大值
1 import math 2 import time 3 import random 4 5 def main(): 6 try: 7 # a,b,c,d=eval(input("enter four numbers: ")) 8 a,b,c,d=random.randint(1,100),random.randint(1,100),random.randint(1,100),random.randint(1,100) 9 print(a,b,c,d) 10 max=a 11 time.clock() 12 if max<b: 13 max=b 14 if max<c: 15 max=c 16 if max<d: 17 max=d 18 print("max=",max) 19 except: 20 print("wrong") 21 print("time is ",time.clock()) 22 main()

1 import math 2 import time 3 import random 4 5 def main(): 6 try: 7 a,b,c,d=eval(input("enter four numbers: ")) 8 print(a,b,c,d) 9 max=a 10 time.clock() 11 if max<b: 12 max=b 13 elif max<c: 14 max=c 15 elif max<d: 16 max=d 17 print("max=",max) 18 except: 19 print("wrong") 20 print("time is ",time.clock()) 21 main()
可以看出 if-if-if和if-elif-elif 的区别,前者是挨个向后运行,后者是只运行符合条件的。
<4>调用自带函数
1 import math 2 import time 3 import random 4 5 def main(): 6 try: 7 a,b,c,d=random.randint(1,100),random.randint(1,100),random.randint(1,100),random.randint(1,100) 8 print(a,b,c,d) 9 print("max=",max(a,b,c,d)) 10 except: 11 print("wrong") 12 print("time is ",time.clock()) 13 main()

花费时间最短
<5>if-if-if 和 if-elif-elif-else
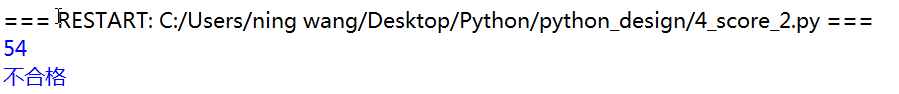
1 from math import * 2 from random import * 3 4 def main(): 5 try: 6 a=randint(50,100) 7 print(a) 8 if a>90: 9 print("优秀") 10 elif a>80: 11 print("良好") 12 elif a>70: 13 print("一般") 14 elif a>=60: 15 print("合格") 16 else: 17 print("不合格") 18 except: 19 print("出错") 20 21 main()
from math import * from random import * def main(): try: a=randint(50,100) print(a) if a>=90: print("优秀") if a>=80 and a<90: print("良好") if a>=70 and a<80: print("一般") if a>=60 and a<70: print("合格") if a<60: print("不合格") except: print("出错") main()
5、循环结构
(1)for 循环
Python可以使用for语句循环遍历整个序列的值
for <var> in <sequence>:
<body>
在for循环中,循环变量var遍历了队列中的每一个值,循环的语句体为每个值执行一次。
(2)求平均数
1 from math import * 2 from random import * 3 4 def main(): 5 try: 6 n=eval(input('数字个数:')) 7 sum=0 8 for i in range(n): 9 num=randint(0,100) 10 print(num) 11 sum=sum+num 12 print("平均值为:",sum/n) 13 except: 14 print("运行出错") 15 main()

(3)while循环无限循环
语法:while语句
while <condition>:
<body>
while语句中<condition>是布尔表达式<body>循环体是一条或多条语句当条件<condition>为真时,循环体重复执行当条件<condition>为假时,循环终止在while循环中,条件总是在循环顶部被判断,即在循环体执行之前,这种结构又被称为前测循环
(4)Break 语句- 跳出最内层for/while 循环
import math
sum=0
num=0
while num<20:
num=num+1
sum=sum+num
if sum>100:
break
print("num=",num)
print("sum=",sum)

(5)for/while 中的continue用法
continue语句, 其作用为结束本次循环。即跳出循环体中下面尚未执行的语句,对于while循环,继续求解循环条件。而对于for循环程序流程接着遍历循环列表
continue语句和break语句的区别是:
continue语句只结束本次循环,而不终止整个循环的执行。而break语句则是结束整个循环过程,不再判断执行循环的条件是否成立:
1 import math 2 num=0 3 while num<10: 4 num=num+1 5 if num%2==0: 6 print("find an even number",num) 7 continue 8 print("find a number",num) 9

