今天我们来讲一下Android中BroadcastReceiver的相关知识。
BroadcastReceiver也就是“广播接收者”的意思,顾名思义,它就是用来接收来自系统和应用中的广播。
在Android系统中,广播体现在方方面面,例如当开机完成后系统会产生一条广播,接收到这条广播就能实现开机启动服务的功能;当网络状态改变时系统会产生一条广播,接收到这条广播就能及时地做出提示和保存数据等操作;当电池电量改变时,系统会产生一条广播,接收到这条广播就能在电量低时告知用户及时保存进度,等等。
Android中的广播机制设计的非常出色,很多事情原本需要开发者亲自操作的,现在只需等待广播告知自己就可以了,大大减少了开发的工作量和开发周期。而作为应用开发者,就需要数练掌握Android系统提供的一个开发利器,那就是BroadcastReceiver。下面我们就对BroadcastReceiver逐一地分析和演练,了解和掌握它的各种功能和用法。
首先,我们来演示一下创建一个BroadcastReceiver,并让这个BroadcastReceiver能够根据我们的需要来运行。
要创建自己的BroadcastReceiver对象,我们需要继承android.content.BroadcastReceiver,并实现其onReceive方法。下面我们就创建一个名为MyReceiver广播接收者:
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "MyReceiver";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, msg);
- }
- }
在onReceive方法内,我们可以获取随广播而来的Intent中的数据,这非常重要,就像无线电一样,包含很多有用的信息。
在创建完我们的BroadcastReceiver之后,还不能够使它进入工作状态,我们需要为它注册一个指定的广播地址。没有注册广播地址的BroadcastReceiver就像一个缺少选台按钮的收音机,虽然功能俱备,但也无法收到电台的信号。下面我们就来介绍一下如何为BroadcastReceiver注册广播地址。
静态注册
静态注册是在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置的,我们就来为MyReceiver注册一个广播地址:
- <receiver android:name=".MyReceiver">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
配置了以上信息之后,只要是android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST这个地址的广播,MyReceiver都能够接收的到。注意,这种方式的注册是常驻型的,也就是说当应用关闭后,如果有广播信息传来,MyReceiver也会被系统调用而自动运行。
动态注册
动态注册需要在代码中动态的指定广播地址并注册,通常我们是在Activity或Service注册一个广播,下面我们就来看一下注册的代码:
- MyReceiver receiver = new MyReceiver();
- IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
- filter.addAction("android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST");
- registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
注意,registerReceiver是android.content.ContextWrapper类中的方法,Activity和Service都继承了ContextWrapper,所以可以直接调用。在实际应用中,我们在Activity或Service中注册了一个BroadcastReceiver,当这个Activity或Service被销毁时如果没有解除注册,系统会报一个异常,提示我们是否忘记解除注册了。所以,记得在特定的地方执行解除注册操作:
- @Override
- protected void onDestroy() {
- super.onDestroy();
- unregisterReceiver(receiver);
- }
执行这样行代码就可以解决问题了。注意,这种注册方式与静态注册相反,不是常驻型的,也就是说广播会跟随程序的生命周期。
我们可以根据以上任意一种方法完成注册,当注册完成之后,这个接收者就可以正常工作了。我们可以用以下方式向其发送一条广播:
- public void send(View view) {
- Intent intent = new Intent("android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST");
- intent.putExtra("msg", "hello receiver.");
- sendBroadcast(intent);
- }
注意,sendBroadcast也是android.content.ContextWrapper类中的方法,它可以将一个指定地址和参数信息的Intent对象以广播的形式发送出去。
点击发送按钮,执行send方法,控制台打印如下:
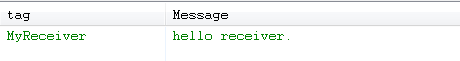
看到这样的打印信息,表明我们的广播已经发出去了,并且被MyReceiver准确无误的接收到了。
上面的例子只是一个接收者来接收广播,如果有多个接收者都注册了相同的广播地址,又会是什么情况呢,能同时接收到同一条广播吗,相互之间会不会有干扰呢?这就涉及到普通广播和有序广播的概念了。
普通广播(Normal Broadcast)
普通广播对于多个接收者来说是完全异步的,通常每个接收者都无需等待即可以接收到广播,接收者相互之间不会有影响。对于这种广播,接收者无法终止广播,即无法阻止其他接收者的接收动作。
为了验证以上论断,我们新建三个BroadcastReceiver,演示一下这个过程,FirstReceiver、SecondReceiver和ThirdReceiver的代码如下:
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class FirstReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "NormalBroadcast";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, "FirstReceiver: " + msg);
- }
- }
- public class SecondReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "NormalBroadcast";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, "SecondReceiver: " + msg);
- }
- }
- public class ThirdReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "NormalBroadcast";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, "ThirdReceiver: " + msg);
- }
- }
然后再次点击发送按钮,发送一条广播,控制台打印如下:
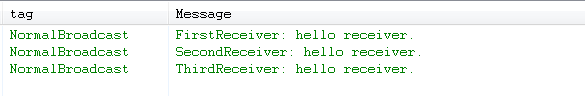
看来这三个接收者都接收到这条广播了,我们稍微修改一下三个接收者,在onReceive方法的最后一行添加以下代码,试图终止广播:
- abortBroadcast();
再次点击发送按钮,我们会发现,控制台中三个接收者仍然都打印了自己的日志,表明接收者并不能终止广播。