(6)for/while 中的else用法
Break 语句- 跳出最内层for/while 循环
<for… else: …> <while… else: …>语句与循环的搭配使用,else:后的表达式在for循环列表遍历完毕后或while 条
件语句不满足的情况下执行,例如:
1 import math 2 def main(): 3 n=eval(input("输入素数范围:")) 4 for x in range(2,n): 5 for i in range(2,x): 6 if x%i==0: 7 break 8 else: 9 print(x,"是素数") 10 main()
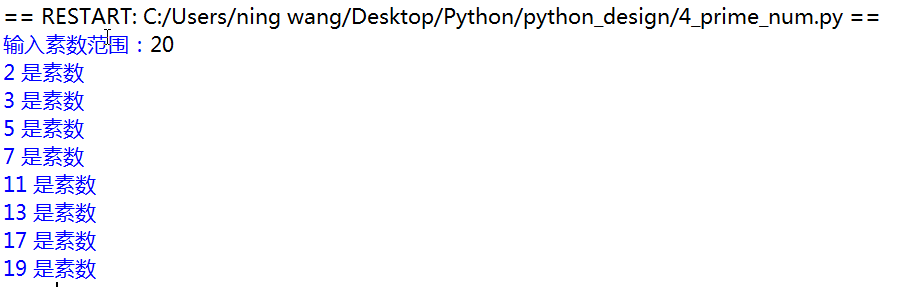
while/for 循环和else的使用,就是执行完循环后,再执行else;
而if-else 则是,只执行if或者else。
6、交互式循环
交互式循环是无限循环的一种允许用户通过交互的方式重复程序的特定部分
(1)交互求平均数(while 循环)
1 import math 2 import random 3 def main(): 4 sum=0 5 num=0 6 moredata='yes' 7 while moredata[0]=='y': 8 x=eval(input("enter your number:")) 9 num=num+1 10 sum=sum+x 11 moredata=input('do you have more numbers(enter yes or no):') 12 print('the average of the number is:',sum/num) 13 main() 14
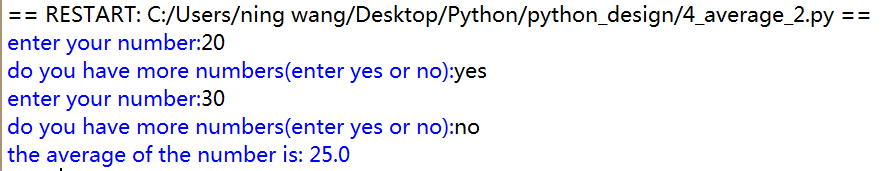
根据输入来进行判断是否进行下一步
(2)哨兵循环1
执行循环直到遇到特定的值,循环语句才终止执行的循环结构设计方法
哨兵循环是求平均数的更好方案,思路如下:
设定一个哨兵值作为循环终止的标志任何值都可以做哨兵,但要与实际数据有所区别
1 import math 2 import random 3 def main(): 4 sum=0 5 num=0 6 x=eval(input('enter a number (negative to quit):')) 7 while x>=0: 8 num=num+1 9 sum=sum+x 10 x=eval(input('enter a number (negative to quit):')) 11 print('the average of the number is:',sum/num) 12 main() 13
关键是哨兵如何选取,初始哨兵如何赋值。
(3)哨兵循环2
利用非数字字符串表示输入结束
所有其他字符串将被转换成数字,作为数据处理空字符串以”” (引号中间没有空格)代表,可以作为哨兵,用户输入回车,Python就返回空字符串
1 import math 2 import random 3 4 def main(): 5 sum=0 6 num=0 7 x=input('enter a number (<enter> to quit):') 8 while x!='': 9 num=num+1 10 x=eval(x) 11 sum=sum+x 12 x=input('enter a number (<enter> to quit):') 13 print('the average of the number is:',sum/num) 14 main()

eval()将字符串转换为数字格式,“”表示回车键
注意比较while和for循环的区别:while,需要一个初始值来开始循环,随后改变初始值,确定循环的次数;for 是确定的循环次数。
7、文件循环
(1)
1 def main(): 2 fileName=input("what file are the number in ") 3 infile=open(fileName,'r') 4 sum=0 5 count=0 6 for line in infile: 7 sum=sum+eval(line) 8 count=count+1 9 print("average is =",sum/count) 10 main()
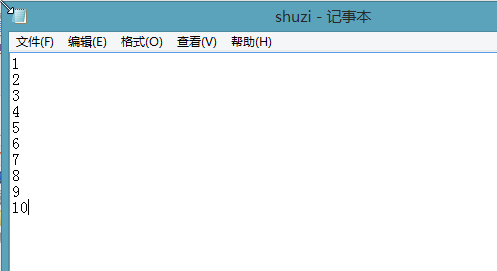