有序广播(Ordered Broadcast)
有序广播比较特殊,它每次只发送到优先级较高的接收者那里,然后由优先级高的接受者再传播到优先级低的接收者那里,优先级高的接收者有能力终止这个广播。
为了演示有序广播的流程,我们修改一下上面三个接收者的代码,如下:
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class FirstReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "OrderedBroadcast";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, "FirstReceiver: " + msg);
- Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
- bundle.putString("msg", msg + "@FirstReceiver");
- setResultExtras(bundle);
- }
- }
- public class SecondReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "OrderedBroadcast";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = getResultExtras(true).getString("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, "SecondReceiver: " + msg);
- Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
- bundle.putString("msg", msg + "@SecondReceiver");
- setResultExtras(bundle);
- }
- }
- public class ThirdReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "OrderedBroadcast";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- String msg = getResultExtras(true).getString("msg");
- Log.i(TAG, "ThirdReceiver: " + msg);
- }
- }
我们注意到,在FirstReceiver和SecondReceiver中最后都使用了setResultExtras方法将一个Bundle对象设置为结果集对象,传递到下一个接收者那里,这样以来,优先级低的接收者可以用getResultExtras获取到最新的经过处理的信息集合。
代码改完之后,我们需要为三个接收者注册广播地址,我们修改一下AndroidMainfest.xml文件:
- <receiver android:name=".FirstReceiver">
- <intent-filter android:priority="1000">
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
- <receiver android:name=".SecondReceiver">
- <intent-filter android:priority="999">
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
- <receiver android:name=".ThirdReceiver">
- <intent-filter android:priority="998">
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
我们看到,现在这三个接收者的<intent-filter>多了一个android:priority属性,并且依次减小。这个属性的范围在-1000到1000,数值越大,优先级越高。
现在,我们需要修改一下发送广播的代码,如下:
- public void send(View view) {
- Intent intent = new Intent("android.intent.action.MY_BROADCAST");
- intent.putExtra("msg", "hello receiver.");
- sendOrderedBroadcast(intent, "scott.permission.MY_BROADCAST_PERMISSION");
- }
注意,使用sendOrderedBroadcast方法发送有序广播时,需要一个权限参数,如果为null则表示不要求接收者声明指定的权限,如果不为null,则表示接收者若要接收此广播,需声明指定权限。这样做是从安全角度考虑的,例如系统的短信就是有序广播的形式,一个应用可能是具有拦截垃圾短信的功能,当短信到来时它可以先接受到短信广播,必要时终止广播传递,这样的软件就必须声明接收短信的权限。
所以我们在AndroidMainfest.xml中定义一个权限:
- <permission android:protectionLevel="normal"
- android:name="scott.permission.MY_BROADCAST_PERMISSION" />
然后声明使用了此权限:
- <uses-permission android:name="scott.permission.MY_BROADCAST_PERMISSION" />
关于这部分如果有不明白的地方可以参考我之前写过的一篇文章:Android声明和使用权限
然后我们点击发送按钮发送一条广播,控制台打印如下:
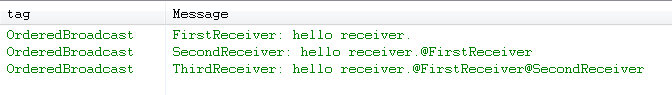
我们看到接收是按照顺序的,第一个和第二个都在结果集中加入了自己的标记,并且向优先级低的接收者传递下去。
既然是顺序传递,试着终止这种传递,看一看效果如何,我们修改FirstReceiver的代码,在onReceive的最后一行添加以下代码:
- abortBroadcast();
然后再次运行程序,控制台打印如下:
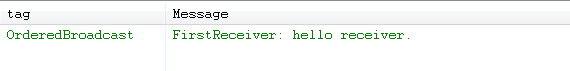
此次,只有第一个接收者执行了,其它两个都没能执行,因为广播被第一个接收者终止了。
上面就是BroadcastReceiver的介绍,下面我将会举几个常见的例子加深一下大家对广播的理解和应用:
1.开机启动服务
我们经常会有这样的应用场合,比如消息推送服务,需要实现开机启动的功能。要实现这个功能,我们就可以订阅系统“启动完成”这条广播,接收到这条广播后我们就可以启动自己的服务了。我们来看一下BootCompleteReceiver和MsgPushService的具体实现:
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class BootCompleteReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "BootCompleteReceiver";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- Intent service = new Intent(context, MsgPushService.class);
- context.startService(service);
- Log.i(TAG, "Boot Complete. Starting MsgPushService...");
- }
- }
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.app.Service;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.IBinder;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class MsgPushService extends Service {