txt.文件每行一个数,用line读取,每一行的数,强制转化为数字,计算,输出
(2)异常处理
1 def main(): 2 fileName=input("what file are the number in ") 3 infile=open(fileName,'r') 4 sum=0 5 count=0 6 for line in infile: 7 try: 8 sum=sum+eval(line) 9 count=count+1 10 except: 11 continue 12 print("average is =",sum/count) 13 main()
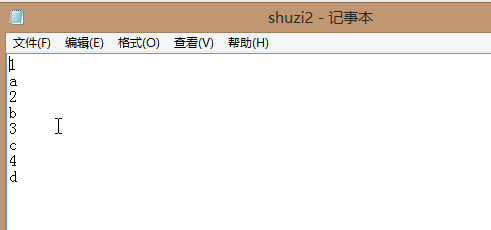
将字母剔除出去。
1 def main(): 2 fileName=input("what file are the number in ") 3 infile=open(fileName,'r') 4 sum=0 5 count=0 6 for line in infile: 7 try: 8 count=count+1 9 sum=sum+eval(line) 10 # count=count+1 11 12 except: 13 continue 14 print("average is =",sum/count) 15 main()

更改个数和累和的顺序得到的结果就不一样,这是因为更改后,在结束循环之前已经把数字个数加了一遍,所以将不是数字的个数也记录在内了。
(3)遍历行的while程序
1 def main(): 2 fileName=input("what file are the number in ") 3 file=open(fileName,'r') 4 sum=0 5 count=0 6 #line=file.readline() 7 line=0 8 while line!="": 9 try: 10 line=file.readline() 11 sum=sum+eval(line) 12 count=count+1 13 # line=file.readline() 14 except: 15 continue 16 print("average is =",sum/count) 17 main()

使用name.readline()遍历行,这段程序和上面程序分别使用了while和for 循环。while循环加入try-except后一定要注意哪出错,否则容易形成死循环。
再有一定要注意try-except使用时机,有时候while循环就是利用异常哨兵来停止循环的。
(4)分割行的line.split()程序
1 def main(): 2 fileName=input("what file are the number in ") 3 infile=open(fileName,'r') 4 sum=0.0 5 count=0 6 line=infile.readline() 7 while line!="": 8 for xstr in line.split(","): 9 sum=sum+eval(xstr) 10 count=count+1 11 line=infile.readline() 12 print("average is =",sum/count) 13 main()
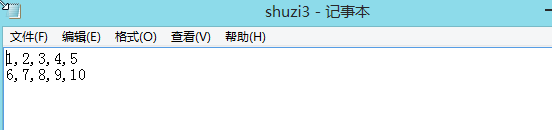
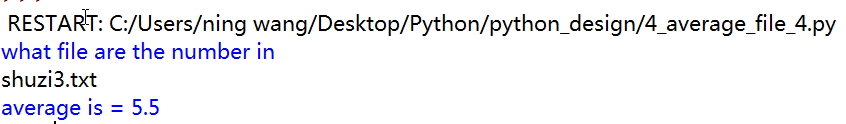
1 def main(): 2 fileName=input("what file are the number in ") 3 infile=open(fileName,'r') 4 sum=0.0 5 count=0 6 line=infile.readline() 7 while line!="": 8 for xstr in line.split(","): 9 try: 10 sum=sum+eval(xstr) 11 count=count+1 12 except: 13 continue 14 line=infile.readline() 15 print("average is =",sum/count) 16 main()
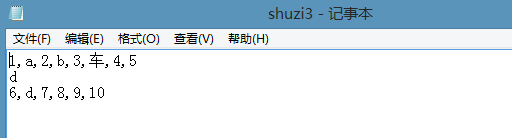

加入异常处理后,可以有效剔除字母和汉字,但是注意格式,如果大小写不一致的话会出现下面的问题
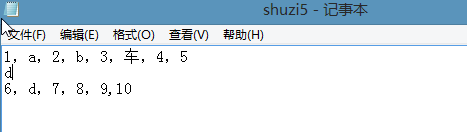
只有最后的10前面是字母形式的逗号
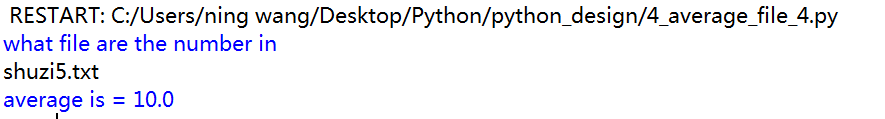
异常处理,将所有中文形式的逗号剔除,最终只剩下10是符合要求的形式,所以结果为10.
6、后测循环
(1)while-if
1 #输入一个非负数的程序 2 a=-1 3 while a<=0: 4 a=eval(input("输入一个非负数:")) 5 if a<0: 6 print("输入错误")

1 #输入一个非负数 2 while True: 3 a=eval(input("输入一个非负数:")) 4 if a>=0: 5 break 6 else: 7 print('输入错误')

一个是利用break,强制退出;一个是利用条件在while处退出。