- private static final String TAG = "MsgPushService";
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- super.onCreate();
- Log.i(TAG, "onCreate called.");
- }
- @Override
- public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
- Log.i(TAG, "onStartCommand called.");
- return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
- return null;
- }
- }
然后我们需要在AndroidManifest.xml中配置相关信息:
- <!-- 开机广播接受者 -->
- <receiver android:name=".BootCompleteReceiver">
- <intent-filter>
- <!-- 注册开机广播地址-->
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
- <!-- 消息推送服务 -->
- <service android:name=".MsgPushService"/>
我们看到BootCompleteReceiver注册了“android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED”这个开机广播地址,从安全角度考虑,系统要求必须声明接收开机启动广播的权限,于是我们再声明使用下面的权限:
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
经过上面的几个步骤之后,我们就完成了开机启动的功能,将应用运行在模拟器上,然后重启模拟器,控制台打印如下:
如果我们查看已运行的服务就会发现,MsgPushService已经运行起来了。
2.网络状态变化
在某些场合,比如用户浏览网络信息时,网络突然断开,我们要及时地提醒用户网络已断开。要实现这个功能,我们可以接收网络状态改变这样一条广播,当由连接状态变为断开状态时,系统就会发送一条广播,我们接收到之后,再通过网络的状态做出相应的操作。下面就来实现一下这个功能:
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.net.ConnectivityManager;
- import android.net.NetworkInfo;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- public class NetworkStateReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "NetworkStateReceiver";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- Log.i(TAG, "network state changed.");
- if (!isNetworkAvailable(context)) {
- Toast.makeText(context, "network disconnected!", 0).show();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 网络是否可用
- *
- * @param context
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean isNetworkAvailable(Context context) {
- ConnectivityManager mgr = (ConnectivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
- NetworkInfo[] info = mgr.getAllNetworkInfo();
- if (info != null) {
- for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) {
- if (info[i].getState() == NetworkInfo.State.CONNECTED) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
- }
再注册一下这个接收者的信息:
- <receiver android:name=".NetworkStateReceiver">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
因为在isNetworkAvailable方法中我们使用到了网络状态相关的API,所以需要声明相关的权限才行,下面就是对应的权限声明:
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
我们可以测试一下,比如关闭WiFi,看看有什么效果。
3.电量变化
如果我们阅读软件,可能是全屏阅读,这个时候用户就看不到剩余的电量,我们就可以为他们提供电量的信息。要想做到这一点,我们需要接收一条电量变化的广播,然后获取百分比信息,这听上去挺简单的,我们就来实现以下:
- package com.scott.receiver;
- import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.BatteryManager;
- import android.util.Log;
- public class BatteryChangedReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
- private static final String TAG = "BatteryChangedReceiver";
- @Override
- public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
- int currLevel = intent.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_LEVEL, 0); //当前电量
- int total = intent.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SCALE, 1); //总电量
- int percent = currLevel * 100 / total;
- Log.i(TAG, "battery: " + percent + "%");
- }
- }
然后再注册一下广播接地址信息就可以了:
- <receiver android:name=".BatteryChangedReceiver">
- <intent-filter>
- <action android:name="android.intent.action.BATTERY_CHANGED"/>
- <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
- </intent-filter>
- </receiver>
当然,有些时候我们是要立即获取电量的,而不是等电量变化的广播,比如当阅读软件打开时立即显示出电池电量。我们可以按以下方式获取:
- Intent batteryIntent = getApplicationContext().registerReceiver(null,
- new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANG